Unveiling the Earth’s Seismic Scars: Exploring World Fault Lines with Google Earth
Related Articles: Unveiling the Earth’s Seismic Scars: Exploring World Fault Lines with Google Earth
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Earth’s Seismic Scars: Exploring World Fault Lines with Google Earth. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Earth’s Seismic Scars: Exploring World Fault Lines with Google Earth

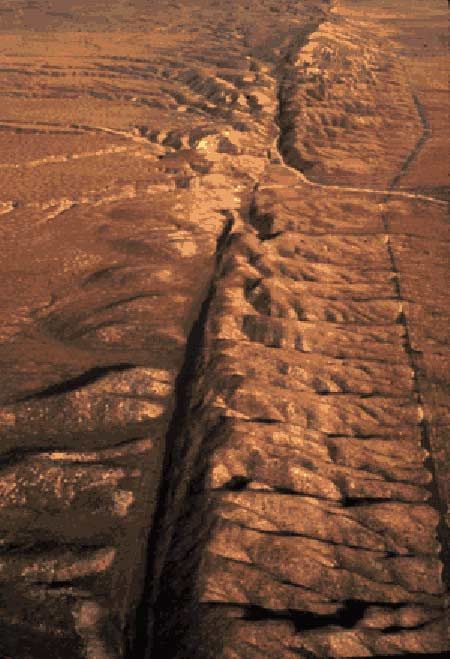
The Earth’s surface, seemingly solid and stable, is in fact a dynamic and ever-shifting landscape. Beneath the familiar continents and oceans lie a network of fractures known as fault lines, invisible to the naked eye yet responsible for some of the most dramatic and destructive events in our planet’s history. These fault lines, where tectonic plates meet and interact, are the epicenters of earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, and the gradual reshaping of the Earth’s topography.
Google Earth, a powerful tool for visualizing our planet, offers a unique perspective on these geological features. By overlaying fault line data onto its detailed 3D maps, it allows users to explore the intricate network of these seismic scars and gain a deeper understanding of the Earth’s dynamic processes.
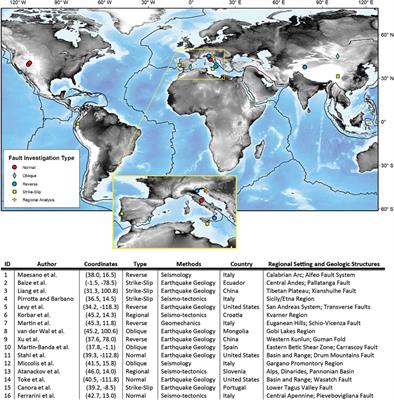
Delving into the Data: Understanding the World Fault Lines Map on Google Earth
The World Fault Lines Map on Google Earth is not a singular entity but rather a composite of data from various sources, including:
- Global Seismic Hazard Maps: These maps, compiled by organizations like the United States Geological Survey (USGS) and the International Seismological Centre (ISC), depict areas with high seismic activity, highlighting the locations of major fault lines.
- Geological Surveys and Research: Data from geological surveys and research institutions across the globe contribute to the map, providing detailed information on specific fault lines, their characteristics, and their history of activity.
- Satellite Imagery and Remote Sensing: Advanced satellite technology plays a crucial role in mapping fault lines. High-resolution images and radar data reveal subtle surface deformations associated with fault movement, offering valuable insights into the underlying geological structures.
Navigating the Map: Exploring Fault Lines with Ease
Google Earth’s user-friendly interface allows for seamless exploration of the World Fault Lines Map. Users can zoom in and out, pan across the globe, and even change the map’s perspective to view fault lines from different angles. This interactive experience provides a dynamic and engaging way to visualize these geological features and understand their global distribution.
