Unveiling the Earth’s Midline: A Comprehensive Guide to the Equator
Related Articles: Unveiling the Earth’s Midline: A Comprehensive Guide to the Equator
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Earth’s Midline: A Comprehensive Guide to the Equator. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Unveiling the Earth’s Midline: A Comprehensive Guide to the Equator
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Unveiling the Earth’s Midline: A Comprehensive Guide to the Equator
- 3.1 Understanding the Equator: A Foundation for Geographical Understanding
- 3.2 The Equator’s Impact: Shaping Climate and Culture
- 3.3 Beyond the Line: Exploring the Equator’s Diverse Regions
- 3.4 Navigating the World: The Equator’s Role in Exploration and Mapping
- 3.5 Frequently Asked Questions about the Equator
- 3.6 Tips for Understanding the Equator
- 3.7 Conclusion: The Equator – A Line of Significance
- 4 Closure
Unveiling the Earth’s Midline: A Comprehensive Guide to the Equator

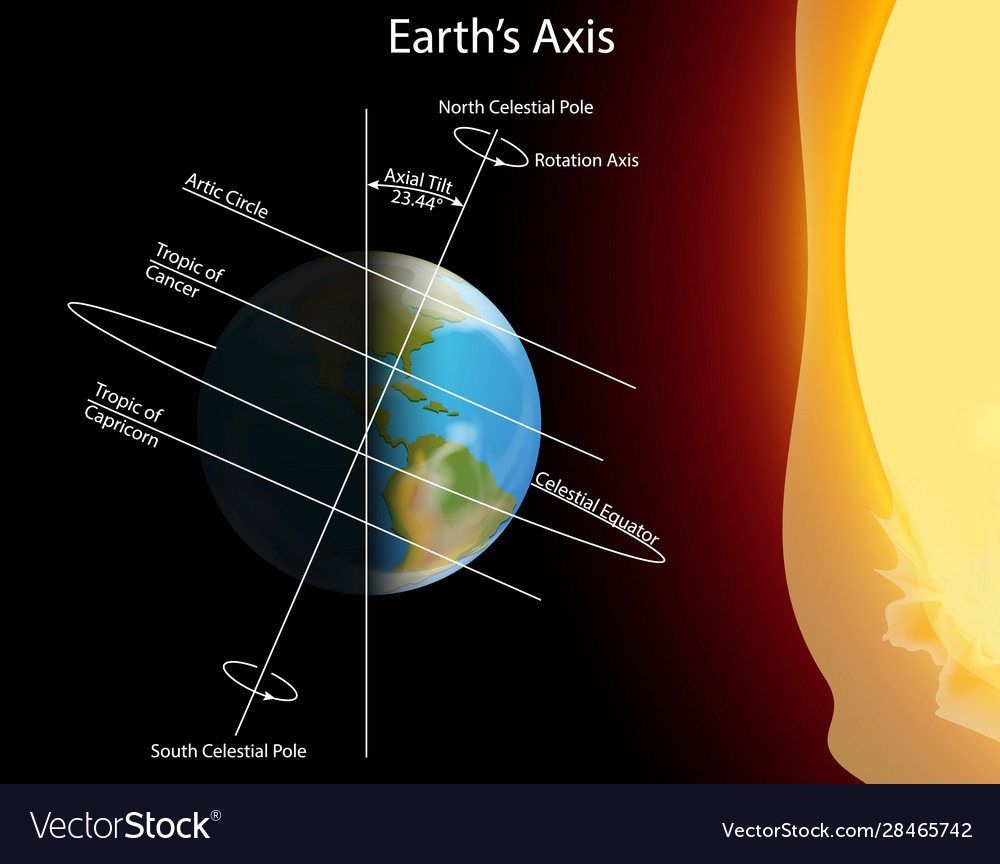
The Earth, our home planet, is a vast and complex sphere, teeming with life and marked by diverse geographical features. One of the most prominent and significant lines on this sphere is the Equator, an imaginary circle that encircles the Earth at zero degrees latitude. This seemingly simple line holds immense importance, influencing climate, navigation, and even the very shape of our planet.
