Unveiling Geographic Insights: A Comprehensive Guide to Power BI Map Visuals and Latitude-Longitude Data
Related Articles: Unveiling Geographic Insights: A Comprehensive Guide to Power BI Map Visuals and Latitude-Longitude Data
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unveiling Geographic Insights: A Comprehensive Guide to Power BI Map Visuals and Latitude-Longitude Data. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling Geographic Insights: A Comprehensive Guide to Power BI Map Visuals and Latitude-Longitude Data

Power BI’s map visuals offer a powerful tool for visualizing and analyzing data with a geographic dimension. By leveraging latitude and longitude coordinates, users can create interactive maps that reveal patterns, trends, and insights hidden within their datasets. This article delves into the intricacies of utilizing Power BI map visuals, exploring their capabilities, benefits, and practical applications.
Understanding the Foundation: Latitude and Longitude
Latitude and longitude form the cornerstone of geographic data representation. Latitude lines run horizontally around the Earth, measuring distance north or south of the equator, while longitude lines run vertically, measuring distance east or west of the Prime Meridian. These coordinates, expressed in decimal degrees, provide a unique identifier for every location on Earth.
Power BI’s Map Visuals: A Gateway to Geographic Exploration
Power BI offers a variety of map visuals designed to cater to different data visualization needs. These include:
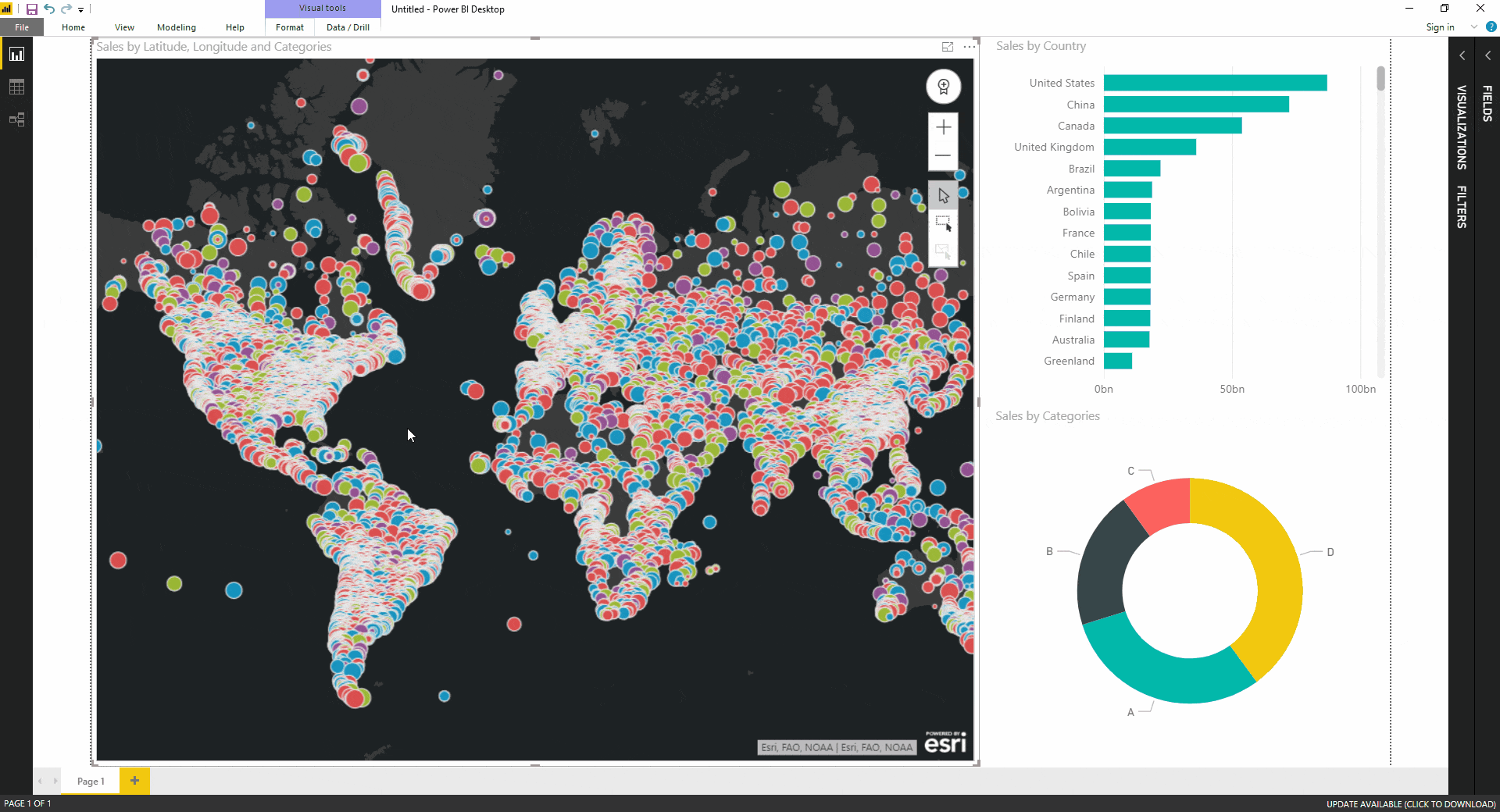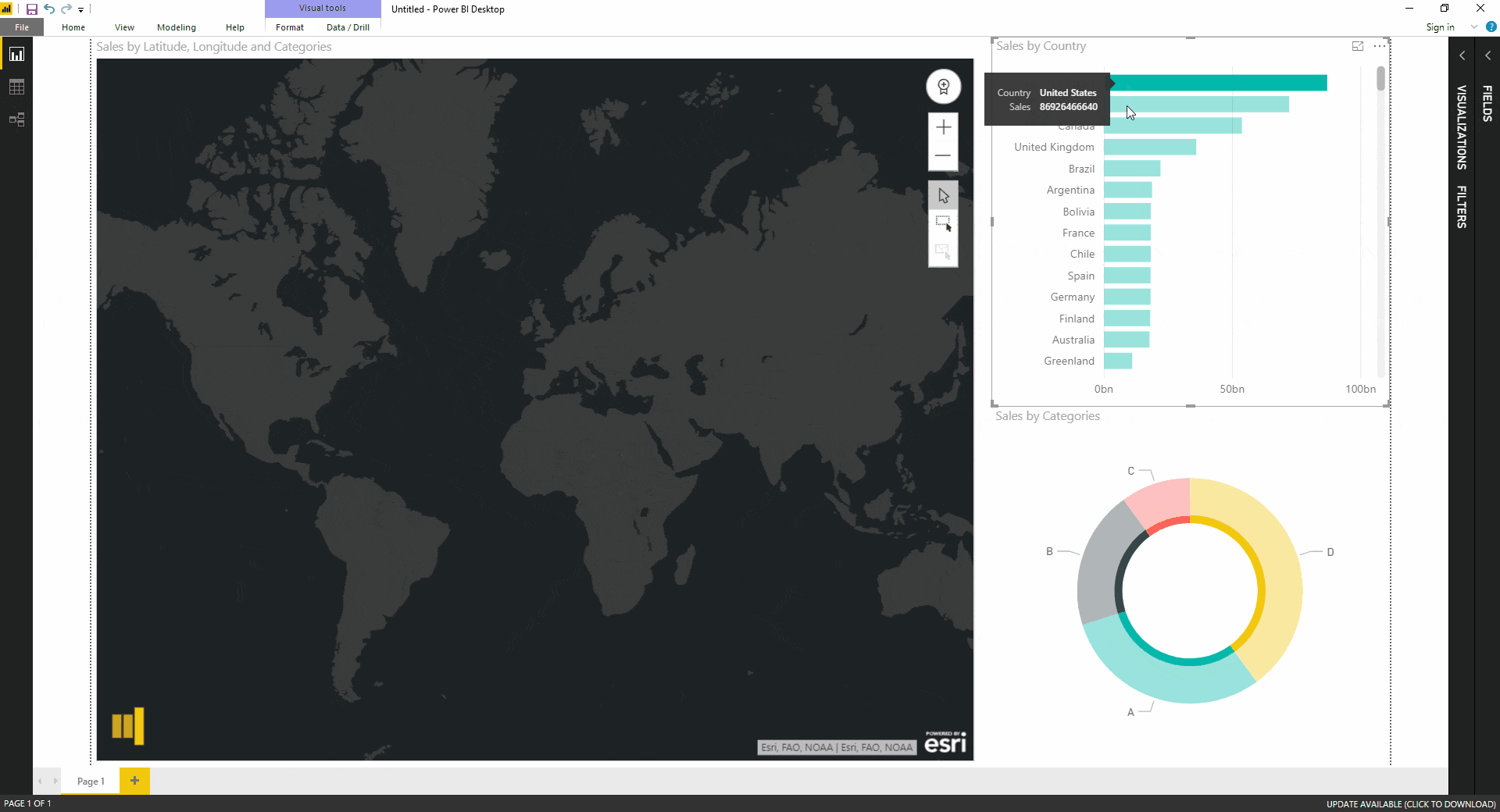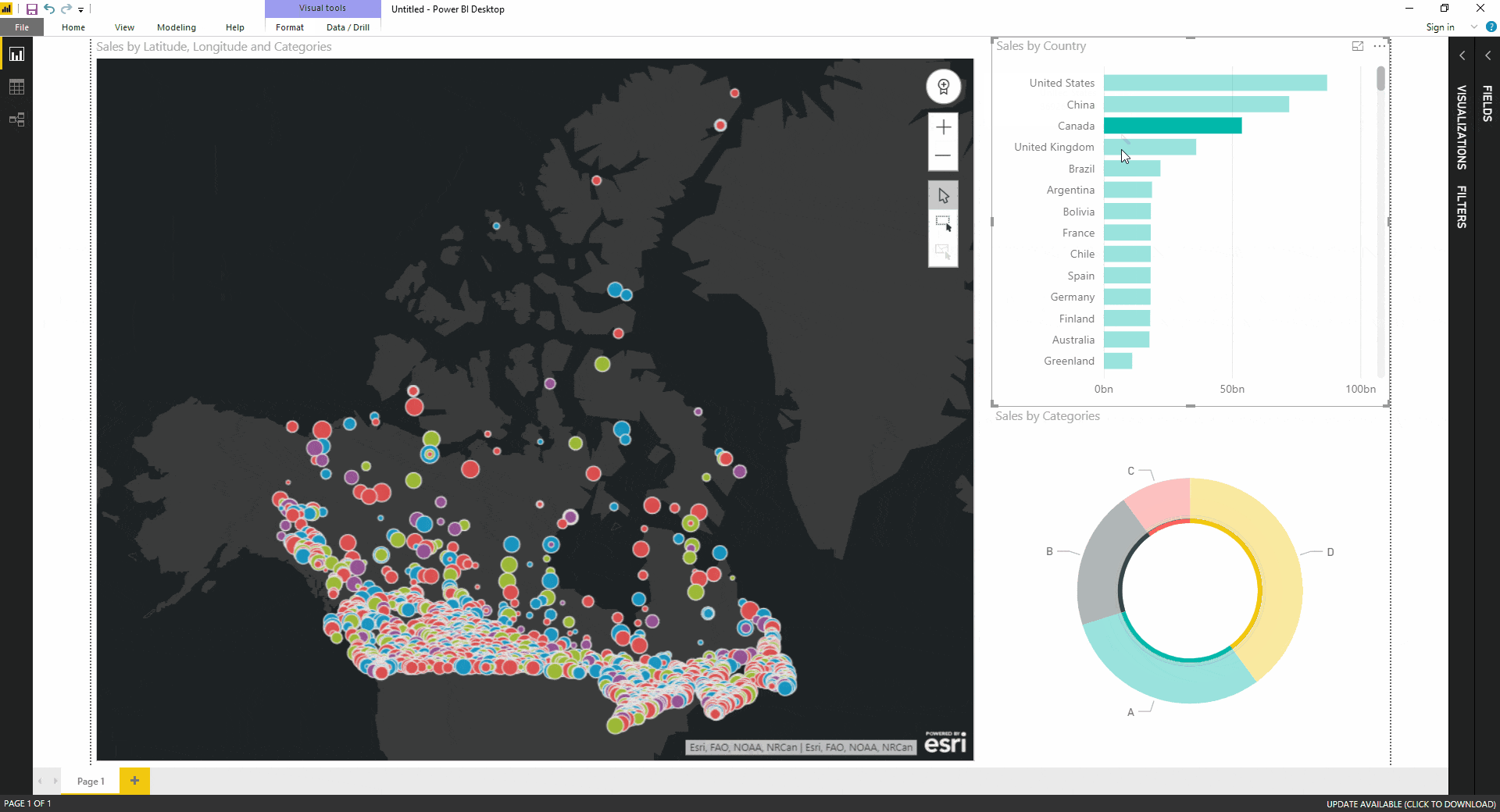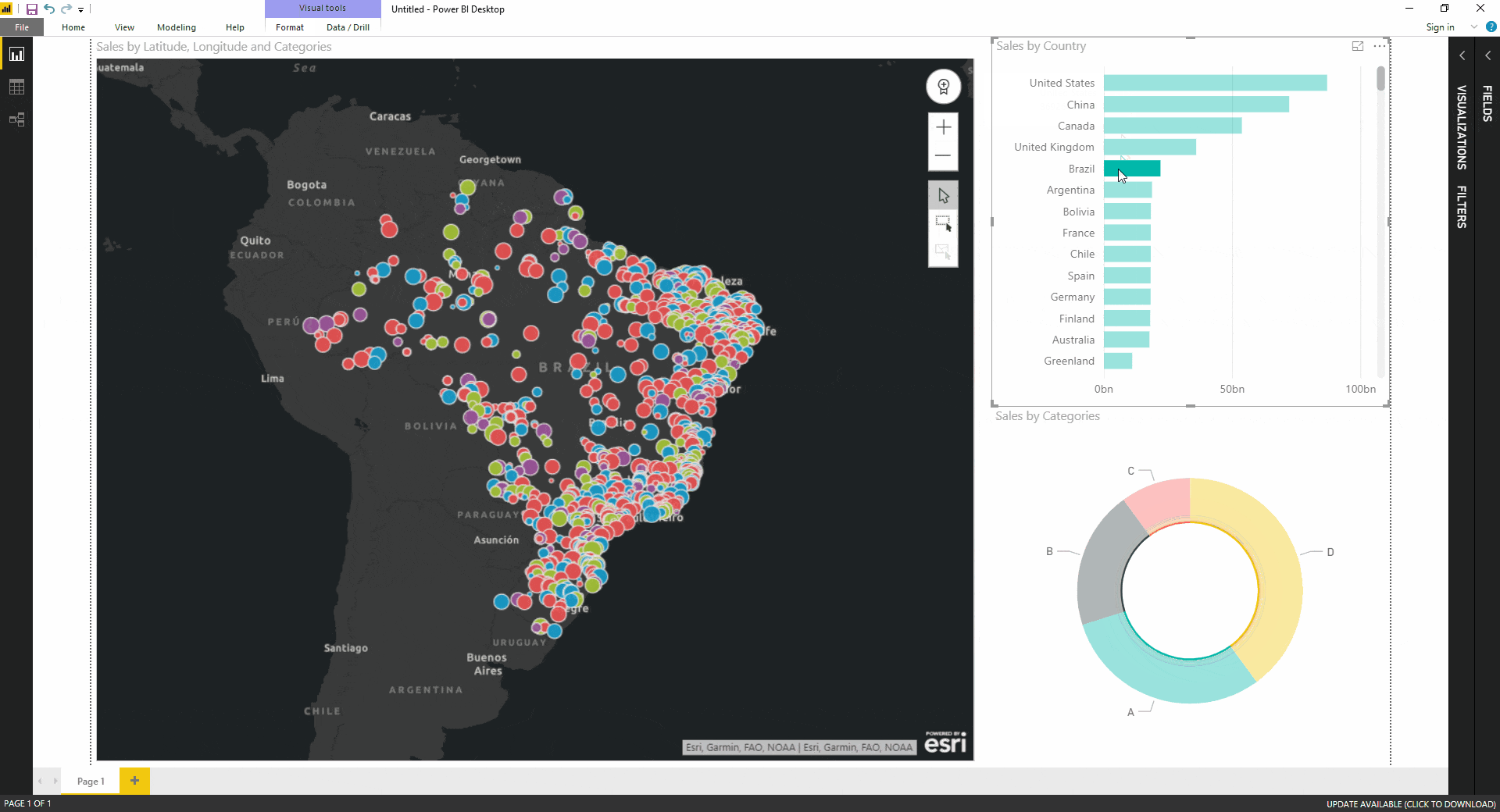
- Map: The foundational map visual, allowing users to plot data points on a world map, highlighting their geographic distribution.