The Significance of Fault Lines: Understanding the Earth’s Dynamic Processes
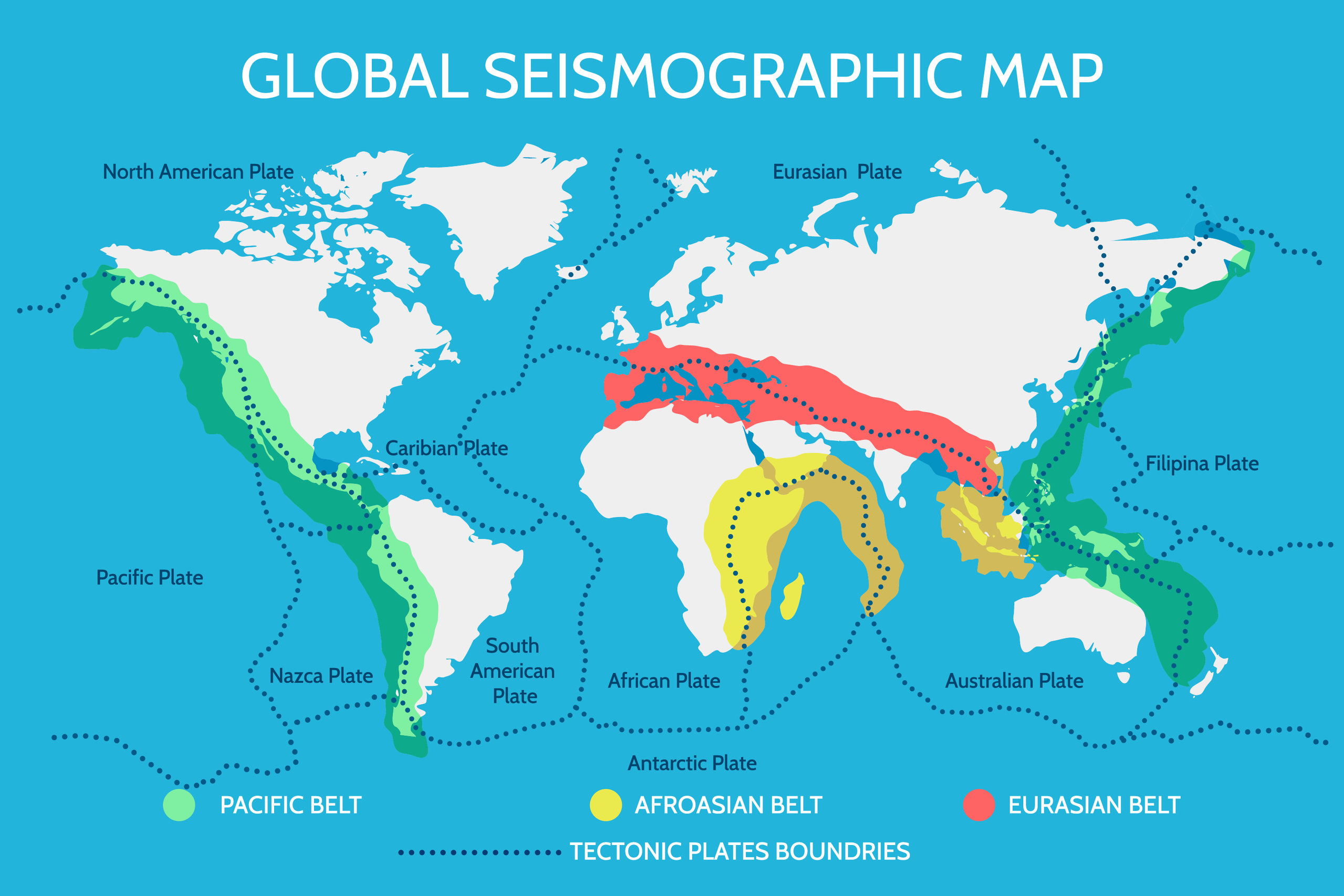
Fault lines are not merely lines on a map but rather crucial elements in the Earth’s geological framework. They represent boundaries between tectonic plates, massive slabs of the Earth’s crust that are constantly in motion. The interactions between these plates drive a multitude of geological phenomena, including:
