Unveiling the Earth’s Tropical Tapestry: A Comprehensive Guide to the Equator and Tropics
Related Articles: Unveiling the Earth’s Tropical Tapestry: A Comprehensive Guide to the Equator and Tropics
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Earth’s Tropical Tapestry: A Comprehensive Guide to the Equator and Tropics. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Earth’s Tropical Tapestry: A Comprehensive Guide to the Equator and Tropics
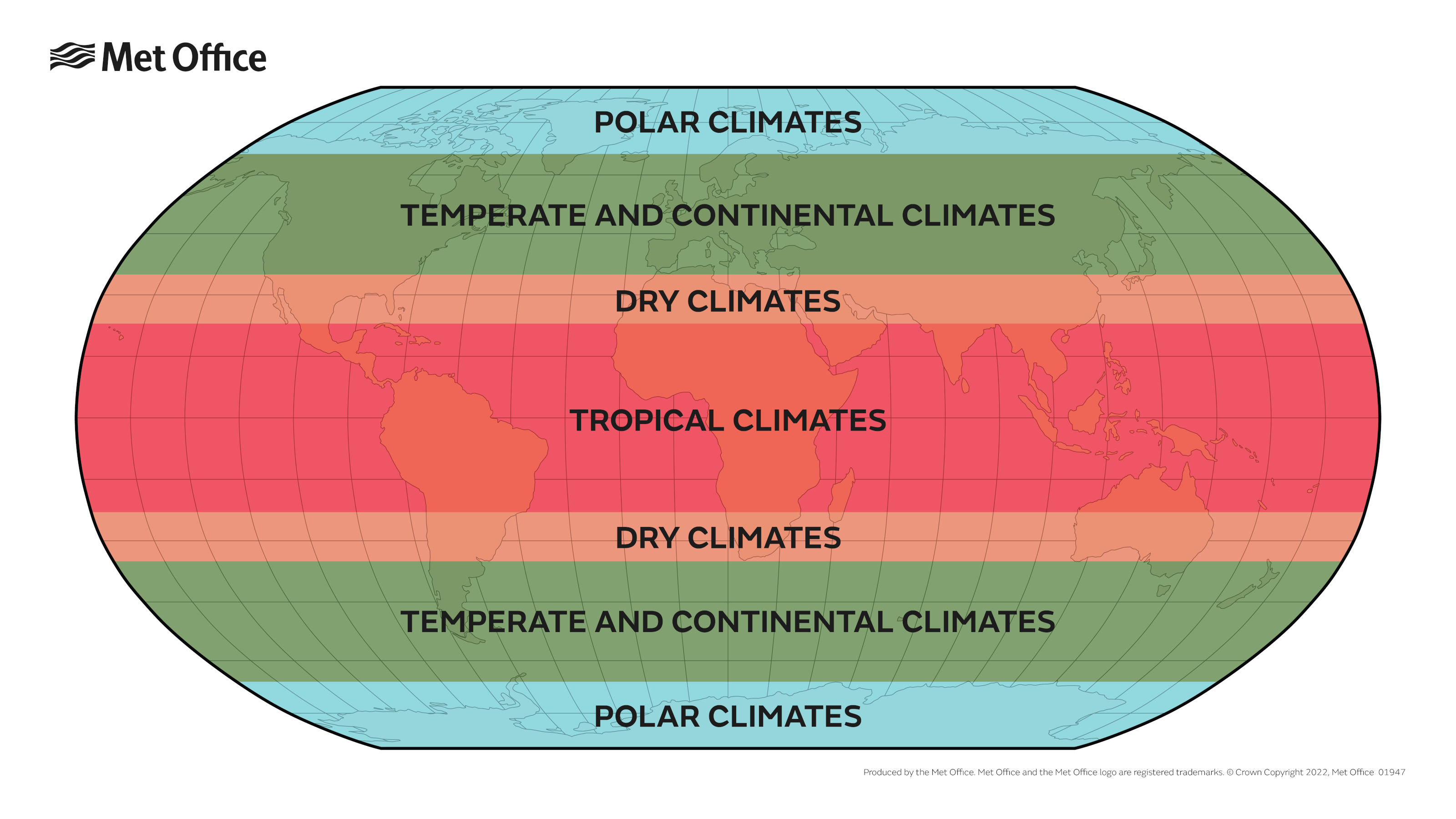
The Earth, a vibrant sphere suspended in the cosmos, is adorned with an intricate tapestry of geographical features. Among these, the equator and tropics stand out as crucial elements shaping our planet’s climate, biodiversity, and human civilization. Understanding these lines of latitude, their influence on weather patterns, and their impact on the natural world is essential for comprehending the Earth’s complex and interconnected systems.
