Visualizing Data in Three Dimensions: Harnessing the Power of Excel and Geographic Coordinates
Related Articles: Visualizing Data in Three Dimensions: Harnessing the Power of Excel and Geographic Coordinates
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Visualizing Data in Three Dimensions: Harnessing the Power of Excel and Geographic Coordinates. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Visualizing Data in Three Dimensions: Harnessing the Power of Excel and Geographic Coordinates
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Visualizing Data in Three Dimensions: Harnessing the Power of Excel and Geographic Coordinates
- 3.1 Understanding Latitude and Longitude: The Foundation of Geographic Mapping
- 3.2 Bringing Geographic Data to Life in Excel: A Step-by-Step Guide
- 3.3 Benefits of Visualizing Data with Excel and Geographic Coordinates
- 3.4 Applications of 3D Maps in Excel: Unlocking Insights Across Disciplines
- 3.5 FAQs: Addressing Common Questions
- 3.6 Tips for Creating Effective 3D Maps in Excel
- 3.7 Conclusion: Empowering Data Visualization with Excel and Geographic Coordinates
- 4 Closure
Visualizing Data in Three Dimensions: Harnessing the Power of Excel and Geographic Coordinates

The ability to visualize data in three dimensions has revolutionized fields ranging from urban planning to environmental science. Excel, the ubiquitous spreadsheet software, offers a powerful tool for creating these visual representations, leveraging the fundamental principles of latitude and longitude. This article delves into the intricacies of creating three-dimensional maps within Excel, highlighting its capabilities and practical applications.
Understanding Latitude and Longitude: The Foundation of Geographic Mapping
Latitude and longitude form the bedrock of geographical mapping, providing a precise system for pinpointing locations on Earth’s surface. Latitude, measured in degrees north or south of the equator, defines a location’s distance from the equator. Longitude, measured in degrees east or west of the prime meridian, indicates a location’s distance from the prime meridian, which runs through Greenwich, England.
These coordinates, when combined, provide a unique identifier for any point on the globe. This system enables the precise plotting of locations, facilitating the creation of maps, analyzing spatial relationships, and visualizing geographical data.
Bringing Geographic Data to Life in Excel: A Step-by-Step Guide
Excel, while primarily known for its spreadsheet capabilities, offers a surprisingly robust set of tools for creating three-dimensional maps. This process involves several key steps:
-
Gathering Data: The first step involves acquiring data containing latitude and longitude coordinates. This data could be sourced from various sources, including:
- Geocoding Websites: Websites like Google Maps or Bing Maps provide geocoding services, converting addresses or place names into latitude and longitude coordinates.
- Data Files: Datasets containing geographic information, such as census data or environmental monitoring data, often include latitude and longitude columns.
- GPS Devices: GPS devices record latitude and longitude coordinates, allowing for the mapping of specific locations or routes.
-
Importing Data into Excel: Once the data is gathered, it needs to be imported into Excel. This can be done through various methods, such as:
- Copying and Pasting: Simply copy the data from its source and paste it into an Excel spreadsheet.
- Importing from a File: Excel supports importing data from various file formats, including CSV, TXT, and XML.
- Connecting to a Data Source: Excel can connect to external databases or data sources, allowing for direct data retrieval.
-
Preparing the Data: Before creating the map, it’s essential to ensure the data is properly formatted. This involves:
- Verifying Coordinates: Ensure that the latitude and longitude columns contain valid coordinates in the correct format (decimal degrees, degrees, minutes, seconds, etc.).
- Cleaning the Data: Remove any duplicate entries, missing values, or errors in the data.
- Organizing Columns: Arrange the data in a clear and logical manner, with separate columns for latitude, longitude, and any other relevant data.
-
Creating the Map: Excel offers several methods for creating three-dimensional maps:
- Scatter Plot with Latitude and Longitude: The most basic method involves creating a scatter plot with latitude on the x-axis and longitude on the y-axis. This creates a two-dimensional representation of the data.