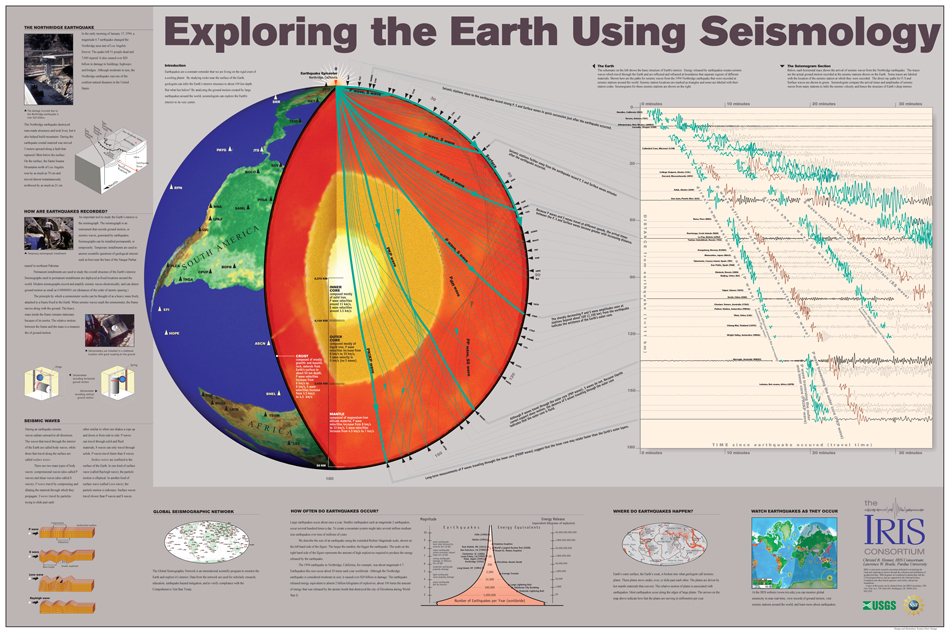
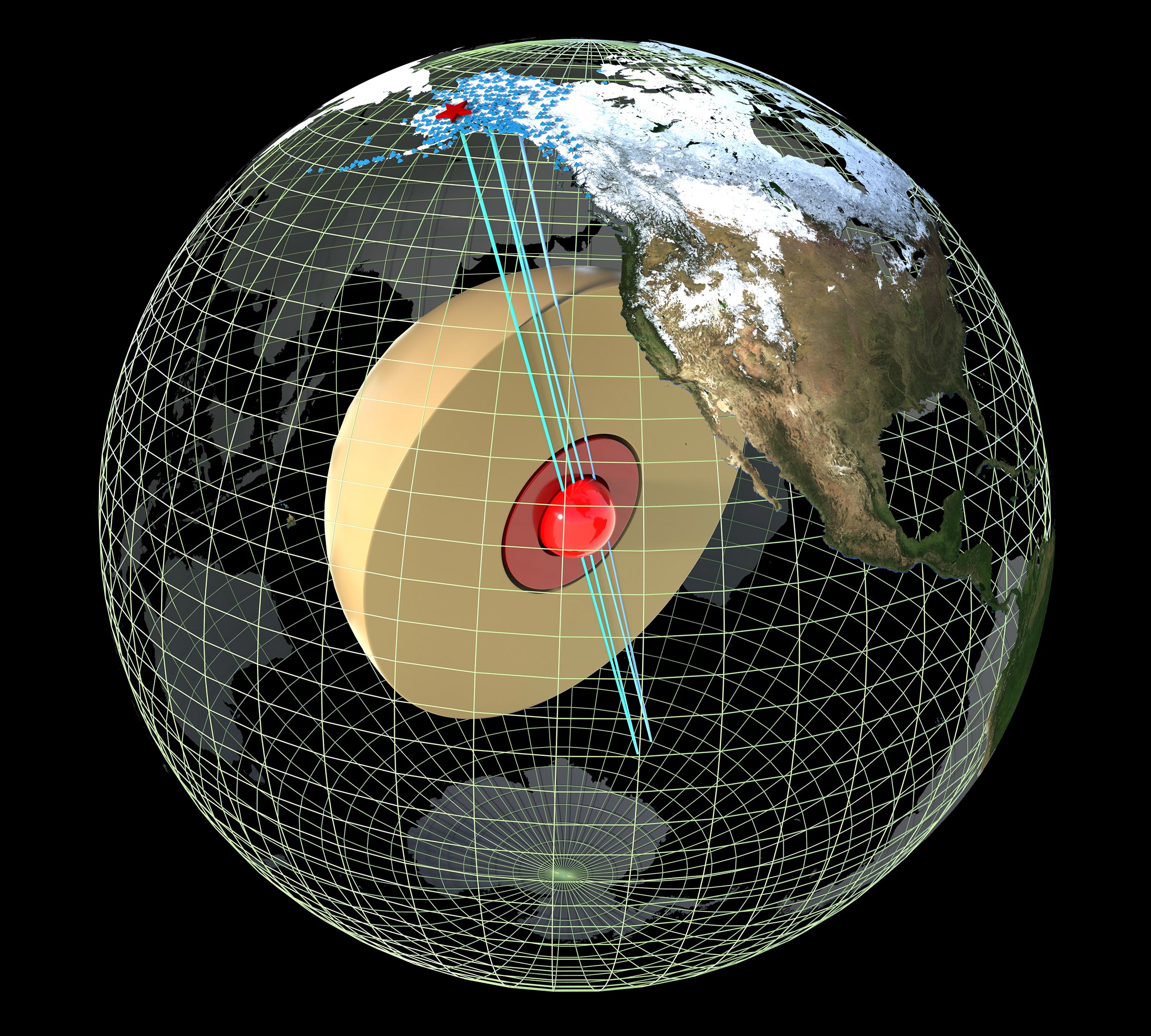
- Earthquakes: When tectonic plates slide past each other, collide, or pull apart along fault lines, the resulting stress and sudden release of energy create earthquakes. The magnitude and frequency of these events are directly linked to the characteristics of the fault line and the amount of accumulated stress.
