Unveiling the World: A Comprehensive Look at Flat Maps with the Equator
Related Articles: Unveiling the World: A Comprehensive Look at Flat Maps with the Equator
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the World: A Comprehensive Look at Flat Maps with the Equator. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the World: A Comprehensive Look at Flat Maps with the Equator

Flat maps, those ubiquitous representations of our spherical planet, have long served as essential tools for navigation, exploration, and understanding the world around us. Among the various types of flat maps, those featuring the equator prominently hold a significant place, offering a unique perspective on our planet’s geography and its relationship to the sun. This article delves into the intricacies of flat maps with the equator, exploring their construction, uses, and importance in our understanding of the world.
Understanding the Equator: A Line of Significance
The equator, an imaginary line circling the Earth at 0 degrees latitude, serves as the fundamental reference point for understanding global geography. It divides the Earth into the Northern and Southern Hemispheres, marking the region where the sun’s rays strike directly at the solstices. The equator’s importance lies in its role as a key indicator of:
- Climate Zones: The equator marks the beginning of the tropical climate zone, characterized by high temperatures and abundant rainfall. This zone is home to diverse ecosystems and a wealth of biodiversity.
- Day and Night: The equator experiences nearly equal day and night lengths throughout the year, making it a crucial point of reference for timekeeping and astronomical calculations.
- Global Coordinates: Latitude and longitude, the foundation of global navigation, are measured relative to the equator and the prime meridian, respectively.
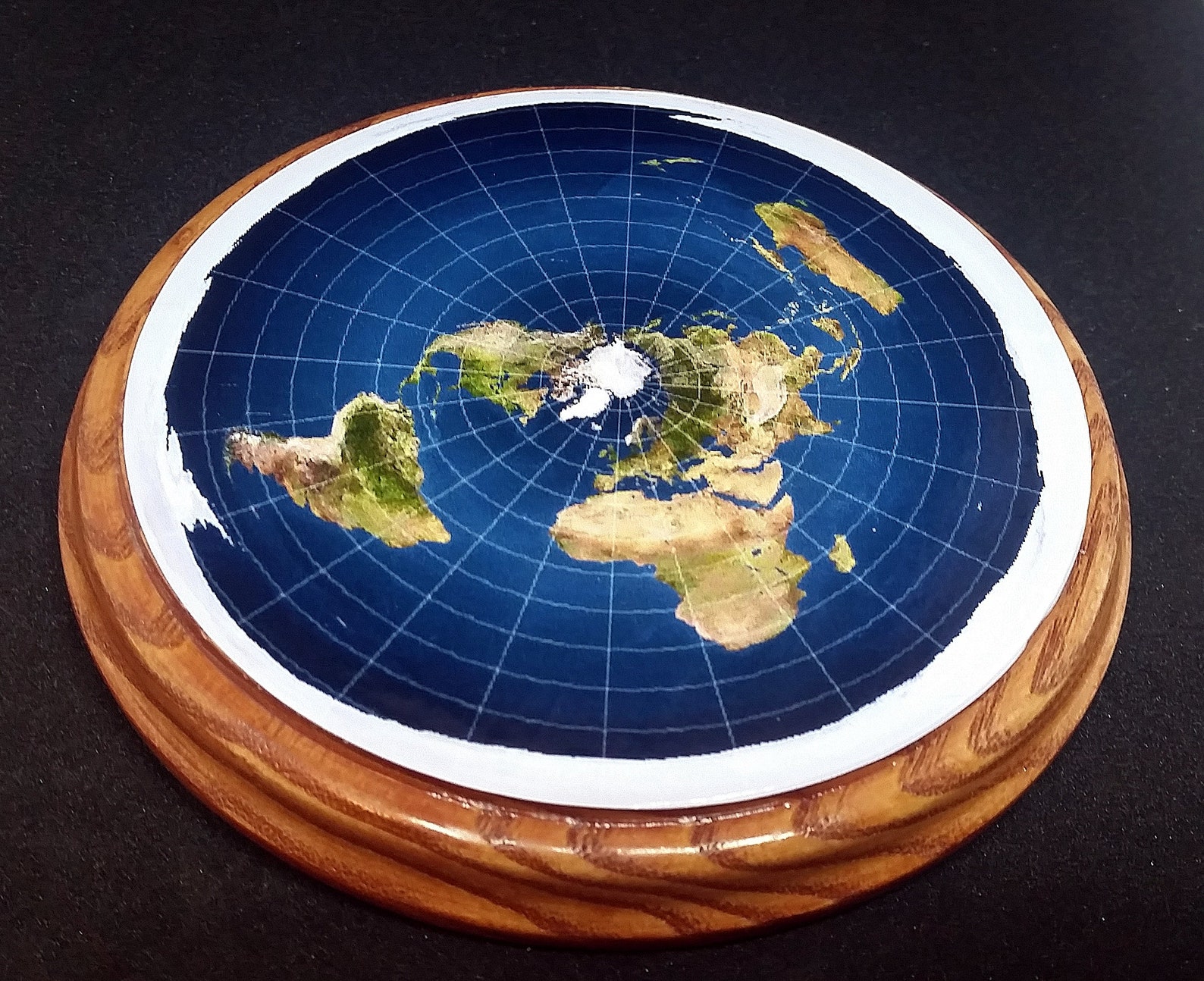
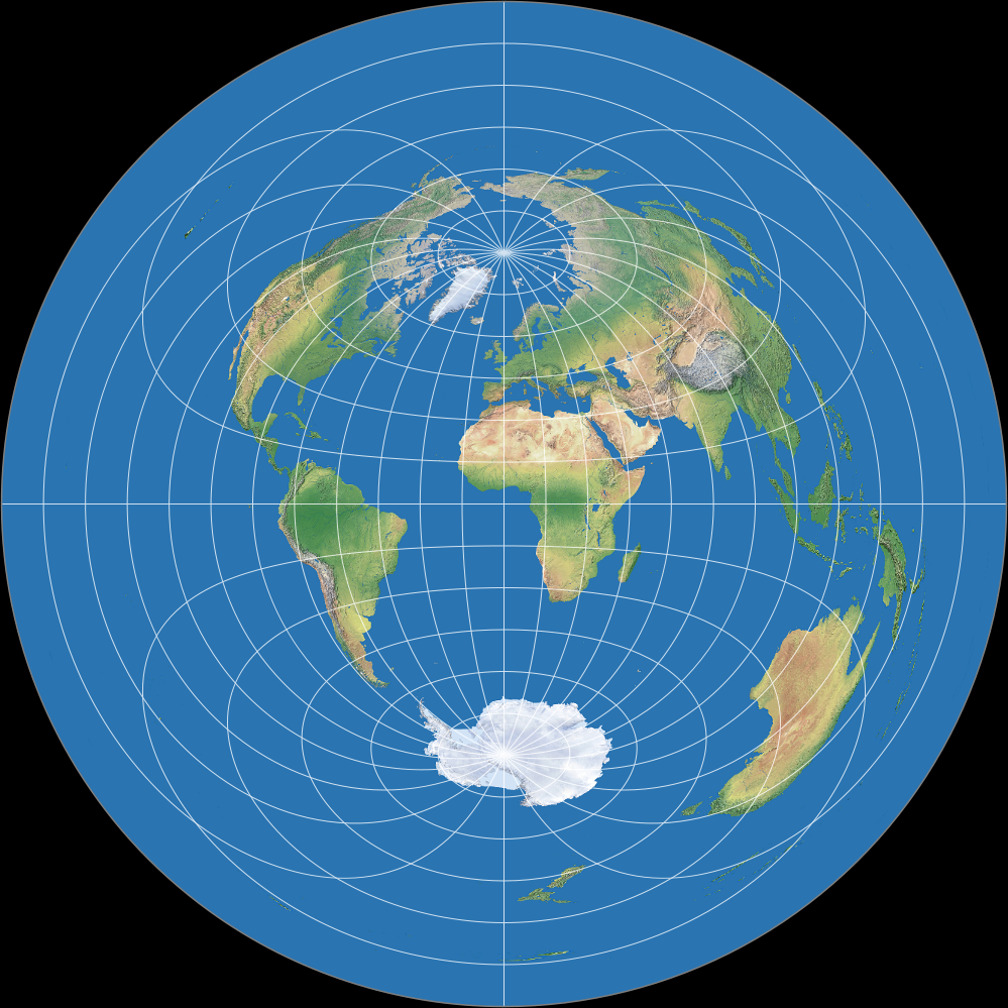
Flat Maps with the Equator: Bridging the Gap Between Sphere and Plane
The challenge of accurately representing the Earth’s spherical shape on a flat surface has occupied cartographers for centuries. Flat maps with the equator prominently displayed employ various projection methods to achieve this, each with its strengths and limitations.
