Unveiling Geographic Insights: Power BI’s Filled Maps and the Power of Latitude and Longitude
Related Articles: Unveiling Geographic Insights: Power BI’s Filled Maps and the Power of Latitude and Longitude
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unveiling Geographic Insights: Power BI’s Filled Maps and the Power of Latitude and Longitude. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling Geographic Insights: Power BI’s Filled Maps and the Power of Latitude and Longitude

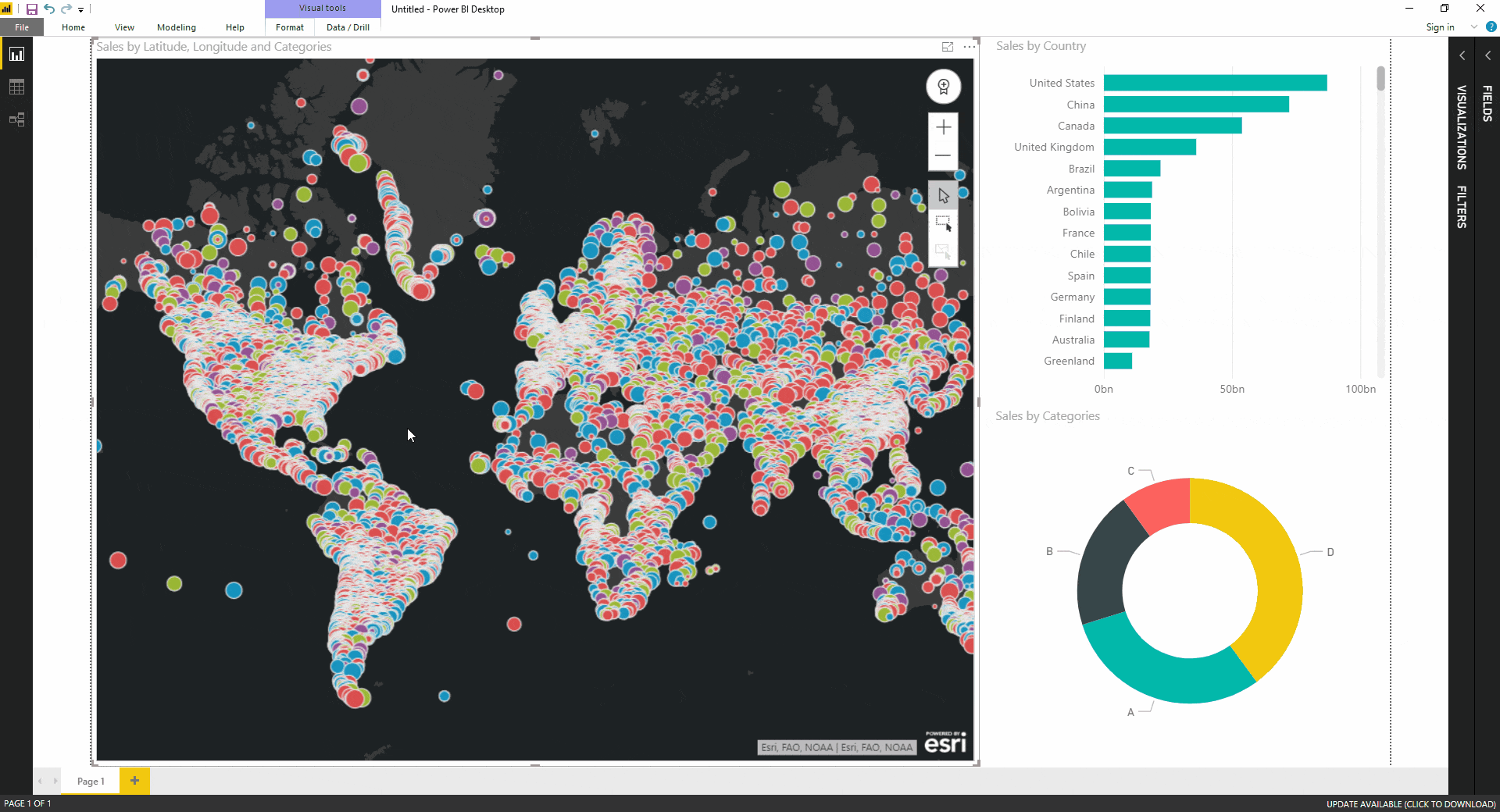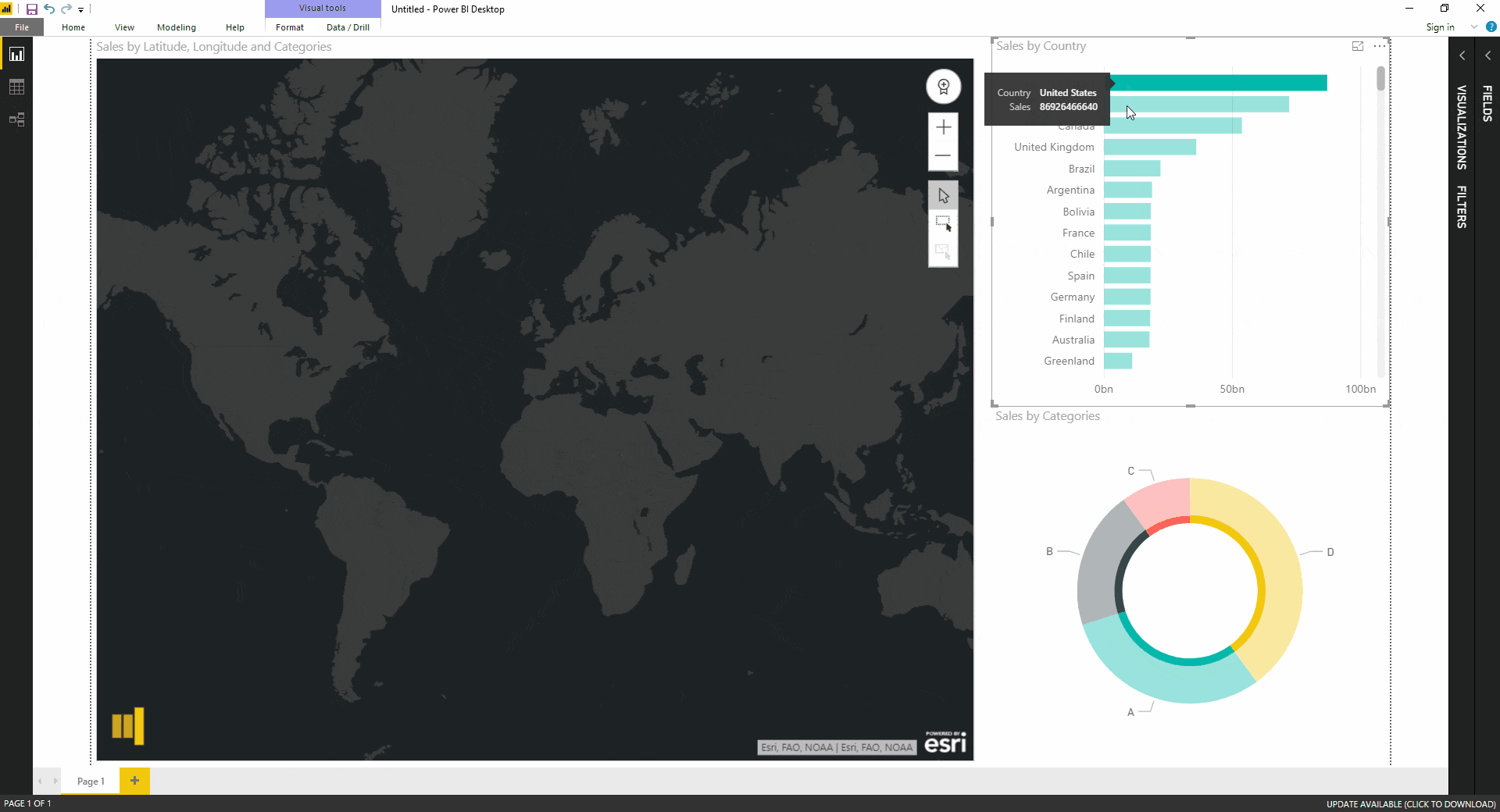