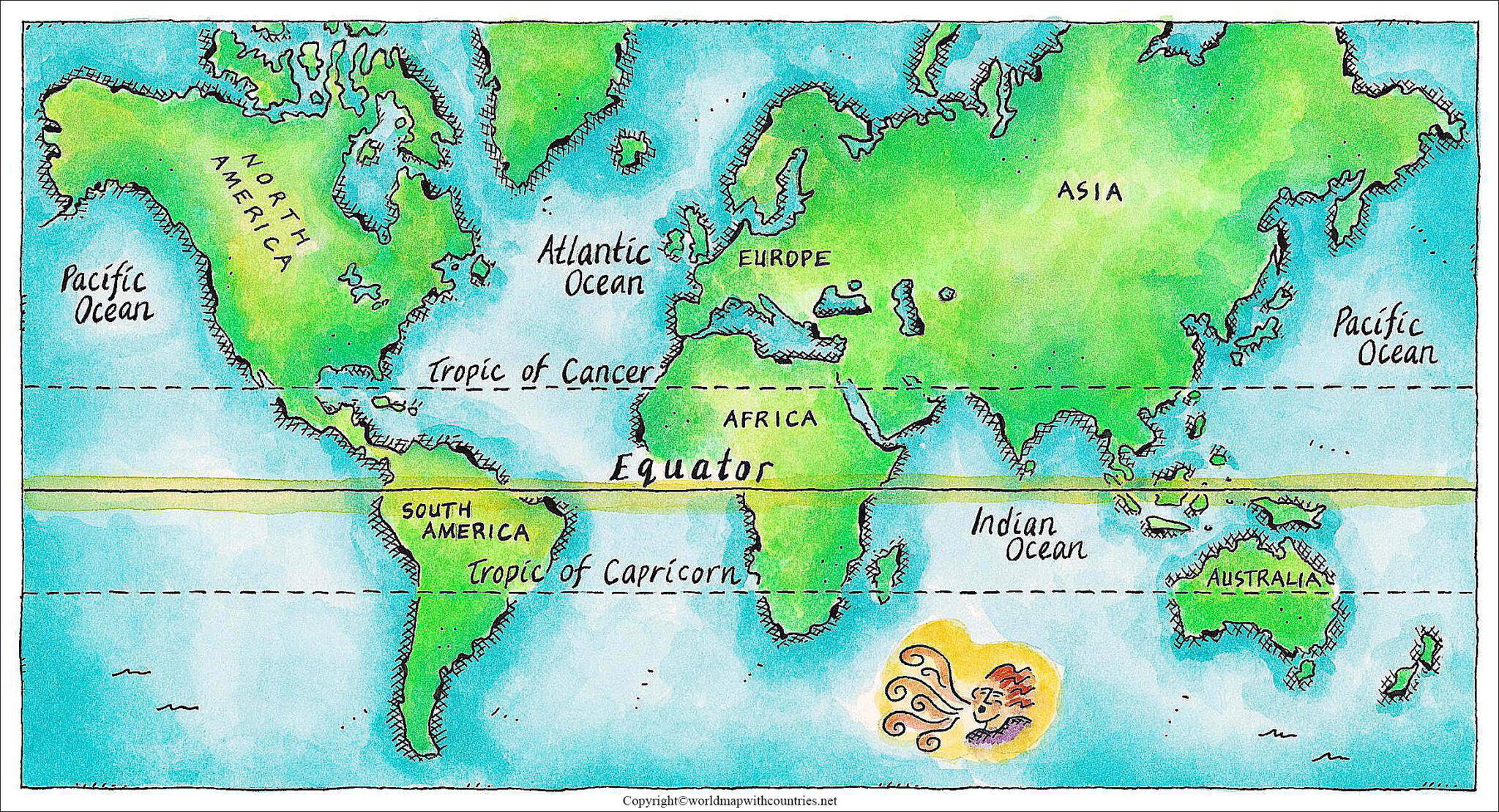
The Equator: A Line of Symmetry and Sun
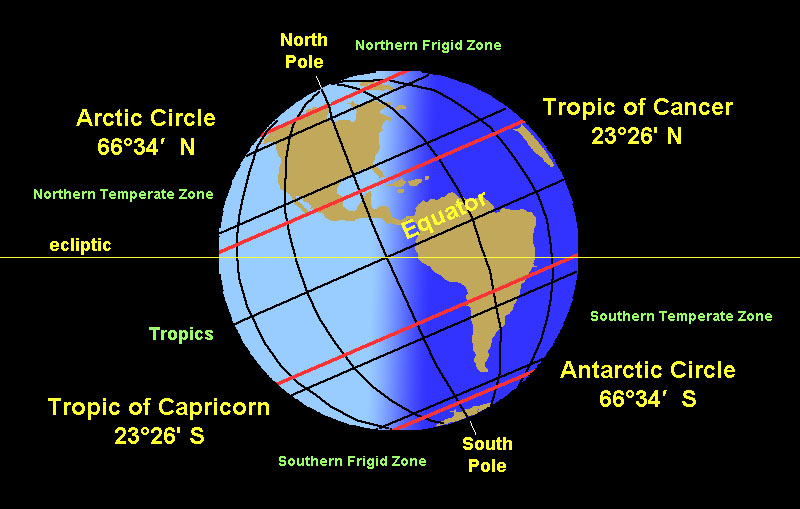
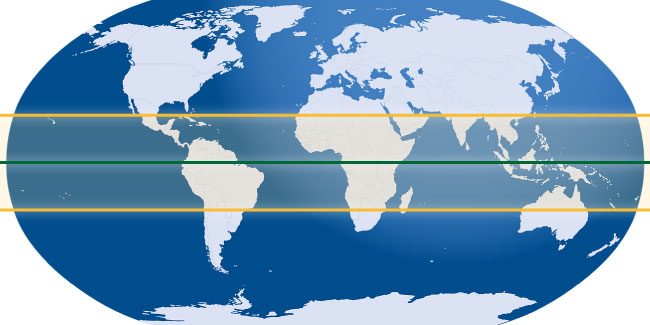
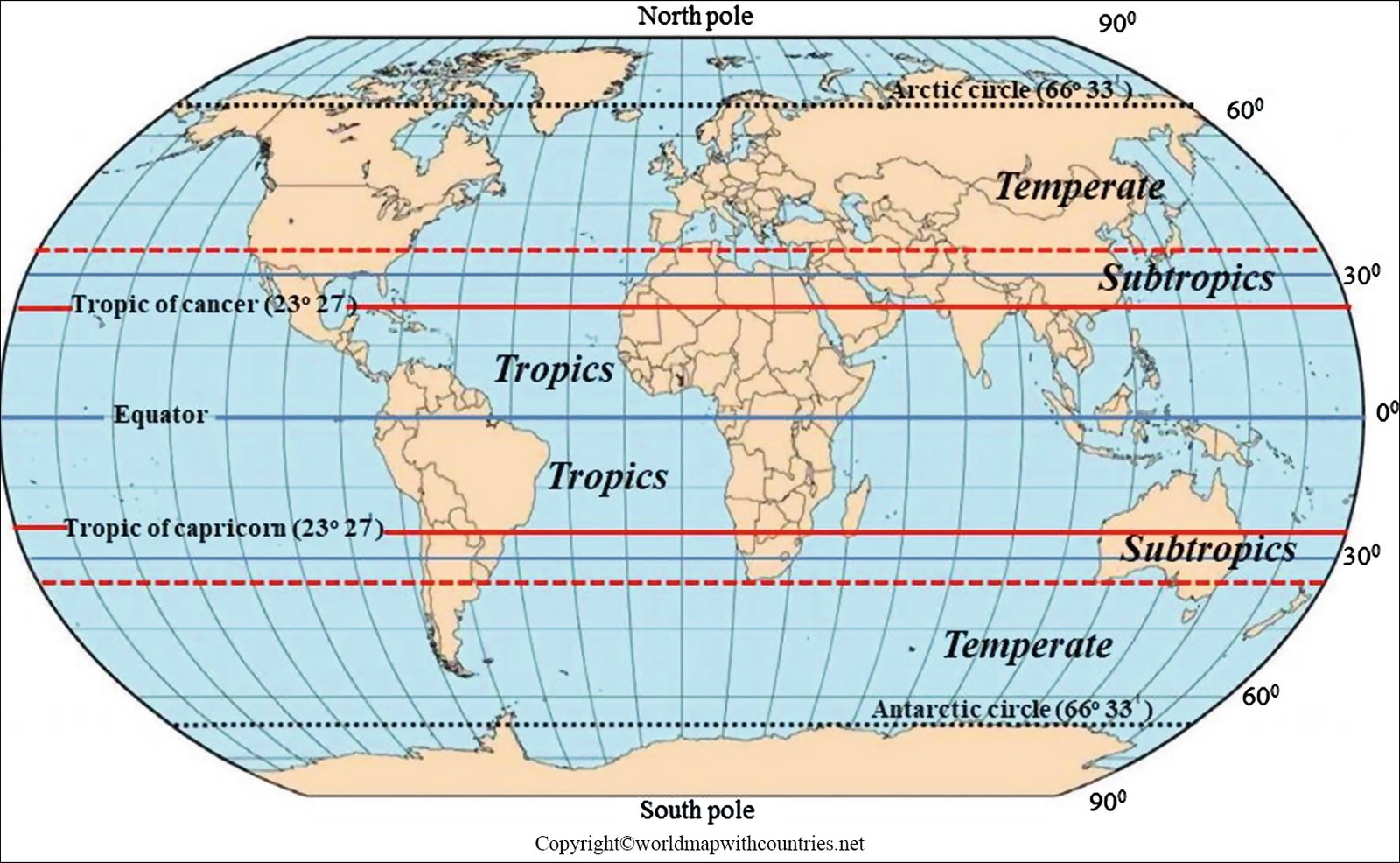
The equator, an imaginary circle that divides the Earth into the Northern and Southern Hemispheres, is a fundamental reference point in geography. It lies at 0 degrees latitude and is the only line of latitude that encompasses the entire globe. The equator’s significance stems from its unique relationship with the sun.
Due to the Earth’s tilt on its axis, the sun’s rays strike the equator directly throughout the year. This constant exposure to the sun’s energy results in a consistently warm climate, with minimal variation in temperature between seasons. The equator is thus characterized by a tropical climate, marked by high temperatures, abundant rainfall, and lush vegetation.
The Tropics: Bands of Heat and Life
The tropics, encompassing the regions between the Tropic of Cancer (23.5 degrees North) and the Tropic of Capricorn (23.5 degrees South), are defined by their proximity to the equator. These areas share many of the characteristics of the equatorial zone, experiencing high temperatures and significant rainfall.
The tropics are home to a staggering diversity of life, from vibrant rainforests teeming with exotic flora and fauna to coral reefs teeming with marine life. The region’s abundant sunlight and rainfall create ideal conditions for the growth of diverse plant and animal species, leading to a rich tapestry of ecosystems.
Understanding the Impact of the Equator and Tropics
The equator and tropics play a critical role in shaping the Earth’s climate, biodiversity, and human civilization. Their influence extends far beyond their geographical boundaries, impacting global weather patterns, agricultural practices, and even cultural development.