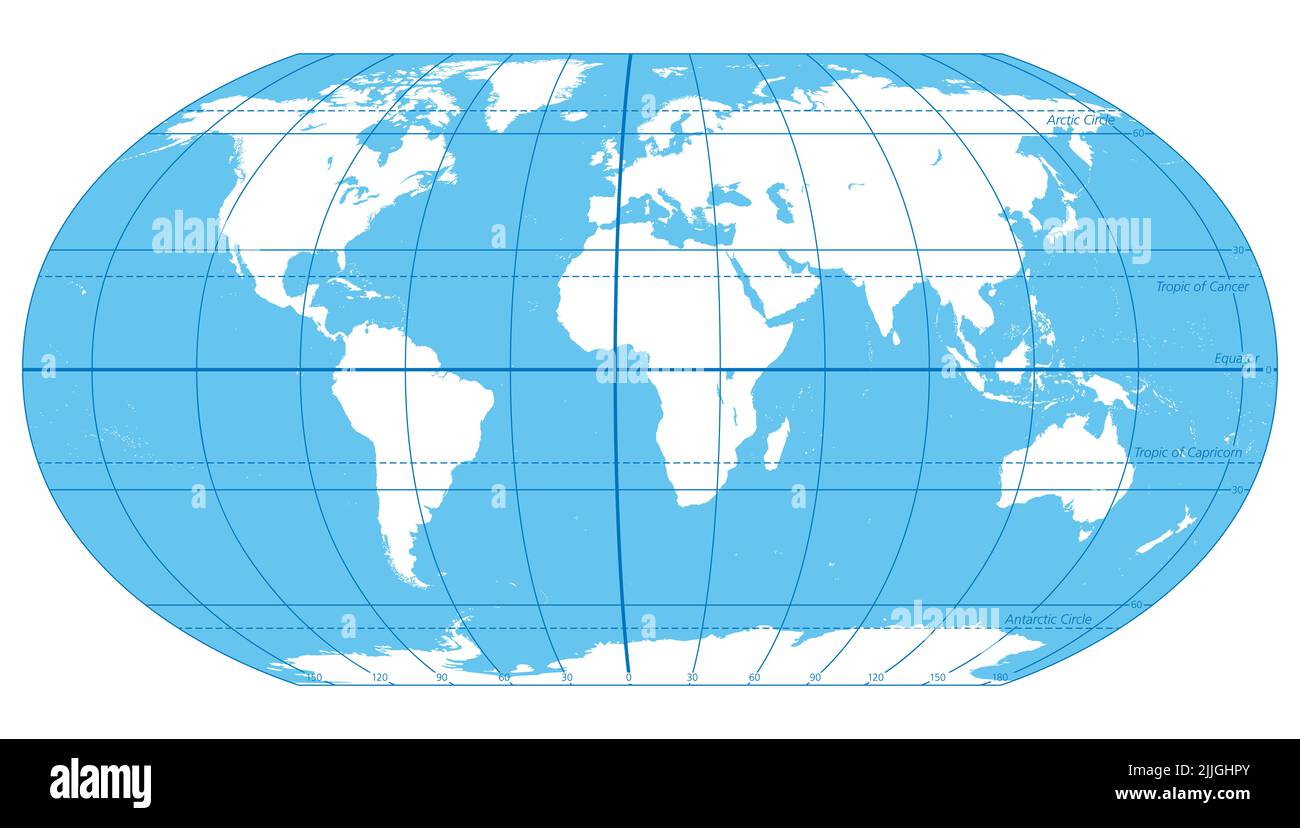
Mercator Projection: A Widely Used but Distorted View
The Mercator projection, commonly found in world maps, features the equator as a straight line running horizontally across the center. While it preserves angles and shapes locally, it significantly distorts areas, particularly towards the poles. This means that Greenland appears larger than Africa, despite being significantly smaller in reality. This distortion can lead to misinterpretations when comparing land masses or understanding global proportions.