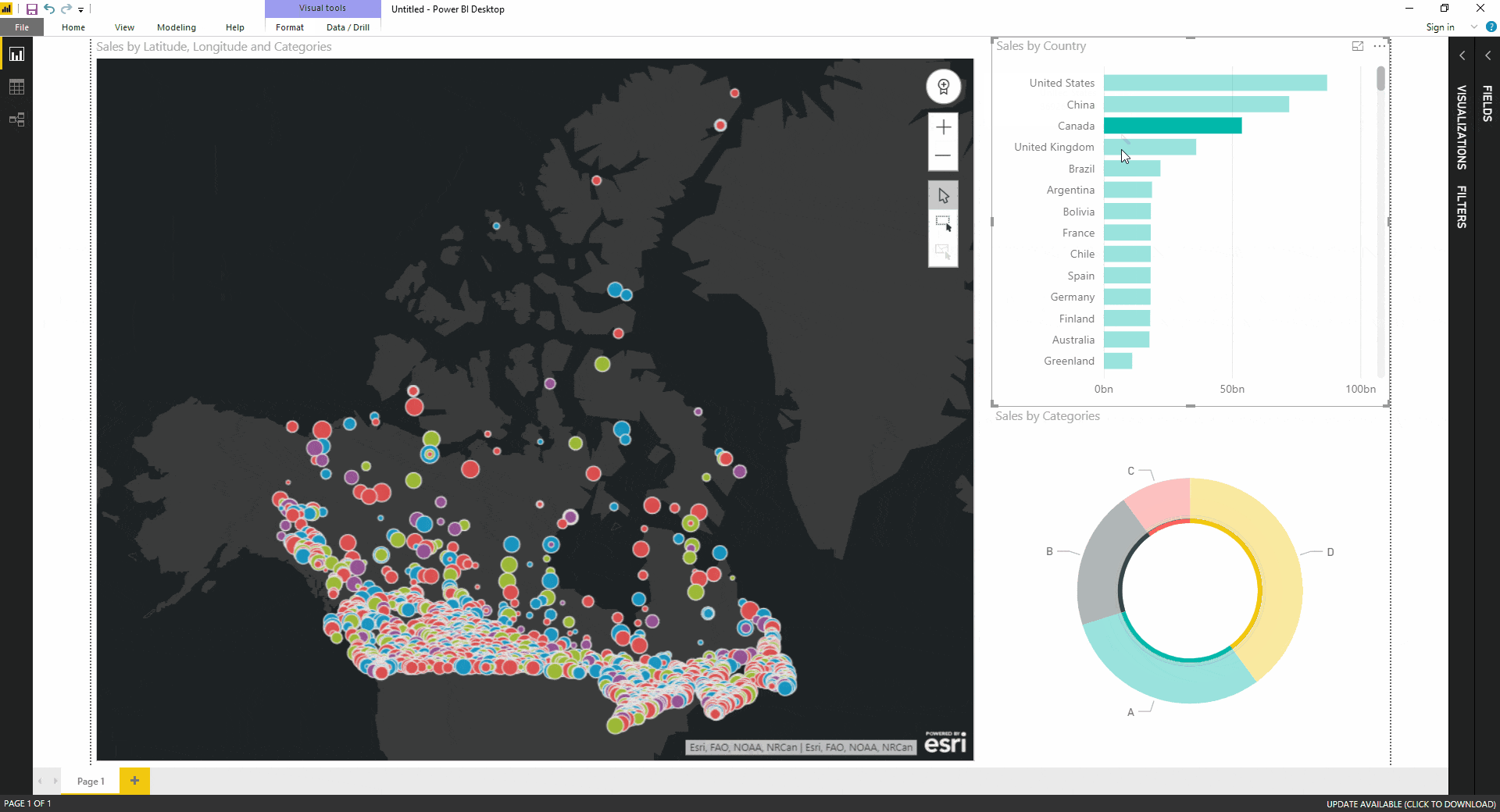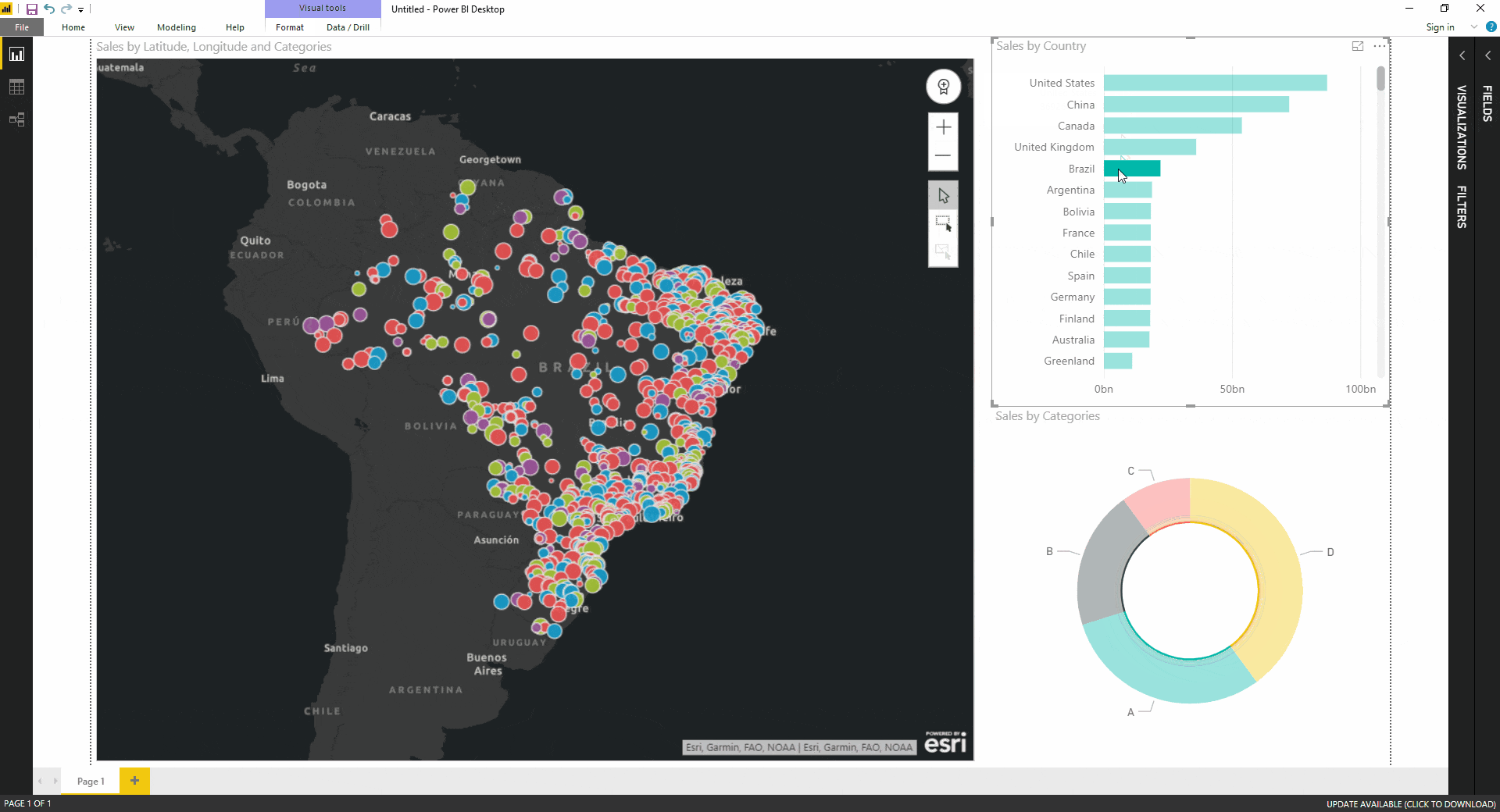
Power BI, a robust business intelligence tool, offers an array of visualization options to effectively communicate data. Among these, filled maps stand out as a powerful tool for visually representing geographic data, allowing users to gain valuable insights from spatial distributions. By leveraging the fundamental principles of latitude and longitude, filled maps enable users to transform raw data into compelling visual narratives, highlighting trends, patterns, and anomalies across geographical regions.
