Visualizing Data on the Globe: A Guide to Plotting Latitude and Longitude with Python
Related Articles: Visualizing Data on the Globe: A Guide to Plotting Latitude and Longitude with Python
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Visualizing Data on the Globe: A Guide to Plotting Latitude and Longitude with Python. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Visualizing Data on the Globe: A Guide to Plotting Latitude and Longitude with Python
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Visualizing Data on the Globe: A Guide to Plotting Latitude and Longitude with Python
- 3.1 The Power of Python for Geographic Data Visualization
- 3.2 Key Libraries for Latitude and Longitude Plotting
- 3.3 Step-by-Step Guide: Plotting Latitude and Longitude Data with Python
- 3.4 Beyond Basic Plotting: Advanced Techniques and Considerations
- 3.5 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- 3.6 Tips for Effective Latitude and Longitude Plotting
- 3.7 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Visualizing Data on the Globe: A Guide to Plotting Latitude and Longitude with Python
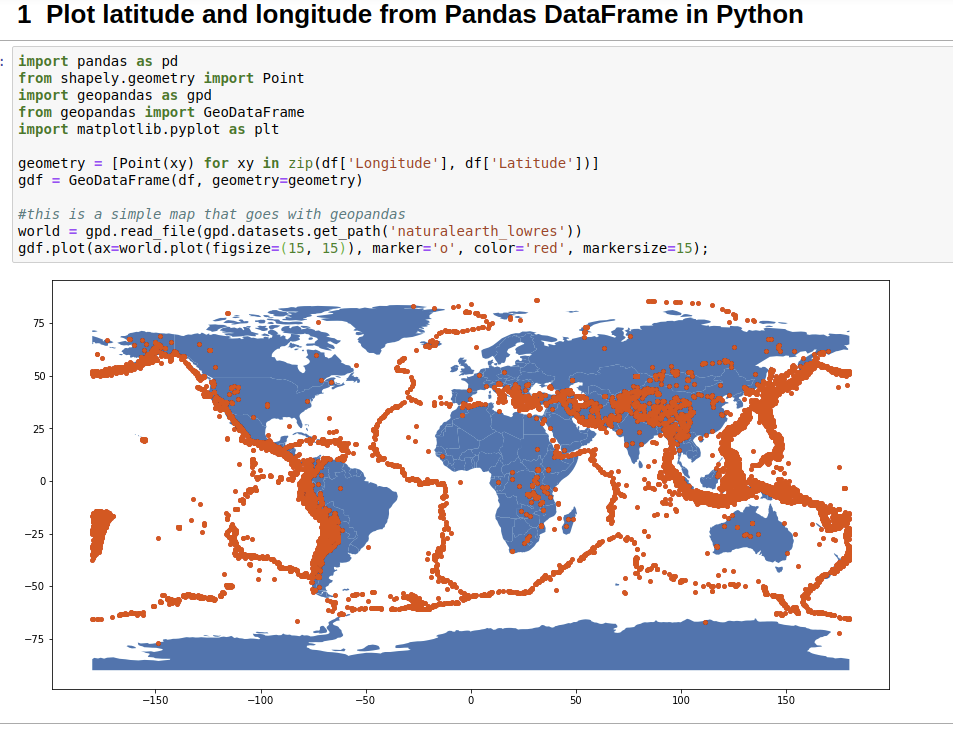
The ability to visualize data on a map is crucial in many fields, from environmental science to urban planning, transportation analysis, and even social research. Latitude and longitude coordinates, the fundamental building blocks of geographic information systems (GIS), provide the framework for plotting data on the Earth’s surface. Python, with its powerful libraries and versatility, offers a robust platform for creating compelling and informative maps using these coordinates.
This article delves into the world of plotting latitude and longitude data using Python, exploring the key libraries, techniques, and considerations involved. We will discuss the benefits of using Python for this purpose, highlighting its flexibility, ease of use, and rich ecosystem of visualization tools.
The Power of Python for Geographic Data Visualization
Python’s dominance in data science and analysis extends to the realm of geospatial data. Its extensive libraries, specifically designed for handling geographic data and creating maps, make it an ideal choice for visualizing latitude and longitude information.
