Unveiling the Geographic Tapestry of North America: A Journey Through Latitude and Longitude
Related Articles: Unveiling the Geographic Tapestry of North America: A Journey Through Latitude and Longitude
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Geographic Tapestry of North America: A Journey Through Latitude and Longitude. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Geographic Tapestry of North America: A Journey Through Latitude and Longitude

North America, a vast and diverse continent spanning from the Arctic Circle to the tropics, presents a captivating geographic landscape. Understanding its intricate network of latitude and longitude lines is essential to deciphering its diverse ecosystems, rich history, and complex cultural tapestry. This article delves into the significance of latitude and longitude in unraveling the intricacies of North America, exploring its geography, history, and cultural influences.
The Grid System: Latitude and Longitude
Latitude and longitude form an indispensable grid system, allowing geographers, cartographers, and explorers to pinpoint any location on Earth with precision. Latitude lines, running parallel to the equator, measure distances north or south of the equator. The equator, at 0 degrees latitude, divides the Earth into the Northern and Southern Hemispheres. As one travels further from the equator, latitude values increase, reaching 90 degrees at the North and South Poles.
Longitude lines, on the other hand, run vertically from the North Pole to the South Pole, intersecting the equator at right angles. They measure distances east or west of the Prime Meridian, which runs through Greenwich, England, at 0 degrees longitude. As one moves eastward or westward, longitude values increase, reaching 180 degrees at the International Date Line, which roughly follows the 180th meridian.
North America’s Latitude and Longitude: A Framework for Understanding
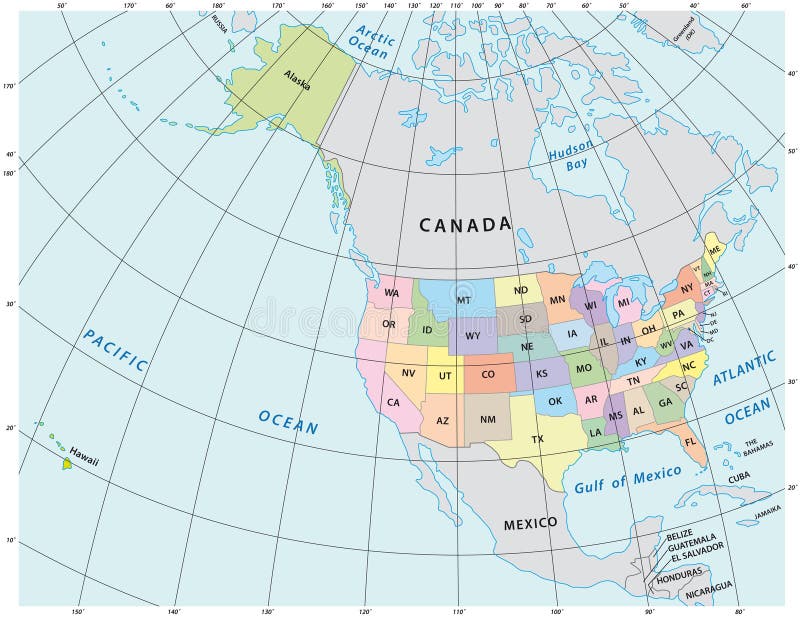
Within this global grid system, North America occupies a unique position, extending from approximately 70 degrees North latitude to 10 degrees North latitude and from 170 degrees West longitude to 55 degrees West longitude. This vast expanse encompasses diverse climates, landscapes, and cultures.
Latitude’s Influence on Climate and Ecosystems:
Latitude significantly influences North America’s climate and ecosystems. The northern regions, located above 60 degrees North latitude, experience long, cold winters and short, cool summers, characterized by vast tundra and boreal forests. Moving south, the temperate zones, between 30 and 60 degrees North latitude, exhibit a wider range of temperatures, with distinct seasons and diverse ecosystems, including deciduous forests, grasslands, and agricultural lands. The southern regions, below 30 degrees North latitude, experience warm to hot temperatures year-round, with tropical rainforests, deserts, and coastal plains.
Longitude’s Role in Shaping Geography and Culture:
Longitude plays a crucial role in shaping the geographic features and cultural landscapes of North America. The continent’s western coast, facing the Pacific Ocean, experiences the moderating influence of the Pacific Ocean currents, leading to relatively mild climates and diverse marine ecosystems. The eastern coast, facing the Atlantic Ocean, is influenced by the Gulf Stream, a warm current that brings milder temperatures and abundant rainfall to the region.
The interior of North America, situated between the eastern and western coasts, experiences a greater range of temperatures and precipitation, with vast prairies, mountains, and deserts. The Rocky Mountains, stretching from Canada to Mexico, form a prominent geographical barrier, influencing weather patterns and shaping the continent’s interior.
A Historical Perspective: Latitude and Longitude in Exploration and Navigation
Latitude and longitude have played a pivotal role in shaping the history of North America. Early European explorers relied on these coordinates to navigate the vast oceans and chart new lands. The development of accurate instruments for determining latitude and longitude, such as the sextant and chronometer, revolutionized seafaring and facilitated the exploration and settlement of North America.
The Importance of Latitude and Longitude in Modern Life
In the modern era, latitude and longitude remain essential tools for navigation, communication, and scientific research. GPS systems, relying on a network of satellites, utilize these coordinates to determine precise locations, enabling navigation and mapping applications. Latitude and longitude are also crucial for understanding weather patterns, predicting natural disasters, and managing environmental resources.
FAQs
Q: How can I use latitude and longitude to find a specific location on a map?
A: Latitude and longitude coordinates are expressed as decimal degrees, with latitude values ranging from -90 to +90 degrees and longitude values ranging from -180 to +180 degrees. To locate a specific point on a map, simply find the intersection of the corresponding latitude and longitude lines.
Q: What is the difference between latitude and longitude?
A: Latitude measures distances north or south of the equator, while longitude measures distances east or west of the Prime Meridian. Latitude lines are parallel to the equator, while longitude lines converge at the poles.
Q: How do latitude and longitude affect climate?
A: Latitude influences climate by determining the amount of solar radiation a region receives. Areas closer to the equator receive more direct sunlight and experience warmer temperatures, while regions further from the equator receive less direct sunlight and experience colder temperatures.
Q: What are some examples of how latitude and longitude are used in everyday life?
A: Latitude and longitude are used in everyday life for navigation, mapping, weather forecasting, and environmental monitoring. GPS systems, online maps, and weather apps all rely on these coordinates to provide location information and other services.
Tips
Tip 1: Use an online map tool or a globe to visualize the grid system of latitude and longitude. This will help you understand how these lines intersect and how they are used to pinpoint locations.
Tip 2: Practice reading and interpreting latitude and longitude coordinates. Pay attention to the signs (positive or negative) and the units of measurement (degrees).
Tip 3: Explore the relationship between latitude and longitude and other geographic features, such as climate, vegetation, and population density. This will help you understand how these coordinates influence the distribution of life on Earth.
Conclusion
Latitude and longitude form a fundamental framework for understanding the geography, history, and culture of North America. By understanding this grid system, we gain insights into the continent’s diverse climates, landscapes, and human settlements. From the vast tundras of the Arctic to the lush rainforests of the tropics, from the bustling metropolises of the east coast to the rugged mountains of the west, the tapestry of North America is woven together by the intricate interplay of latitude and longitude. These invisible lines provide a powerful tool for exploring and appreciating the continent’s rich and complex heritage.


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Geographic Tapestry of North America: A Journey Through Latitude and Longitude. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!