Understanding the Equator: A Foundation for Geographical Understanding
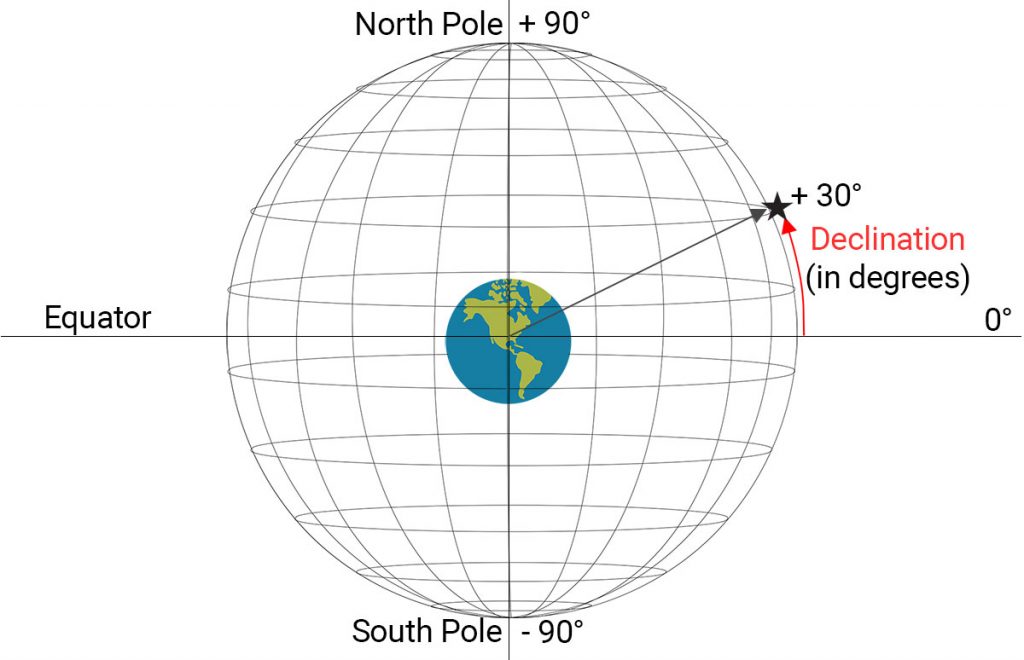
The Equator serves as the foundation for understanding the Earth’s geographical coordinates. It divides the planet into two hemispheres: the Northern Hemisphere and the Southern Hemisphere. Every point on the Equator is equidistant from both the North Pole and the South Pole. This unique position makes the Equator a vital reference point for mapping and navigation.
1. Latitude and Longitude:
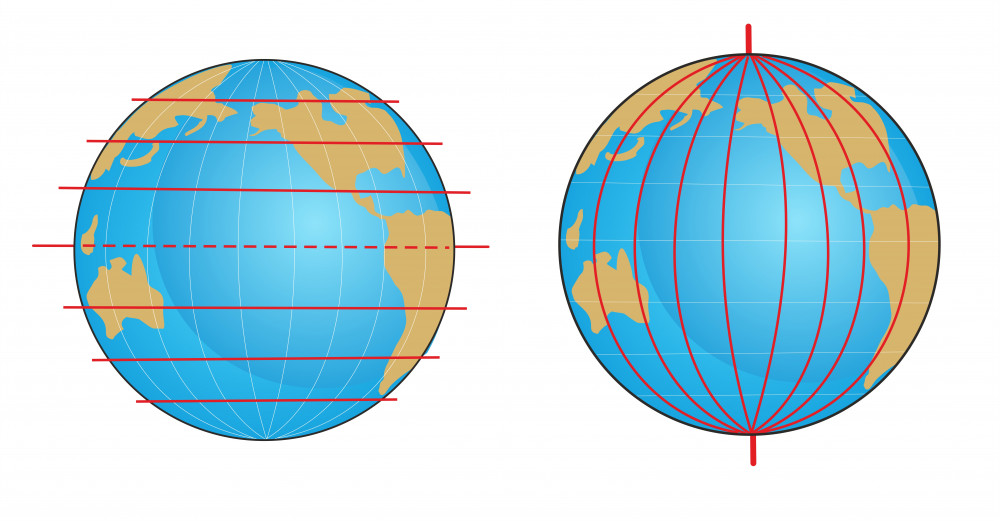
The Equator forms the zero-degree line of latitude. Latitude lines, which are imaginary circles parallel to the Equator, measure distances north or south of the Equator. Longitude lines, on the other hand, are imaginary semi-circles that converge at the poles, measuring distances east or west of the prime meridian. Together, latitude and longitude create a grid system that allows for precise location identification on the Earth’s surface.
