Unveiling Spatial Insights: A Comprehensive Guide to Zip Code Mapping in R
Related Articles: Unveiling Spatial Insights: A Comprehensive Guide to Zip Code Mapping in R
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unveiling Spatial Insights: A Comprehensive Guide to Zip Code Mapping in R. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Unveiling Spatial Insights: A Comprehensive Guide to Zip Code Mapping in R
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Unveiling Spatial Insights: A Comprehensive Guide to Zip Code Mapping in R
- 3.1 The Power of Zip Code Mapping:
- 3.2 Essential Tools for Zip Code Mapping in R:
- 3.3 A Step-by-Step Guide to Creating Zip Code Maps in R:
- 3.4 Illustrative Example: Mapping Population Density by Zip Code
- 3.5 FAQs about Zip Code Mapping in R:
- 3.6 Tips for Effective Zip Code Mapping in R:
- 3.7 Conclusion:
- 4 Closure
Unveiling Spatial Insights: A Comprehensive Guide to Zip Code Mapping in R
The ability to visualize and analyze geographic data is increasingly crucial in various fields. From marketing and urban planning to public health and environmental studies, understanding spatial relationships and trends is essential. Zip code data, readily available and often linked to demographic and socioeconomic information, provides a granular lens for exploring these relationships. R, a powerful and versatile statistical programming language, offers a robust toolkit for creating informative and insightful maps using zip code data. This guide will explore the process of creating zip code maps in R, highlighting the benefits and applications of this approach.
The Power of Zip Code Mapping:
Zip code maps are more than just visual representations of geographic locations. They offer a powerful means to:
- Identify spatial patterns and trends: By visualizing data associated with specific zip codes, users can identify clusters, outliers, and spatial relationships that might not be apparent in tabular data. This can be particularly useful for understanding demographic trends, disease prevalence, or market segmentation.
- Visualize spatial relationships: Maps can effectively illustrate the proximity and connectivity of different zip codes, enabling analysis of spatial accessibility, transportation patterns, and potential spillover effects.
- Communicate complex data visually: Maps provide an intuitive and engaging way to communicate data to a wider audience, making complex information more accessible and understandable.
- Support decision-making: Insights gained from zip code maps can inform decision-making in various fields, from targeted marketing campaigns to resource allocation and public policy development.
Essential Tools for Zip Code Mapping in R:
R offers a wide range of packages designed for spatial data analysis and visualization. Key packages for creating zip code maps include:
-
sf: This package provides a framework for working with spatial data in R, enabling the import, manipulation, and visualization of geospatial objects like polygons (representing zip code boundaries). -
ggplot2: This powerful and versatile package is the foundation for creating high-quality, customizable maps in R. -
maps: This package provides access to pre-built maps of various regions, including US states and counties, which can be used as a base for overlaying zip code data. -
maptools: This package offers functions for manipulating and converting spatial data, including functions to transform zip code data into spatial objects. -
tidyverse: This collection of packages, includingdplyrandtidyr, facilitates data manipulation and preparation, making it easier to work with zip code data before creating maps.
A Step-by-Step Guide to Creating Zip Code Maps in R:
-
Data Acquisition:
- Obtain Zip Code Shapefiles: Shapefiles are digital files that contain geographic information about areas, including zip code boundaries. Numerous sources provide shapefiles, including the US Census Bureau, the US Postal Service, and various mapping websites.
-
Import Data into R: Use the
sf::st_read()function to import the shapefile into R as a spatial object.
-
Data Preparation:
-
Join with Additional Data: Merge your zip code data with other relevant datasets using the
dplyr::left_join()function. This can include demographic data, economic indicators, or any other information associated with specific zip codes. - Data Transformation: Ensure data is in the correct format for mapping. This might involve converting data types or reshaping the data for visualization.
-
Join with Additional Data: Merge your zip code data with other relevant datasets using the
-
Map Creation with
ggplot2:-
Base Map: Use the
ggplot()function to create a base map using thesfobject representing zip code boundaries. -
Coloring and Styling: Employ
geom_sf()to visualize the zip code polygons. Use color palettes or fill colors to represent data values, highlighting patterns and trends. -
Adding Labels and Annotations: Utilize
geom_text()orgeom_label()to add labels for zip codes or other relevant information. -
Customization: Leverage
ggplot2‘s extensive options to customize the map’s appearance, including title, legend, axis labels, and overall theme.