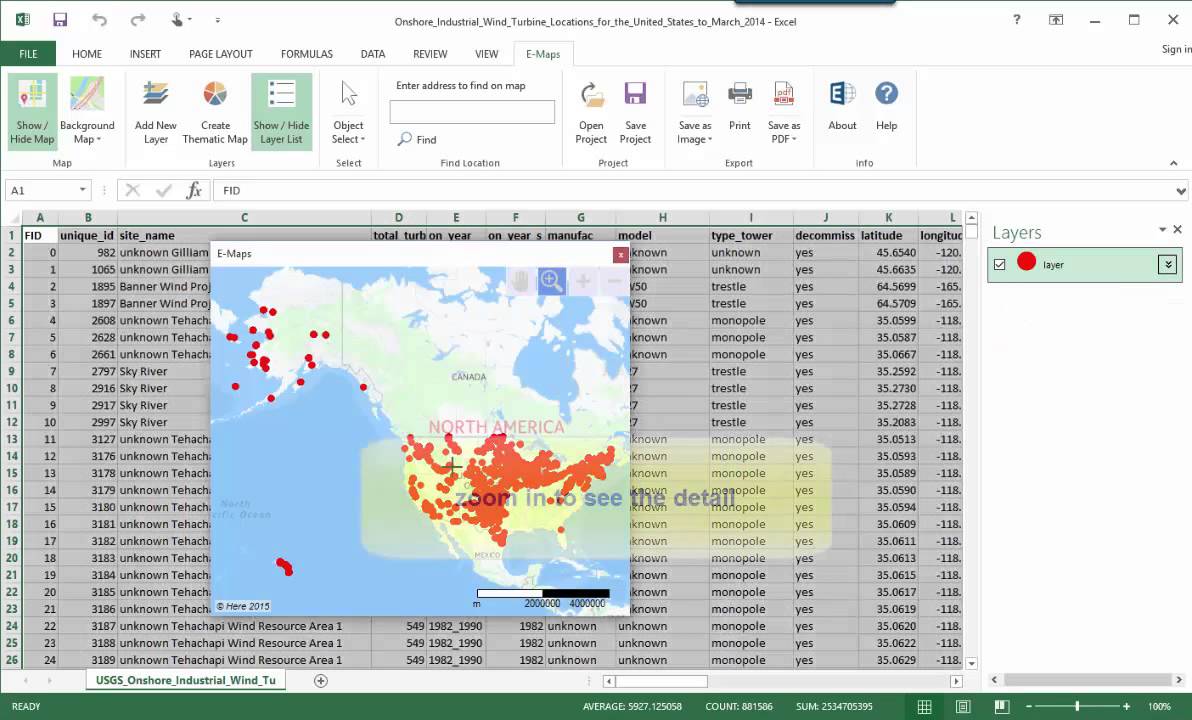
- 3D Scatter Plot: Excel’s 3D scatter plot feature allows for the creation of a three-dimensional map. This method involves adding a third dimension, typically representing a variable such as elevation, population density, or temperature.
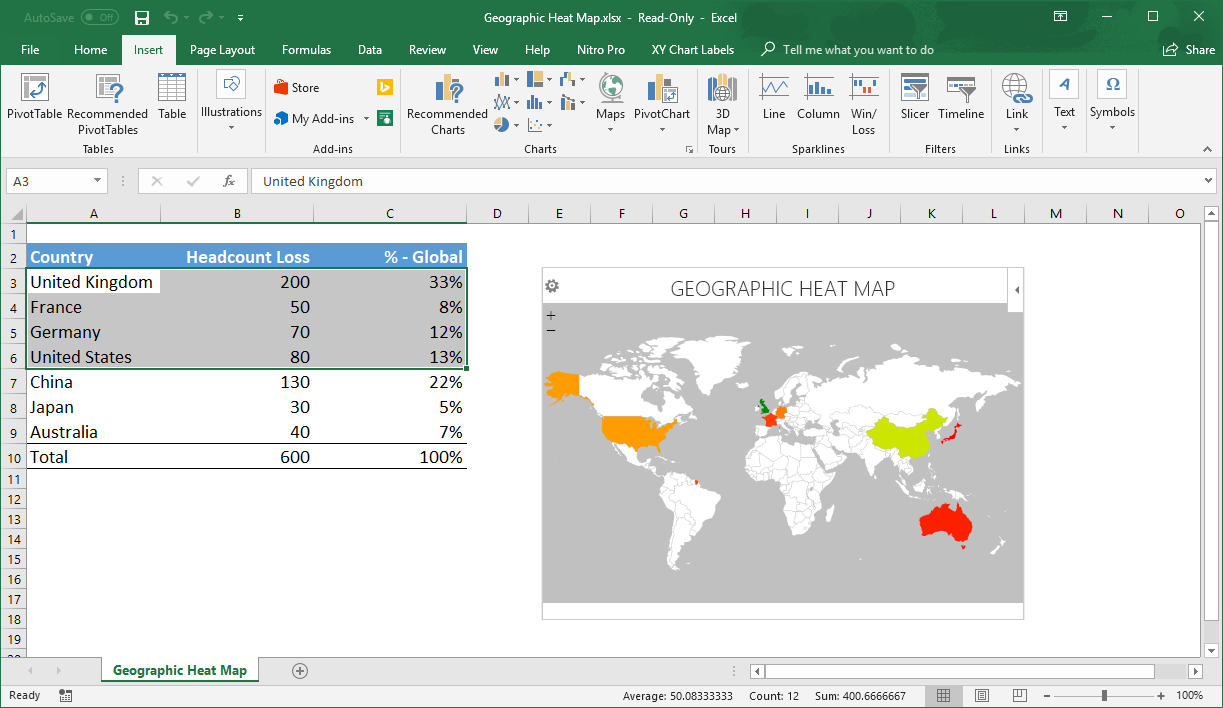
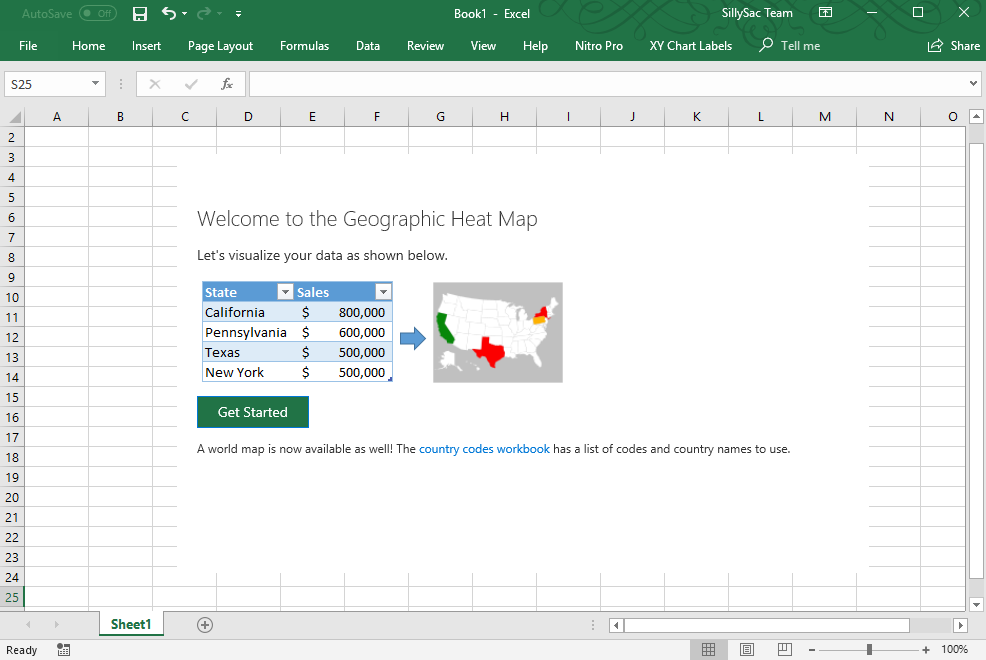
- Map Chart: Excel’s Map chart type offers a dedicated tool for creating maps. This chart type automatically uses latitude and longitude coordinates to plot locations on a map, providing a more visually appealing and intuitive representation.
-
Customizing the Map: Once the map is created, it can be customized to enhance its visual appeal and clarity:
- Adding Markers: Different markers can be used to represent different locations or data points, making the map more informative.
- Changing Colors: Colors can be used to represent different categories or data values, enhancing the visual impact of the map.
- Adding Labels: Labels can be added to identify specific locations or data points, providing context and clarity.
- Adjusting Perspective: The 3D perspective of the map can be adjusted to provide the most appropriate view for the data being visualized.
-
Exporting the Map: The final step involves exporting the map in a suitable format for sharing or further analysis:
- Image Formats: Excel allows for exporting maps as images (PNG, JPEG, etc.), making them suitable for presentations or online sharing.
