Visualizing Data: The Power of Mapping Zip Codes
Related Articles: Visualizing Data: The Power of Mapping Zip Codes
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Visualizing Data: The Power of Mapping Zip Codes. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Visualizing Data: The Power of Mapping Zip Codes
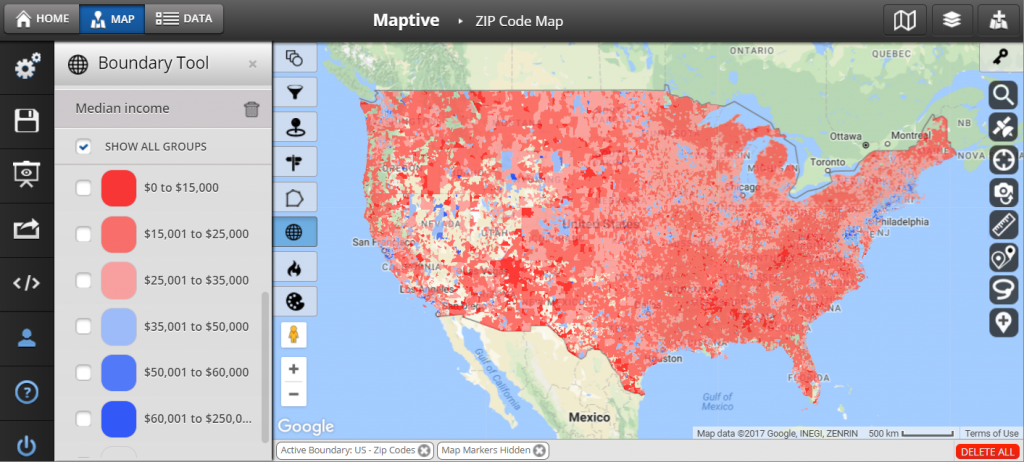
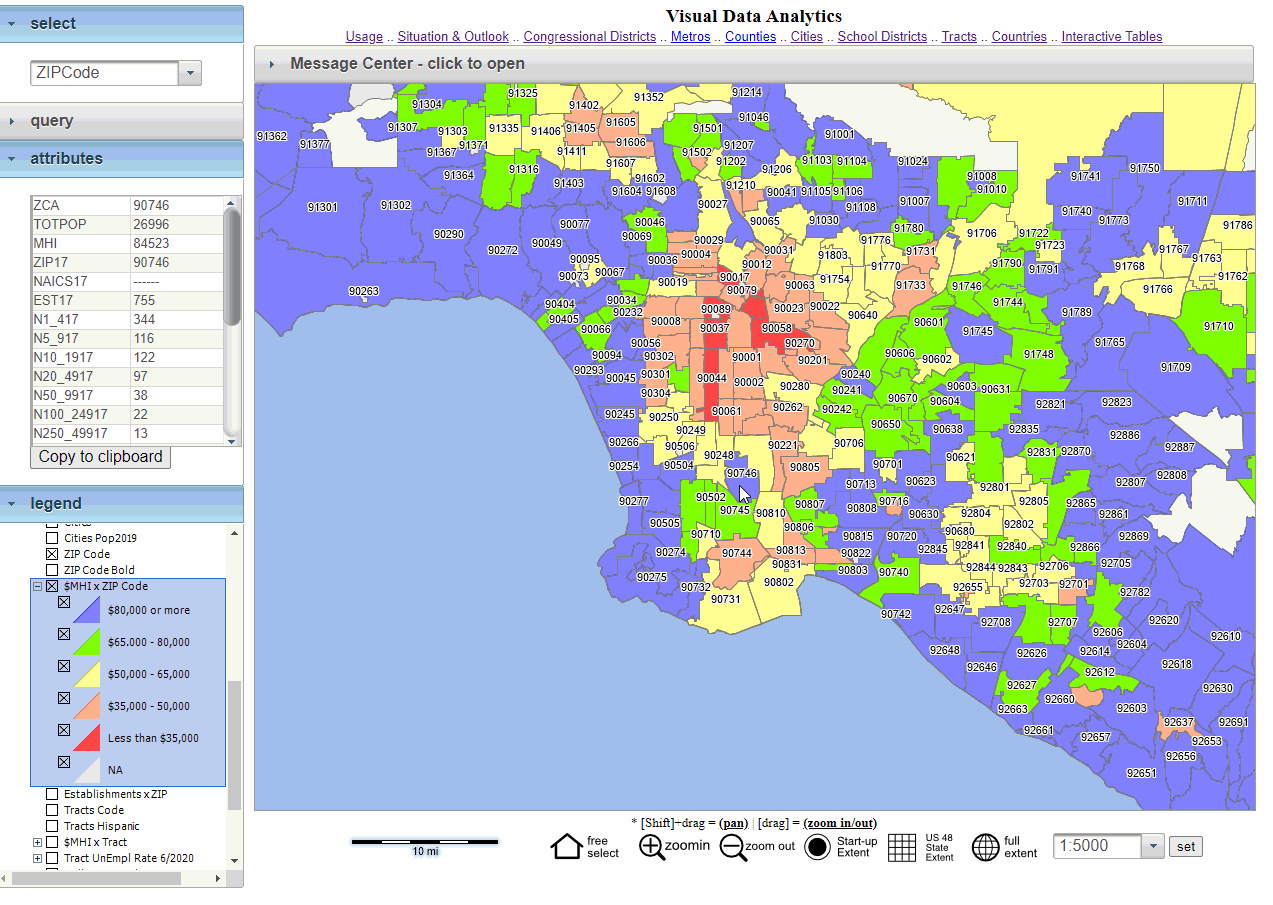
The seemingly mundane act of plotting zip codes on a map unlocks a wealth of information, transforming abstract data into tangible insights. This process, known as geographic visualization, offers a powerful tool for understanding population distribution, market trends, demographic patterns, and much more.