Understanding the Foundation: Latitude and Longitude
Before delving into the intricacies of filled maps, it is crucial to grasp the concept of latitude and longitude – the fundamental building blocks of geographical coordinates. Latitude, measured in degrees north or south of the equator, determines a location’s position along the north-south axis. Longitude, measured in degrees east or west of the prime meridian, defines a location’s position along the east-west axis.
These two coordinates, working in tandem, provide a unique address for every point on Earth, enabling precise location identification and mapping. Power BI leverages this system to accurately position data points on its filled maps, creating a visually intuitive representation of geographical data.
Unveiling the Potential: Power BI’s Filled Maps
Power BI’s filled maps offer a dynamic and versatile visualization tool, empowering users to explore geographical data in a visually engaging manner. These maps provide a canvas for representing various data types, including:
- Sales performance: Analyze sales data across different regions, identifying areas with high or low performance, pinpointing potential growth opportunities, and understanding regional market trends.
- Customer demographics: Visualize customer distribution by location, revealing target markets, understanding customer concentration, and informing marketing campaigns.
- Operational efficiency: Track the performance of various branches, stores, or facilities based on location, identifying areas requiring optimization and pinpointing potential bottlenecks.
- Environmental data: Analyze environmental variables like air quality, pollution levels, or weather patterns across different regions, understanding spatial variations and informing policy decisions.
- Disease outbreaks: Track the spread of infectious diseases across geographical areas, enabling public health officials to identify hotspots, monitor trends, and implement targeted interventions.
Building a Filled Map: A Step-by-Step Guide
Creating a filled map in Power BI is a straightforward process, requiring only a few key steps:
- Data Preparation: Ensure your data includes latitude and longitude columns, representing the location of each data point.
- Map Selection: Choose the "Filled Map" visualization from the Power BI visualization pane.
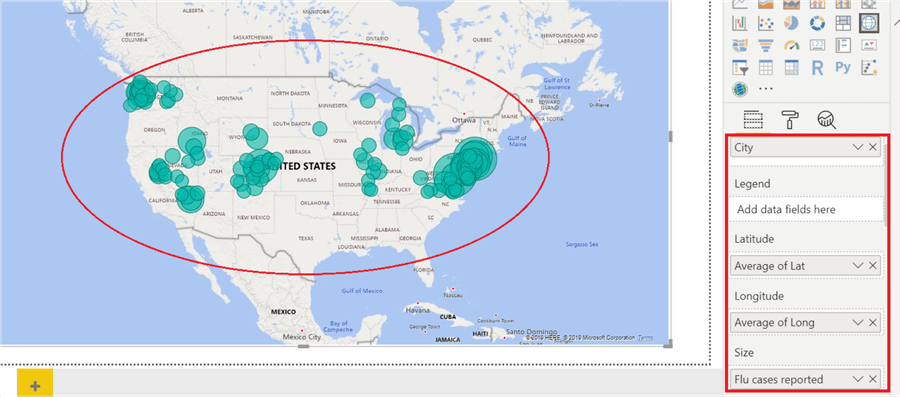
- Data Linking: Link the latitude and longitude columns from your data to the corresponding map fields in Power BI.