-
Base Map: Use the
Illustrative Example: Mapping Population Density by Zip Code
# Load necessary libraries
library(sf)
library(ggplot2)
library(dplyr)
# Import zip code shapefile
zip_codes <- st_read("path/to/zip_code_shapefile.shp")
# Load population data by zip code
population_data <- read.csv("path/to/population_data.csv")
# Merge data
zip_codes_pop <- left_join(zip_codes, population_data, by = "zip_code")
# Create map
ggplot(zip_codes_pop) +
geom_sf(aes(fill = population_density), color = "grey50") +
scale_fill_gradient(low = "lightblue", high = "darkblue", name = "Population Density") +
labs(title = "Population Density by Zip Code", x = "Longitude", y = "Latitude") +
theme_bw()This code snippet demonstrates the basic steps involved in creating a zip code map in R, showcasing population density variations across different zip codes. The flexibility of R and its mapping packages allows for countless variations and customizations, enabling users to explore and communicate spatial data effectively.
FAQs about Zip Code Mapping in R:
1. What are the limitations of zip code mapping?
While zip code maps provide valuable insights, it’s crucial to acknowledge their limitations:
- Spatial Resolution: Zip codes represent relatively large geographic areas, potentially masking variations within those areas.
- Data Accuracy: The accuracy of zip code data depends on the source and may vary.
- Ecological Fallacy: Drawing conclusions about individuals based on aggregated zip code data can be misleading.
2. How can I handle missing data in zip code maps?
Missing data can be addressed in several ways:
- Imputation: Use statistical methods to estimate missing values based on available data.
- Exclusion: Remove data points with missing values, but be mindful of potential bias.
- Visualization: Represent missing data visually using specific colors or symbols.
3. How can I create interactive zip code maps?
R packages like leaflet and htmlwidgets allow for creating interactive maps that can be embedded in web applications. These maps offer features such as zoom, pan, and data exploration through hover or click events.
4. What are some real-world applications of zip code mapping?
Zip code maps are widely used in:
- Marketing: Identifying target demographics and optimizing marketing campaigns.
- Urban Planning: Analyzing spatial distribution of services, infrastructure, and population density.
- Public Health: Mapping disease prevalence, identifying health disparities, and planning interventions.
- Environmental Studies: Visualizing pollution levels, tracking environmental hazards, and understanding land use patterns.
Tips for Effective Zip Code Mapping in R:
- Data Quality: Prioritize using high-quality, accurate zip code data.
- Clear Visualization: Choose appropriate color palettes, legends, and annotations to ensure clarity and avoid visual clutter.
- Contextualization: Provide context for the map by including relevant geographic features, such as roads, rivers, or landmarks.
- Interactive Elements: Consider incorporating interactive elements for data exploration and user engagement.
- Transparency and Communication: Clearly communicate the limitations of the data and the interpretation of the map.
Conclusion:
Zip code mapping in R offers a powerful and flexible approach to exploring and visualizing geographic data. By leveraging the capabilities of R’s spatial packages and its data manipulation tools, users can create insightful maps that reveal spatial patterns, support decision-making, and communicate complex information effectively. As data becomes increasingly spatial, the ability to create and interpret zip code maps will become increasingly essential for understanding and addressing challenges across various fields.
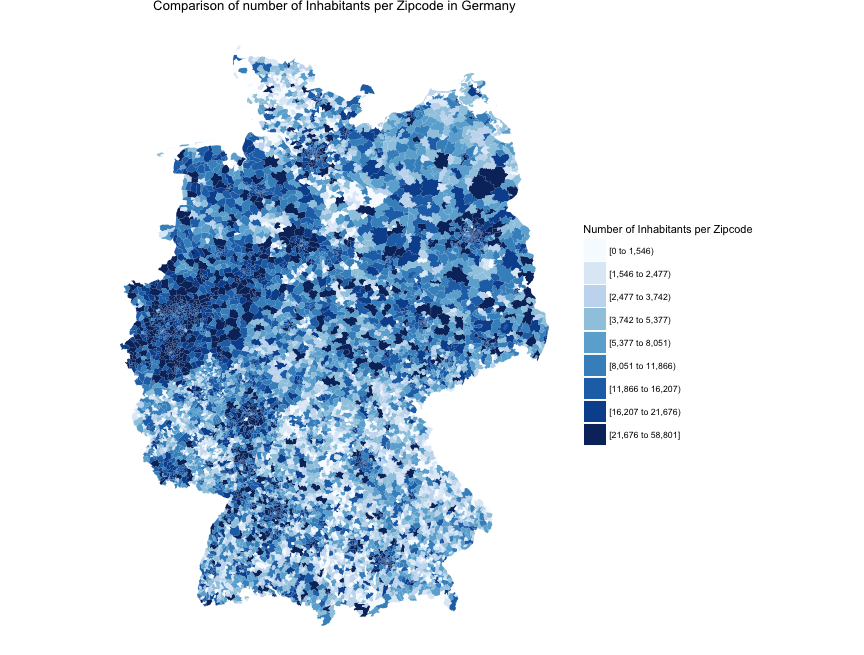
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling Spatial Insights: A Comprehensive Guide to Zip Code Mapping in R. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