Equirectangular Projection: A Balanced but Less Familiar Perspective
The equirectangular projection, also known as the Plate Carrée projection, presents the equator as a straight line, with meridians (lines of longitude) also appearing as straight lines. This projection offers a balanced representation of areas, but it distorts shapes, particularly towards the poles, resulting in stretched continents and exaggerated distances.
Other Projections: Exploring Alternatives
Other projections, such as the Winkel Tripel projection and the Robinson projection, aim to minimize distortions by incorporating compromises between area and shape preservation. These projections often feature the equator prominently and offer a more balanced representation of the globe.
Benefits of Flat Maps with the Equator:
Despite their inherent limitations, flat maps with the equator offer several benefits:
- Visualizing Global Connections: These maps provide a clear visual representation of the Earth’s continents and oceans, highlighting their relative positions and connections.
- Understanding Climate Patterns: The equator’s prominence on these maps helps visualize the distribution of climate zones, showcasing the influence of latitude on temperature and rainfall patterns.
- Navigational Reference: The equator serves as a fundamental reference point for navigation, allowing users to easily locate positions relative to the equator and prime meridian.
- Educational Tool: Flat maps with the equator are invaluable educational tools, helping students visualize the Earth’s shape, understand geographic concepts, and explore the diversity of the world.
FAQs: Addressing Common Queries
1. Why are there different types of flat maps?
Different projections are used to minimize distortion in various aspects, such as area, shape, or distance. The choice of projection depends on the intended use of the map.
2. Is it possible to create a completely accurate flat map of the Earth?
No, it is impossible to create a completely accurate flat map of the Earth because the Earth is a sphere, and any attempt to flatten it will inevitably result in distortion.
3. What are the limitations of flat maps with the equator?
These maps can distort shapes, areas, and distances, particularly towards the poles. They may not accurately represent the true proportions of land masses or distances between locations.
4. How can I use flat maps with the equator effectively?
It is crucial to understand the limitations of the specific projection used and to interpret the information presented with caution. Consider the purpose of the map and choose a projection that minimizes the distortion relevant to your needs.
Tips for Using Flat Maps with the Equator:
- Be aware of distortions: Understand the limitations of the chosen projection and interpret information accordingly.
- Use multiple maps: Compare different projections to gain a comprehensive understanding of global geography.
- Consult globes: Globes provide a more accurate representation of the Earth’s shape and can be used to verify information presented on flat maps.
- Focus on specific regions: If you are interested in a particular region, use maps designed for that area, which minimize distortion within that specific geographic zone.
Conclusion: Embracing the Complexity of Representation
Flat maps with the equator, despite their inherent limitations, offer a valuable tool for understanding our planet’s geography and its relationship to the sun. By acknowledging their limitations and using them effectively, we can harness their power to visualize global connections, understand climate patterns, and navigate the world around us. Ultimately, these maps serve as a reminder of the complexity of representing a spherical world on a flat surface, encouraging us to appreciate the intricate relationship between cartography and our understanding of the globe.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the World: A Comprehensive Look at Flat Maps with the Equator. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!