2. The Importance of Latitude:
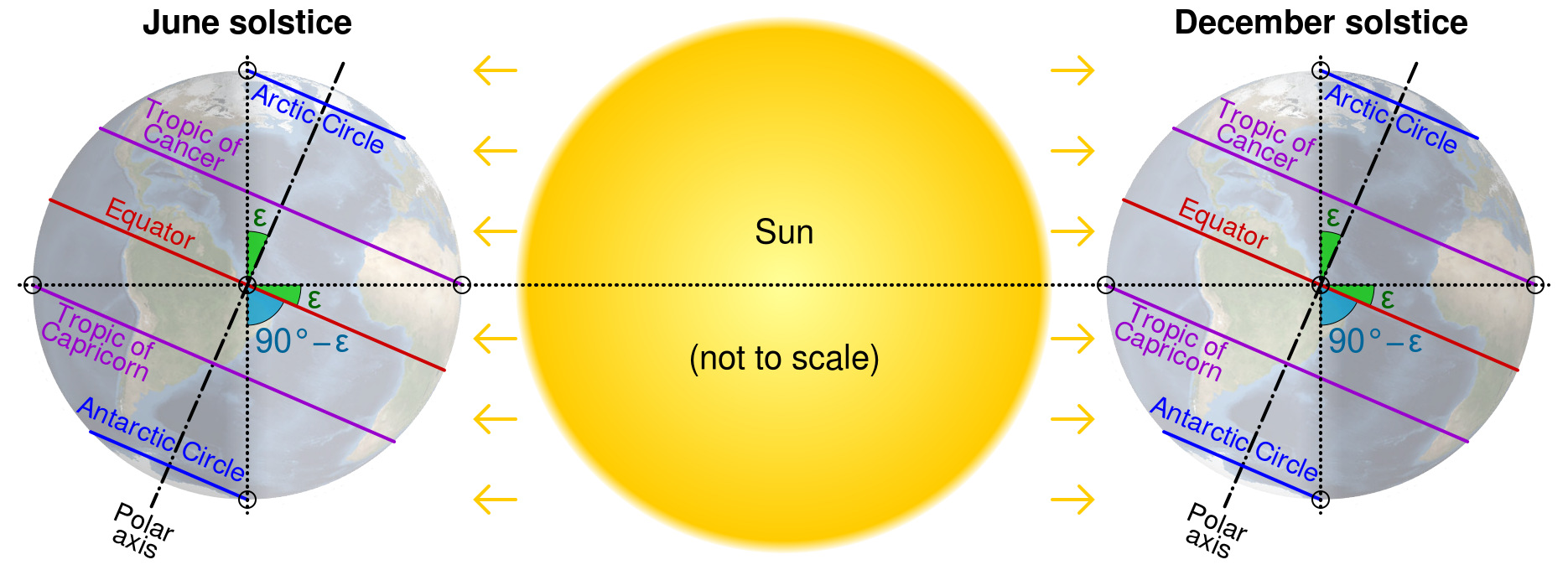
The Equator’s significance extends beyond its role in navigation. Latitude directly influences climate patterns. The region around the Equator, known as the tropics, receives the most direct sunlight throughout the year. This leads to consistently warm temperatures and abundant rainfall, creating a diverse array of ecosystems.
3. The Equatorial Belt:
The area encompassing the Equator and extending approximately 23.5 degrees north and south is known as the equatorial belt. This region is characterized by its tropical climate, lush vegetation, and high biodiversity. It is home to rainforests, savannas, and coral reefs, supporting a vast array of plant and animal life.