1. Robust Libraries: Python boasts a suite of powerful libraries that simplify the process of working with geographic data. Libraries like Geopandas, Shapely, Pyproj, and Cartopy provide essential tools for:
* **Reading and manipulating geographic data:** Loading data from various formats like shapefiles, GeoJSON, and CSV files with latitude and longitude columns.
* **Spatial analysis:** Performing operations like spatial joins, buffer creation, and geometric calculations.
* **Projection and transformation:** Handling different coordinate systems and projections.
* **Creating maps:** Generating static and interactive maps with various basemaps, markers, and layers.2. Flexibility and Customization: Python’s flexibility allows for tailoring visualizations to specific needs. Users can control aspects like:
* **Map projection:** Choosing the most appropriate projection for the desired area and data.
* **Basemap:** Selecting a basemap that best suits the visualization purpose, ranging from simple outlines to detailed imagery.
* **Marker styles:** Customizing the appearance of points on the map using different shapes, colors, and sizes.
* **Additional layers:** Adding layers like roads, boundaries, or demographic data to enrich the map's context.3. Integration with Other Tools: Python’s ability to integrate with other tools and libraries enhances its capabilities. It can be used to:
* **Connect to databases:** Access and visualize geospatial data stored in databases.
* **Automate map generation:** Create maps programmatically for repetitive tasks or dynamic updates.
* **Develop interactive web applications:** Build web-based maps with interactive features using libraries like **Folium** and **Plotly**.Key Libraries for Latitude and Longitude Plotting
Let’s explore some of the key Python libraries that play a pivotal role in visualizing latitude and longitude data:
1. Geopandas: A powerful library built upon the foundation of pandas, Geopandas extends the capabilities of pandas to handle geospatial data. It enables:
* **Reading and writing geospatial data:** Loading data from various formats like shapefiles, GeoJSON, and CSV files containing geographic coordinates.
* **Spatial analysis:** Performing operations like spatial joins, buffer creation, and geometric calculations.
* **Visualizing geospatial data:** Creating static maps using Matplotlib and interactive maps using libraries like Folium.2. Matplotlib: The cornerstone of data visualization in Python, Matplotlib provides a versatile framework for creating static maps. It offers:
* **Basemap support:** Integrating with Basemap toolkit for plotting on different projections.
* **Marker customization:** Adjusting the appearance of points on the map using different shapes, colors, and sizes.
* **Adding layers:** Including additional layers like roads, boundaries, or demographic data to enhance the map's context.3. Cartopy: A library specifically designed for creating maps with geographical projections, Cartopy offers:
* **Advanced projections:** Supporting a wide range of projections, including cylindrical, conic, and azimuthal projections.
* **Geocoding and georeferencing:** Converting addresses and place names to latitude and longitude coordinates.
* **Creating thematic maps:** Visualizing data based on specific themes, like population density or temperature distribution.4. Folium: A library that focuses on creating interactive maps for web applications. Folium leverages the Leaflet JavaScript library to provide:
* **Interactive features:** Enabling zoom, pan, and click interactions on the map.
* **Marker pop-ups:** Displaying information about specific locations when markers are clicked.
* **Layer control:** Allowing users to toggle between different layers and basemaps.Step-by-Step Guide: Plotting Latitude and Longitude Data with Python
Let’s illustrate the process of plotting latitude and longitude data with Python using a practical example. Imagine we have a CSV file containing data about different cities, including their latitude and longitude coordinates. We aim to create a map visualizing these locations.