- Filled Map: This visual allows users to color-code regions based on a chosen measure, providing a visual representation of data density or variation across different geographic areas.
- Shape Map: Similar to the filled map, the shape map allows users to color-code individual shapes within a region, providing a more detailed visual representation of data distribution.
Leveraging Latitude and Longitude for Powerful Insights
By incorporating latitude and longitude data into Power BI map visuals, users can unlock a wealth of analytical possibilities.
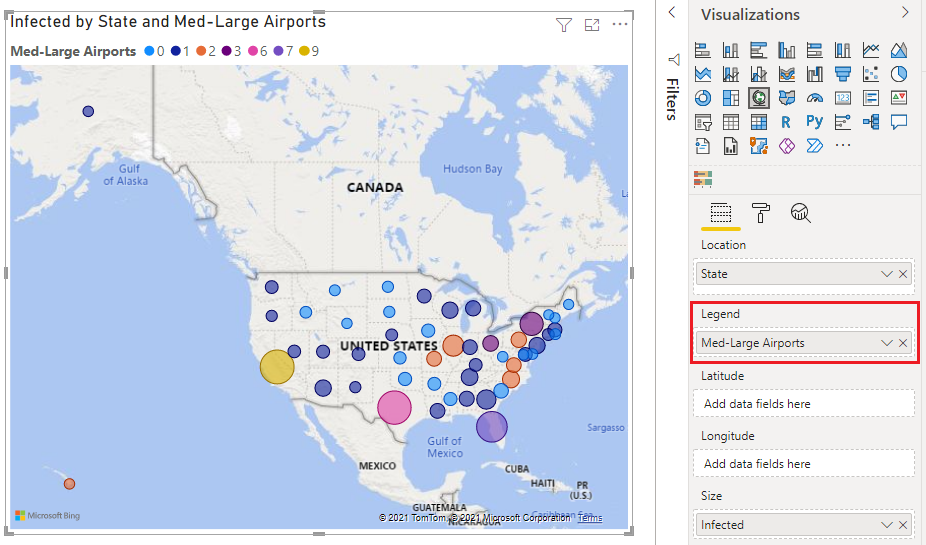
- Visualizing Spatial Distribution: Mapping data points based on their geographic coordinates reveals patterns of distribution, identifying areas of high concentration or sparse data points. This can be valuable for understanding customer demographics, sales performance, or the spread of a phenomenon.
- Analyzing Geographic Trends: By mapping data over time, users can observe how trends evolve across different geographic regions. This can help identify areas experiencing growth or decline, or understand the impact of external factors on different locations.
- Identifying Geographic Relationships: Map visuals can help uncover relationships between data points and their geographic location. For example, analyzing sales data against customer location can reveal areas with high sales potential or identify regions with specific customer preferences.
- Creating Interactive Maps: Power BI map visuals are highly interactive, allowing users to zoom in and out, filter data based on location, and drill down into specific regions for more detailed analysis. This interactivity enhances user engagement and facilitates deeper exploration of data patterns.
Beyond Basic Mapping: Advanced Features for Enhanced Analysis
Power BI map visuals offer advanced features that further enhance their analytical capabilities:
- Customizable Map Styles: Users can customize the appearance of their maps, selecting from various base map styles, adjusting colors, adding labels, and incorporating additional visual elements to enhance clarity and visual appeal.