The Equator’s Impact: Shaping Climate and Culture
The Equator’s influence on the Earth’s climate is undeniable. Its position, receiving the most direct sunlight, results in:
- High Temperatures: The Equator experiences consistently high temperatures throughout the year due to the direct angle of sunlight.
- Heavy Rainfall: The warm air near the Equator holds high moisture content, leading to frequent and often heavy rainfall.
- Tropical Climates: The combination of high temperatures and abundant rainfall creates tropical climates, characterized by lush vegetation and diverse ecosystems.
The Equator’s impact extends beyond climate, shaping cultures and societies that have adapted to its unique environment.
- Equatorial Cultures: Societies living near the Equator have developed unique customs, traditions, and practices tailored to their climate and environment.
- Agriculture and Food: The fertile soils and abundant rainfall near the Equator support diverse agricultural practices, leading to a rich variety of food sources.
- Indigenous Communities: Many indigenous communities have thrived in equatorial regions for centuries, developing deep connections with their environment and sustainable practices.
Beyond the Line: Exploring the Equator’s Diverse Regions
While the Equator itself is an imaginary line, its influence extends to the surrounding regions, creating a unique tapestry of landscapes and cultures.
- Rainforests: The Amazon rainforest in South America, the Congo Basin in Africa, and the Southeast Asian rainforests are all located near the Equator. These rainforests are characterized by their dense vegetation, high biodiversity, and crucial role in regulating global climate.
- Savannas: The African savanna, with its vast grasslands and scattered trees, is another prominent feature of the equatorial belt. This region is home to a diverse array of wildlife, including elephants, lions, and zebras.
- Coral Reefs: The Equator’s warm waters provide ideal conditions for the growth of coral reefs, which are vital ecosystems supporting a vast array of marine life.
Navigating the World: The Equator’s Role in Exploration and Mapping
The Equator has been a vital reference point for explorers and cartographers throughout history.
- Ancient Navigation: Ancient civilizations, such as the Egyptians and the Greeks, were aware of the Equator and its significance in navigation.
- Modern Navigation: The Equator continues to be a crucial reference point for modern navigation, providing a clear dividing line between hemispheres and aiding in precise location identification.
- Global Mapping: The Equator serves as the foundation for global maps, providing a framework for understanding geographical relationships and distances.
Frequently Asked Questions about the Equator
1. What is the exact location of the Equator?
The Equator is an imaginary line that encircles the Earth at zero degrees latitude. It is equidistant from both the North Pole and the South Pole.
2. How long is the Equator?
The Equator is approximately 40,075 kilometers (24,901 miles) long.
3. Why is the Equator important?
The Equator is important for its role in defining geographical coordinates, influencing climate patterns, shaping cultures, and serving as a vital reference point for navigation and mapping.
4. What are the unique characteristics of the equatorial belt?
The equatorial belt is characterized by its tropical climate, lush vegetation, high biodiversity, and diverse cultures.
5. What are some of the challenges faced by people living near the Equator?
People living near the Equator face challenges related to high temperatures, heavy rainfall, and potential natural disasters such as hurricanes and floods.
Tips for Understanding the Equator
- Use a globe or map: Visualizing the Equator on a globe or map will help you understand its location and significance.
- Learn about latitude and longitude: Understanding how latitude and longitude work will enhance your understanding of the Equator’s role in mapping and navigation.
- Explore the equatorial belt: Research the diverse ecosystems and cultures found in the equatorial belt, such as rainforests, savannas, and indigenous communities.
- Consider the impact of climate change: The Equator is particularly vulnerable to the effects of climate change, such as rising sea levels and extreme weather events.
Conclusion: The Equator – A Line of Significance
The Equator, a seemingly simple line on the Earth’s surface, holds immense significance. It shapes climate patterns, influences cultures, and provides a crucial reference point for navigation and mapping. Understanding the Equator’s role is essential for appreciating the Earth’s complexity and the interconnectedness of our planet’s systems. As we continue to explore and understand our world, the Equator will remain a vital point of reference, reminding us of the Earth’s intricate beauty and the importance of respecting and protecting its diverse ecosystems.
/wov007-58b9cea93df78c353c388df1.jpg)


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Earth’s Midline: A Comprehensive Guide to the Equator. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