Climate and Weather Patterns:
- Direct Sunlight: The equator and tropics receive the most direct sunlight throughout the year, leading to consistently warm temperatures and high levels of solar radiation.
- Convection Currents: The intense heat in these regions creates powerful convection currents, driving air circulation patterns that influence global weather systems.
- Monsoon Winds: The tropics are particularly susceptible to monsoon winds, which bring seasonal rainfall and play a crucial role in agriculture and water resources.
Biodiversity and Ecosystems:
- Rich Biodiversity: The tropics are known as "hotspots" of biodiversity, boasting an incredible variety of plant and animal species. The abundant sunlight and rainfall create ideal conditions for the evolution and survival of diverse ecosystems.
- Rainforests: The equatorial and tropical regions are home to vast rainforests, which play a crucial role in regulating the global climate, providing oxygen, and harboring a significant portion of the world’s biodiversity.
- Coral Reefs: The warm waters of the tropics are ideal for the development of coral reefs, which are vital ecosystems that support a wide array of marine life.
Human Civilization and Culture:
- Agriculture: The tropics are often associated with agriculture, as the warm climate and abundant rainfall allow for the growth of a variety of crops, including coffee, cacao, and rice.
- Cultural Diversity: The tropics are home to a diverse range of cultures, each with its unique traditions, languages, and beliefs. The region’s rich history and cultural heritage are shaped by its climate, geography, and natural resources.
- Tourism: The tropics are popular destinations for tourism, attracting visitors seeking warm weather, pristine beaches, and unique cultural experiences.
The Challenges of the Equator and Tropics
While the equator and tropics offer many benefits, they also face significant challenges:
- Deforestation: The rapid clearing of tropical forests for agriculture, logging, and other development activities poses a serious threat to biodiversity and climate regulation.
- Climate Change: The tropics are particularly vulnerable to the impacts of climate change, with rising temperatures, more extreme weather events, and rising sea levels threatening their delicate ecosystems and human populations.
- Poverty and Inequality: Many tropical regions face high levels of poverty and inequality, exacerbated by limited access to education, healthcare, and economic opportunities.
FAQs: Understanding the Equator and Tropics
1. Why is the equator warm?
The equator receives the most direct sunlight throughout the year due to the Earth’s tilt on its axis. This constant exposure to the sun’s energy results in consistently warm temperatures.
2. What is the difference between the equator and the tropics?
The equator is a single line of latitude at 0 degrees, while the tropics are a wider zone encompassing the regions between the Tropic of Cancer and the Tropic of Capricorn. Both areas experience warm climates but the tropics are characterized by more seasonal variation in temperature and rainfall.
3. Why are the tropics so biodiverse?
The tropics’ warm temperatures, abundant rainfall, and consistent sunlight create ideal conditions for the growth and survival of a wide variety of plant and animal species, leading to high biodiversity.
4. What are the challenges facing the tropics?
The tropics face challenges such as deforestation, climate change, poverty, and inequality. These issues threaten the region’s biodiversity, ecosystems, and human populations.
Tips: Exploring the Equator and Tropics
- Use a world map: A world map with the equator and tropics clearly marked is an invaluable tool for understanding the Earth’s geographical features.
- Learn about the climate: Research the different climate zones within the equatorial and tropical regions to better understand their unique characteristics.
- Explore the biodiversity: Discover the fascinating plant and animal life found in tropical rainforests, coral reefs, and other ecosystems.
- Engage with local cultures: Learn about the diverse cultures and traditions that have developed in the tropics, respecting their unique perspectives and practices.
Conclusion: The Equator and Tropics: A Vital Tapestry of Life
The equator and tropics, with their unique geographical position and climatic conditions, are vital elements of the Earth’s complex and interconnected systems. They play a crucial role in shaping global climate patterns, harboring immense biodiversity, and influencing human civilization. Understanding these regions is essential for appreciating the Earth’s beauty, complexity, and the challenges we face in protecting our planet for future generations.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Earth’s Tropical Tapestry: A Comprehensive Guide to the Equator and Tropics. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!