Understanding the Fundamentals
Zip codes, a system developed by the United States Postal Service (USPS), serve as a standardized way to identify locations for mail delivery. Each zip code corresponds to a specific geographic area, typically encompassing a neighborhood or a section of a city. While originally intended for logistical purposes, zip codes have evolved into a valuable data point for various disciplines.
The Benefits of Mapping Zip Codes
Mapping zip codes on a map provides a visual representation of data, enabling analysts to:
- Identify Spatial Patterns: By visualizing the distribution of zip codes, analysts can discern patterns in population density, socioeconomic factors, or the prevalence of specific industries. This allows for a deeper understanding of the geographic characteristics of a region.
- Analyze Market Trends: Businesses can leverage zip code mapping to identify target markets, analyze consumer behavior, and optimize marketing campaigns. For example, a retail chain can use zip code data to determine the ideal locations for new stores, ensuring proximity to potential customers.
- Track Social and Economic Indicators: Zip code mapping can be instrumental in studying social and economic trends. For instance, mapping crime rates by zip code can help law enforcement agencies identify areas with high crime activity and allocate resources effectively. Similarly, mapping unemployment rates by zip code can reveal areas facing economic challenges, allowing policymakers to address specific needs.
- Conduct Geographic Research: Researchers across various disciplines, including urban planning, public health, and environmental studies, utilize zip code mapping to analyze spatial relationships and gain insights into the interconnectedness of different factors within a region.
Methods for Mapping Zip Codes
Several methods are employed to map zip codes, each offering unique advantages depending on the application:
- GIS Software: Geographic Information Systems (GIS) software, such as ArcGIS or QGIS, provides powerful tools for spatial analysis and visualization. Users can import zip code data, overlay it with other geographic layers like roads, boundaries, or demographic data, and create interactive maps.
- Online Mapping Tools: Platforms like Google Maps, Mapbox, and Leaflet offer user-friendly interfaces for creating basic maps with zip code data. These tools allow for easy visualization and sharing of maps, making them suitable for quick analysis or presentations.
- Data Visualization Libraries: Programming languages like Python and R offer libraries like Geopandas and Leaflet, enabling developers to create custom maps with advanced features like interactive elements, data aggregation, and dynamic visualizations.
Examples of Zip Code Mapping Applications
The applications of zip code mapping extend across various fields, including:
- Real Estate: Real estate professionals use zip code maps to analyze property values, identify desirable neighborhoods, and target potential buyers.
- Healthcare: Healthcare providers leverage zip code mapping to understand the distribution of patients, identify areas with limited access to healthcare services, and optimize resource allocation.
- Education: Educational institutions use zip code maps to analyze student demographics, identify areas with high concentrations of students needing specific support, and tailor their outreach programs.
- Marketing: Marketers utilize zip code mapping to target specific demographics, understand consumer behavior, and optimize advertising campaigns.
Addressing Concerns and Limitations
While mapping zip codes offers valuable insights, it’s essential to acknowledge potential limitations and address concerns:
- Data Privacy: The use of zip code data raises privacy concerns, as it can potentially be used to identify individuals. It is crucial to adhere to data privacy regulations and ensure responsible data handling practices.
- Data Accuracy: Zip code boundaries may not always accurately reflect real-world conditions, especially in areas with complex urban landscapes or evolving neighborhoods. This can lead to inaccuracies in data analysis.
- Generalization: Mapping zip codes often involves aggregating data at a zip code level, potentially masking variations within the area. It’s important to consider the scale of analysis and potential limitations when interpreting results.
FAQs Regarding Zip Code Mapping
Q: How can I find zip code data for mapping?
A: Several sources provide zip code data, including the USPS website, public datasets from government agencies, and commercial data providers.
Q: What are the best tools for mapping zip codes?
A: GIS software like ArcGIS and QGIS offer comprehensive features for spatial analysis and visualization. Online mapping platforms like Google Maps and Mapbox provide user-friendly interfaces for creating basic maps.
Q: Can I use zip code mapping to identify individuals?
A: While zip codes can be used to pinpoint a general location, it’s not advisable to use them for identifying specific individuals. Data privacy concerns must be addressed when working with zip code data.
Q: What are some limitations of zip code mapping?
A: Zip code boundaries may not always accurately reflect real-world conditions, and data aggregation at a zip code level can mask variations within the area.
Tips for Effective Zip Code Mapping
- Choose the Right Tools: Select mapping tools that align with your specific needs and data requirements.
- Ensure Data Accuracy: Verify the accuracy of your zip code data and consider potential discrepancies.
- Address Privacy Concerns: Implement data privacy measures and adhere to relevant regulations.
- Consider Scale of Analysis: Be mindful of the scale of your analysis and potential limitations of aggregating data at a zip code level.
- Visualize Clearly: Use clear and concise visualizations to communicate your findings effectively.
Conclusion
Mapping zip codes on a map is a powerful technique for transforming data into meaningful insights. By visualizing spatial patterns, analyzing market trends, tracking social and economic indicators, and conducting geographic research, zip code mapping offers a valuable tool across various disciplines. While acknowledging potential limitations and concerns, responsible and ethical data handling practices ensure the effective and impactful use of this visualization technique.


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Visualizing Data: The Power of Mapping Zip Codes. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