- Data Filtering and Slicing: Map visuals allow users to filter data based on various criteria, such as location, time period, or specific data values. This enables users to isolate specific regions or data points for focused analysis.
- Data Aggregation: Users can aggregate data based on geographic regions, allowing them to visualize trends at a higher level of granularity. This is particularly useful for understanding overall performance across different countries, states, or cities.
- Geocoding Capabilities: Power BI provides tools for geocoding, automatically converting addresses or postal codes into latitude and longitude coordinates. This simplifies the process of incorporating location data into maps.
Practical Applications: Unlocking the Power of Geographic Data
The applications of Power BI map visuals with latitude and longitude data are vast and extend across various industries and domains:
- Sales and Marketing: Mapping customer locations, sales performance, and marketing campaign effectiveness can identify areas with high growth potential, optimize marketing strategies, and personalize customer interactions.
- Real Estate: Analyzing property listings, market trends, and neighborhood demographics can assist in pricing properties, identifying investment opportunities, and understanding market dynamics.
- Healthcare: Mapping disease outbreaks, hospital locations, and patient demographics can help track disease spread, optimize resource allocation, and improve public health outcomes.
- Transportation: Visualizing traffic patterns, transportation routes, and accident locations can optimize traffic flow, improve transportation planning, and enhance safety measures.
- Environmental Science: Mapping pollution levels, natural disasters, and environmental indicators can help monitor environmental changes, assess risks, and guide conservation efforts.
FAQs: Addressing Common Questions About Power BI Map Visuals and Latitude-Longitude Data
Q: What are the essential steps for creating a map visual in Power BI?
A: To create a map visual in Power BI, you need to:
- Import your data: Ensure your dataset contains latitude and longitude columns.
- Select the map visual: Choose the appropriate map visual from the Power BI visualization pane.
- Configure the visual: Select the latitude and longitude columns for the map’s location data.
- Add data points: Add additional data columns to represent measures or dimensions you want to visualize on the map.
- Customize the map: Modify map styles, colors, labels, and other visual elements to enhance clarity and visual appeal.
Q: How can I ensure the accuracy of my map visuals?
A: To ensure map accuracy, it is crucial to:
- Verify data source: Confirm that the latitude and longitude data is accurate and reliable.
- Use appropriate projections: Select a map projection that aligns with the geographic area you are visualizing.
- Validate map coordinates: Double-check the coordinates displayed on the map against known locations.
Q: What are some common challenges associated with using map visuals in Power BI?
A: Some common challenges include:
- Data quality: Inaccurate or incomplete latitude and longitude data can lead to inaccurate map representations.
- Data privacy: Mapping sensitive location data requires careful consideration of privacy regulations and user consent.
- Visual complexity: Overly complex maps with too many data points or visual elements can become cluttered and difficult to interpret.
Tips for Optimizing Power BI Map Visuals
- Start with a clear objective: Define the purpose of your map visual before you begin creating it.
- Choose the right map visual: Select the map visual that best suits your data and analytical needs.
- Use color effectively: Choose a color scheme that enhances visual clarity and highlights important data patterns.
- Keep it simple: Avoid overcrowding the map with too many data points or visual elements.
- Utilize interactive elements: Leverage filtering, zooming, and drilling down capabilities to enable deeper exploration.
Conclusion: Unveiling Geographic Insights with Power BI Map Visuals
Power BI map visuals, powered by latitude and longitude data, provide a powerful tool for visualizing and analyzing data with a geographic dimension. By leveraging these visuals, users can uncover hidden patterns, identify trends, and gain valuable insights into the spatial distribution of their data. From understanding customer demographics to tracking disease outbreaks and optimizing transportation routes, the applications of Power BI map visuals are vast and continue to expand as data becomes increasingly location-aware. By mastering the art of using latitude and longitude data within Power BI map visuals, users can unlock the full potential of geographic insights, driving informed decision-making and achieving strategic objectives.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling Geographic Insights: A Comprehensive Guide to Power BI Map Visuals and Latitude-Longitude Data. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