1. Import Necessary Libraries:
import geopandas as gpd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt2. Load the Data:
# Load the CSV file into a pandas DataFrame
cities_df = pd.read_csv("cities.csv")
# Create a GeoDataFrame from the DataFrame, specifying the latitude and longitude columns
cities_gdf = gpd.GeoDataFrame(
cities_df, geometry=gpd.points_from_xy(cities_df.longitude, cities_df.latitude)
)3. Choose a Basemap:
# Import the Basemap toolkit from Matplotlib
from mpl_toolkits.basemap import Basemap
# Create a basemap object with the desired projection and extent
map = Basemap(projection='merc', llcrnrlat=-90, urcrnrlat=90, llcrnrlon=-180, urcrnrlon=180, resolution='l')4. Plot the Data:
# Plot the cities on the map using the GeoDataFrame
map.plot(cities_gdf.geometry.x, cities_gdf.geometry.y, 'bo', markersize=5)5. Add Labels and Enhance the Map:
# Add labels for the cities
for i, row in cities_df.iterrows():
map.plot(row.longitude, row.latitude, 'bo', markersize=5)
plt.text(row.longitude, row.latitude, row.city_name, fontsize=8, ha='center', va='bottom')
# Add a title to the map
plt.title("Cities Around the World")
# Add a grid to the map
map.drawmeridians(np.arange(0, 360, 30), labels=[0, 0, 0, 1])
map.drawparallels(np.arange(-90, 90, 30), labels=[1, 0, 0, 0])
# Display the map
plt.show()This code snippet demonstrates the fundamental steps involved in plotting latitude and longitude data using Python. The process involves loading the data, creating a basemap, plotting the points, and adding customizations like labels and gridlines.
Beyond Basic Plotting: Advanced Techniques and Considerations
While basic plotting provides a foundation for visualizing geographic data, Python offers a wealth of advanced techniques and considerations for creating more sophisticated and informative maps:
1. Handling Different Coordinate Systems:
* **Projection:** Latitude and longitude coordinates are often expressed in different coordinate systems, such as WGS84 (used by GPS devices) or UTM (used for local mapping). Python libraries like **Pyproj** facilitate conversions between these systems.
* **Datum:** The datum defines the reference point for a coordinate system. Different datums can lead to slight variations in coordinates. Python libraries like **Cartopy** can handle datum transformations.2. Incorporating Spatial Data:
* **Shapefiles:** Shapefiles are commonly used to represent geographic features like countries, states, or cities. Python libraries like **Geopandas** can read and manipulate shapefiles to overlay geographic boundaries on maps.
* **GeoJSON:** A lightweight format for representing geographic data, GeoJSON can be easily integrated with Python libraries like **Geopandas** and **Folium** for creating interactive maps.3. Creating Thematic Maps:
* **Choropleth Maps:** These maps use color variations to represent data values across geographic regions. Python libraries like **Geopandas** and **Cartopy** provide tools for creating choropleth maps.
* **Proportional Symbol Maps:** These maps use symbols of varying sizes to represent data values at different locations. Python libraries like **Matplotlib** and **Cartopy** support creating proportional symbol maps.4. Adding Interactive Features:
* **Folium:** This library enables the creation of interactive web-based maps with features like zoom, pan, and marker pop-ups.
* **Plotly:** Another library that allows for creating interactive maps with features like tooltips, hover effects, and animation.5. Data Visualization Best Practices:
* **Clear and Concise:** Maps should be designed with clarity and simplicity in mind. Avoid cluttering the map with too much information.
* **Meaningful Colors and Symbols:** Choose colors and symbols that effectively communicate the data. Use a color scheme that is visually appealing and accessible to all users.
* **Appropriate Projections:** Select the projection that best represents the area and data being visualized.
* **Proper Labeling and Legends:** Ensure that labels and legends are clear and informative.Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is the difference between latitude and longitude?
* Latitude measures the angular distance north or south of the equator, ranging from 0° at the equator to 90° at the North and South Poles.
* Longitude measures the angular distance east or west of the prime meridian, ranging from 0° at the prime meridian to 180° east or west.2. How do I obtain latitude and longitude coordinates?
* **Geocoding:** Use online services like Google Maps or OpenStreetMap to convert addresses or place names into latitude and longitude coordinates.
* **GPS devices:** GPS receivers provide accurate latitude and longitude coordinates for your current location.
* **Data sources:** Many datasets, such as weather data, census data, or environmental data, include latitude and longitude coordinates.3. What are the benefits of visualizing data on a map?
* **Spatial context:** Maps provide a visual representation of data in its geographical context, revealing patterns and relationships that might not be apparent in tabular data.