- Volcanic Activity: Fault lines often coincide with volcanic zones. As plates converge, one plate can slide beneath the other, leading to the melting of rock and the formation of magma. This magma can then rise to the surface through volcanic vents, creating eruptions that can shape landscapes and influence climate.
- Mountain Formation: The collision of tectonic plates along convergent fault lines can lead to the uplift of landmasses, forming mountain ranges. The Himalayas, the Andes, and the Alps are all prime examples of mountain chains formed through this process.
- Ocean Basin Formation: Divergent fault lines, where plates move apart, create rifts in the Earth’s crust. These rifts can eventually widen, forming new ocean basins and spreading centers where new crust is generated.
The Importance of Fault Line Mapping: Mitigating Risks and Understanding the Earth
Mapping fault lines is not just an academic exercise. It has crucial implications for our understanding of the Earth and for mitigating the risks associated with geological hazards.
- Earthquake Prediction and Mitigation: By mapping fault lines and studying their history of activity, scientists can identify areas at high risk of earthquakes. This information is essential for developing building codes, designing earthquake-resistant infrastructure, and implementing early warning systems.
- Volcanic Hazard Assessment: Fault lines provide valuable insights into volcanic activity. By understanding the location and characteristics of fault lines associated with volcanic zones, scientists can better assess the risks of volcanic eruptions and develop strategies for mitigating their impact.
- Resource Exploration: Fault lines can act as pathways for the movement of fluids, including oil and natural gas. Understanding the distribution and characteristics of fault lines is essential for identifying potential oil and gas reserves.
- Understanding Earth’s History: Fault lines provide a window into the Earth’s geological history. By studying the movement and interaction of tectonic plates along fault lines, scientists can reconstruct the Earth’s past and understand how continents have shifted and oceans have formed over millions of years.
FAQs about World Fault Lines Map on Google Earth
Q: How accurate is the World Fault Lines Map on Google Earth?
A: The accuracy of the map depends on the quality and availability of data. While major fault lines are well-documented, smaller and less active fault lines may not be as accurately represented. It’s important to note that the map is a representation of current knowledge and may be updated as new data becomes available.
Q: Can I use the World Fault Lines Map to predict earthquakes?
A: While the map helps identify areas at higher risk of earthquakes, it cannot predict the timing or magnitude of specific events. Earthquake prediction remains a complex and challenging scientific endeavor.
Q: What are the limitations of the World Fault Lines Map?
A: The map is a simplified representation of a complex geological system. It doesn’t capture the full range of fault line characteristics, such as their depth, orientation, and slip rates. Additionally, the map may not include all known fault lines, particularly smaller and less active ones.
Tips for Utilizing the World Fault Lines Map on Google Earth
- Explore the map with a focus on specific regions: Zooming in on areas of interest, such as your own location, can help visualize the fault lines that may impact your region.
- Compare different data sources: Explore different layers of information, such as seismic hazard maps and geological surveys, to gain a more comprehensive understanding of fault lines in a particular area.
- Use the map as a starting point for further research: The map can serve as a tool for identifying potential research topics or areas of interest related to fault lines and their impact.
Conclusion: The World Fault Lines Map – A Window into the Earth’s Dynamic Processes
The World Fault Lines Map on Google Earth is a powerful tool for visualizing the Earth’s dynamic processes. It allows us to explore the intricate network of fault lines that shape our planet’s surface and understand the forces that drive earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, and the evolution of continents and oceans. By providing a visual representation of these geological features, the map enhances our understanding of the Earth’s history, its present state, and its future potential. As technology advances and data collection improves, the World Fault Lines Map will continue to evolve, offering increasingly detailed and accurate insights into the Earth’s seismic scars and the dynamic processes that shape our planet.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Earth’s Seismic Scars: Exploring World Fault Lines with Google Earth. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!