- Excel File: The map can be saved as an Excel file, allowing for further editing or analysis.
- Other Formats: Excel can also export maps in formats such as PDF or SVG, depending on the specific requirements.
Benefits of Visualizing Data with Excel and Geographic Coordinates
Creating three-dimensional maps in Excel using latitude and longitude coordinates offers numerous advantages:
- Enhanced Data Visualization: 3D maps provide a more intuitive and engaging way to visualize geographic data, facilitating better understanding and interpretation.
- Spatial Analysis: By visualizing data on a map, spatial relationships and patterns can be identified, leading to valuable insights.
- Data Exploration: 3D maps enable the exploration of data from different perspectives, revealing hidden trends and relationships.
- Communication and Collaboration: Visualizations are powerful tools for communicating complex information, facilitating collaboration and decision-making.
- Accessibility: Excel’s widespread availability and ease of use make it an accessible tool for creating maps, enabling a wider range of users to leverage this powerful visualization technique.
Applications of 3D Maps in Excel: Unlocking Insights Across Disciplines
The ability to create three-dimensional maps in Excel has far-reaching applications across various disciplines:
- Business: Businesses can use 3D maps to visualize sales data, customer demographics, and market trends, identifying growth opportunities and optimizing marketing strategies.
- Urban Planning: Urban planners can leverage 3D maps to visualize city layouts, population distribution, and infrastructure development, facilitating informed planning decisions.
- Environmental Science: Environmental scientists can use 3D maps to visualize pollution levels, deforestation patterns, and climate change impacts, providing valuable data for environmental monitoring and policy development.
- Healthcare: Healthcare professionals can use 3D maps to visualize disease outbreaks, patient demographics, and resource allocation, enabling better healthcare planning and response.
- Education: Educators can use 3D maps to engage students in learning about geography, history, and social studies, enhancing understanding and fostering critical thinking.
FAQs: Addressing Common Questions
Q: What is the difference between latitude and longitude?
A: Latitude measures a location’s distance from the equator, while longitude measures its distance from the prime meridian. Latitude is measured in degrees north or south of the equator, while longitude is measured in degrees east or west of the prime meridian.
Q: How do I find latitude and longitude coordinates for a specific location?
A: You can use geocoding websites like Google Maps or Bing Maps to convert addresses or place names into latitude and longitude coordinates. Alternatively, you can use GPS devices or data files that contain geographic information.
Q: Can I create 3D maps with elevation data in Excel?
A: Yes, Excel’s 3D scatter plot feature allows you to create 3D maps with elevation data. You can use the elevation data as the third dimension to create a more realistic and informative representation of the terrain.
Q: How do I customize the appearance of my 3D map in Excel?
A: Excel offers various customization options for 3D maps, including changing marker styles, colors, labels, and the perspective of the map. You can access these options through the chart formatting pane in Excel.
Q: Can I export my 3D map from Excel to other formats?
A: Yes, Excel allows you to export 3D maps in various formats, including image formats (PNG, JPEG, etc.), Excel files, and other formats like PDF or SVG.
Tips for Creating Effective 3D Maps in Excel
- Choose the Right Data: Ensure that the data you use for your map is accurate, relevant, and properly formatted.
- Use Clear and Concise Labels: Add clear labels to identify locations and data points, making the map easier to understand.
- Consider Color Schemes: Use color schemes that are visually appealing and informative, representing different categories or data values effectively.
- Adjust the Perspective: Experiment with different perspectives to find the most suitable view for your data and message.
- Keep it Simple: Avoid overcrowding the map with too much information, ensuring clarity and ease of understanding.
Conclusion: Empowering Data Visualization with Excel and Geographic Coordinates
Excel, with its intuitive interface and powerful features, provides a readily accessible tool for creating three-dimensional maps using latitude and longitude coordinates. This ability to visualize geographic data in three dimensions empowers users across various disciplines, facilitating data exploration, spatial analysis, and communication. By harnessing the power of Excel and geographic coordinates, individuals and organizations can unlock valuable insights, make informed decisions, and effectively communicate complex information in a visually engaging manner.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Visualizing Data in Three Dimensions: Harnessing the Power of Excel and Geographic Coordinates. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!