* **Data exploration:** Maps allow for quick and intuitive exploration of data, enabling users to identify trends, outliers, and areas of interest.
* **Communication:** Maps effectively communicate complex data to a wide audience, making it easier to understand and interpret.4. What are some common applications of plotting latitude and longitude data?
* **Environmental monitoring:** Tracking environmental variables like air quality, water temperature, or deforestation.
* **Urban planning:** Analyzing population density, infrastructure development, or transportation patterns.
* **Disaster response:** Mapping the location of affected areas, evacuation routes, and emergency services.
* **Social research:** Visualizing demographics, crime rates, or socioeconomic indicators.Tips for Effective Latitude and Longitude Plotting
1. Choose the Right Projection: Select a projection that accurately represents the area and data being visualized. For global maps, consider projections like the Mercator projection or the Mollweide projection. For regional maps, consider projections like the UTM projection or the Albers Equal-Area Conic projection.
2. Use a Clear Basemap: Select a basemap that provides the necessary context and does not obscure the data being visualized. Consider using basemaps from reputable sources like OpenStreetMap or Natural Earth.
3. Customize Markers and Colors: Use markers and colors that effectively communicate the data and enhance the visual appeal of the map. Consider using different marker shapes, sizes, and colors to represent different categories or data values.
4. Add Labels and Legends: Include clear and concise labels for important features on the map. Add a legend to explain the meaning of different markers, colors, or symbols.
5. Consider Interactive Features: Explore the use of interactive features like zoom, pan, and marker pop-ups to enhance the user experience and facilitate data exploration.
Conclusion