- Data Aggregation: Define the data field to be represented on the map, selecting an appropriate aggregation method (e.g., sum, average, count) depending on the data type.
- Customization: Customize the map’s appearance by adjusting colors, legends, tooltips, and other visual elements to enhance clarity and impact.
Beyond the Basics: Advanced Techniques for Enhanced Insights
Power BI’s filled maps offer a range of advanced features, enabling users to extract deeper insights from their data:
- Choropleth Maps: By applying color gradients to regions based on data values, choropleth maps visually represent data density, enabling users to identify areas with high or low concentrations of a particular variable.
- Map Layers: Overlay multiple datasets on the same map, allowing for the exploration of relationships between different variables and creating insightful comparisons.
- Interactive Filters: Integrate interactive filters with the map, enabling users to dynamically slice and dice the data based on specific criteria, exploring different scenarios and gaining deeper insights.
- Custom Map Shapes: Import custom map shapes, allowing for the visualization of data on specific regions or locations beyond standard geographical boundaries.
- Geocoding: Utilize Power BI’s geocoding feature to automatically convert addresses or place names into latitude and longitude coordinates, simplifying data preparation for map visualization.
FAQs: Addressing Common Questions
Q: What are the benefits of using filled maps in Power BI?
A: Filled maps offer a visually compelling and intuitive way to represent geographical data, enabling users to:
- Identify trends and patterns: Easily spot spatial variations and trends across geographical regions.
- Make informed decisions: Gain insights into data distribution, enabling better planning and decision-making.
- Communicate insights effectively: Present complex geographical data in an easily understandable and visually appealing format.
- Explore relationships: Analyze relationships between geographical data and other variables through map layering and interactive filters.
Q: What are the limitations of filled maps?
A: While filled maps offer valuable insights, it’s important to be aware of their limitations:
- Data accuracy: The accuracy of filled maps relies heavily on the accuracy of the underlying data. Inaccurate or incomplete data can lead to misleading visualizations.
- Spatial resolution: The level of detail presented on a filled map is limited by the resolution of the underlying map data.
- Data aggregation: The choice of aggregation method can significantly influence the visualization, potentially masking important nuances in the data.
Q: How can I ensure the accuracy and effectiveness of my filled maps?
A: To create accurate and effective filled maps, consider the following:
- Data validation: Ensure the accuracy of latitude and longitude data before creating the map.
- Appropriate aggregation: Choose an aggregation method that accurately represents the data and aligns with the visualization goals.
- Map projection: Select a map projection that accurately represents the geographical area of interest.
- Legend clarity: Use clear and concise legends to effectively communicate the data represented on the map.
Tips for Effective Filled Map Creation
- Focus on the narrative: Ensure your filled map tells a clear and compelling story, highlighting key insights and supporting your analysis.
- Choose appropriate colors: Use a color scheme that is both visually appealing and effectively communicates the data.
- Use tooltips: Provide informative tooltips that display detailed information about each data point on the map.
- Integrate interactivity: Enable users to interact with the map, exploring different scenarios and gaining deeper insights.
Conclusion: Empowering Data-Driven Decisions with Filled Maps
Power BI’s filled maps, leveraging the power of latitude and longitude, offer a potent tool for visualizing geographical data, unlocking valuable insights and facilitating data-driven decisions. By effectively representing spatial variations and trends, filled maps empower users to understand geographic patterns, identify opportunities, and optimize operations. As data becomes increasingly location-centric, filled maps will continue to play a crucial role in harnessing the power of geography to inform business strategies and drive impactful results.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling Geographic Insights: Power BI’s Filled Maps and the Power of Latitude and Longitude. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!