Plotting latitude and longitude data using Python provides a powerful tool for visualizing geographic information and extracting valuable insights. Python’s robust libraries, flexibility, and integration capabilities make it an ideal choice for creating compelling and informative maps. By leveraging the techniques and considerations discussed in this article, users can effectively communicate geospatial data, uncover hidden patterns, and make informed decisions based on spatial context. As the field of geospatial data analysis continues to evolve, Python’s role in visualizing latitude and longitude data will only grow in importance, enabling deeper understanding and more impactful applications across various disciplines.


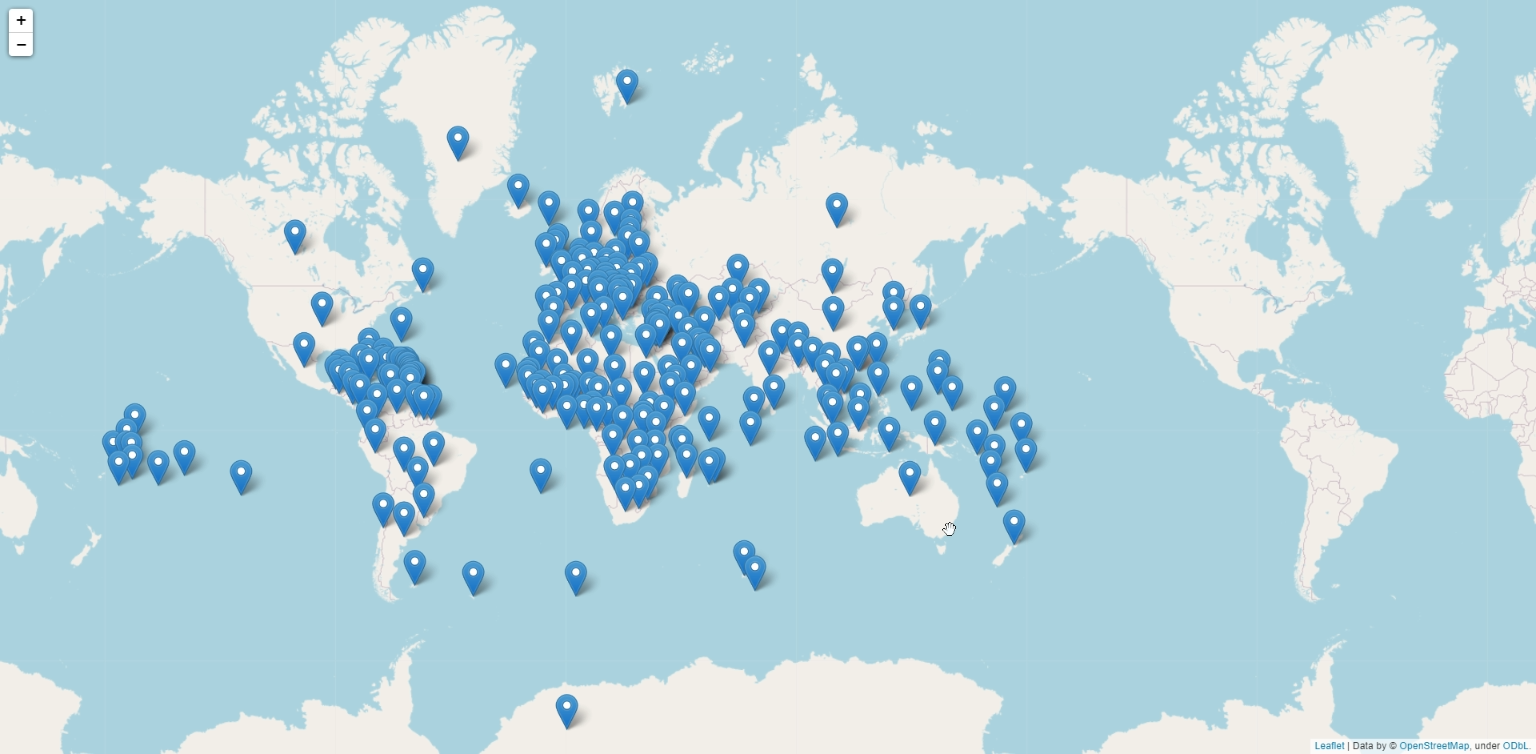
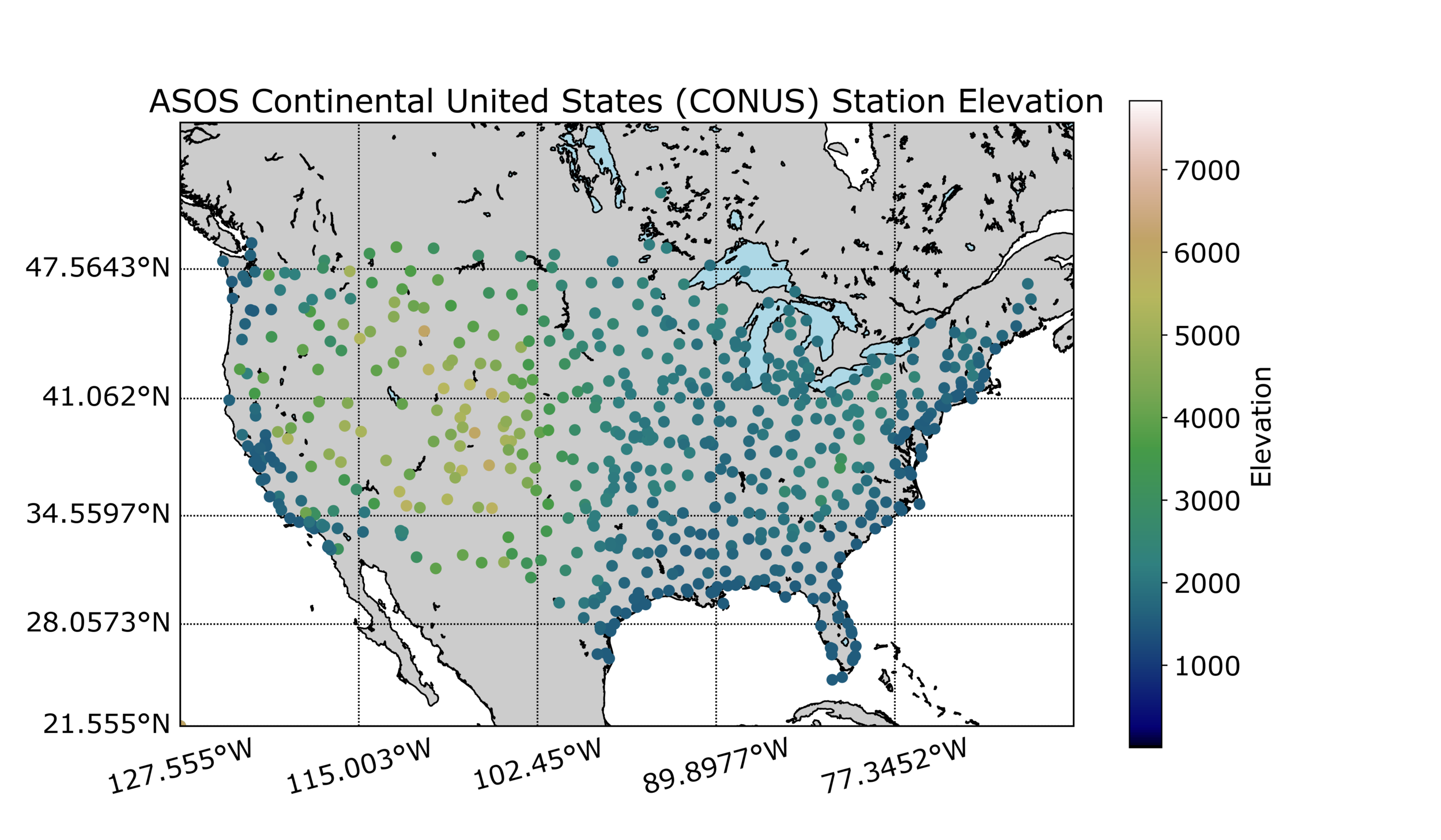
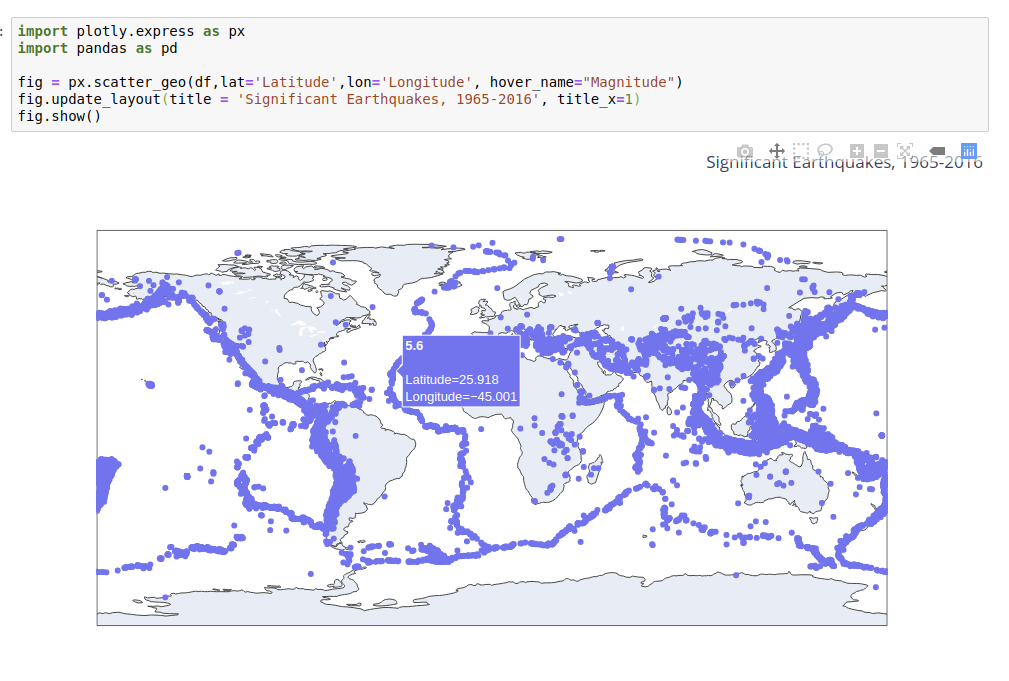


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Visualizing Data on the Globe: A Guide to Plotting Latitude and Longitude with Python. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!