Unraveling the Grid: Understanding Longitude and Latitude
Related Articles: Unraveling the Grid: Understanding Longitude and Latitude
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unraveling the Grid: Understanding Longitude and Latitude. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unraveling the Grid: Understanding Longitude and Latitude

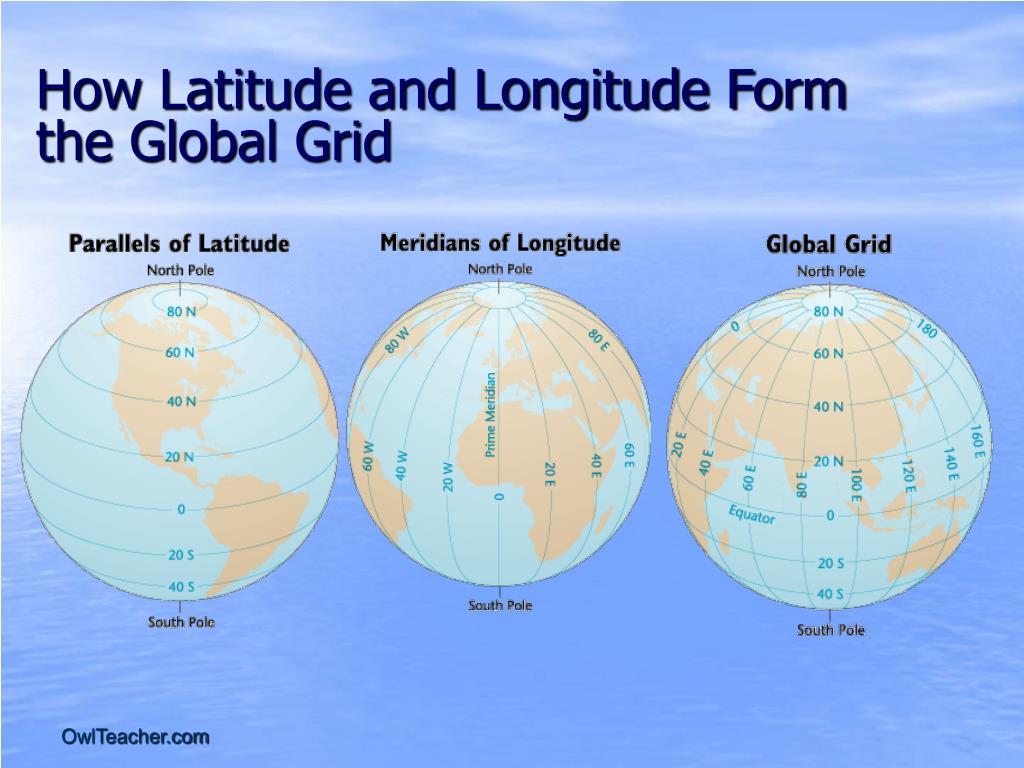
Imagine our Earth as a giant orange. Now picture someone slicing the orange into thin, perfectly even slices. These slices represent lines of longitude, imaginary lines that run vertically from the North Pole to the South Pole.
Next, imagine cutting the orange horizontally into smaller pieces. These horizontal cuts represent lines of latitude, imaginary lines that circle the Earth parallel to the equator.
Together, these lines of longitude and latitude form a grid system, a powerful tool that helps us pinpoint any location on Earth. This grid system is the foundation of maps, enabling us to navigate, explore, and understand our planet.
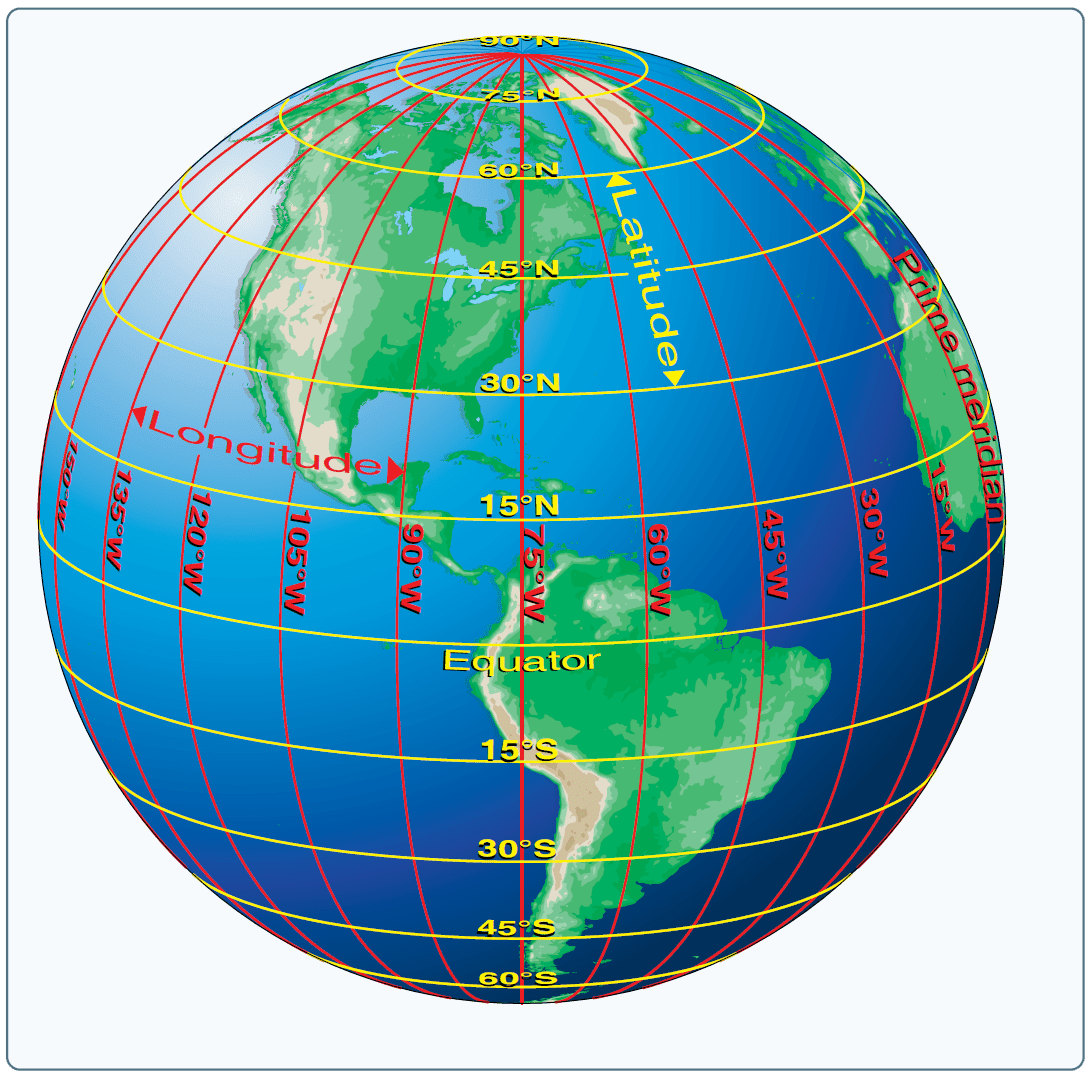
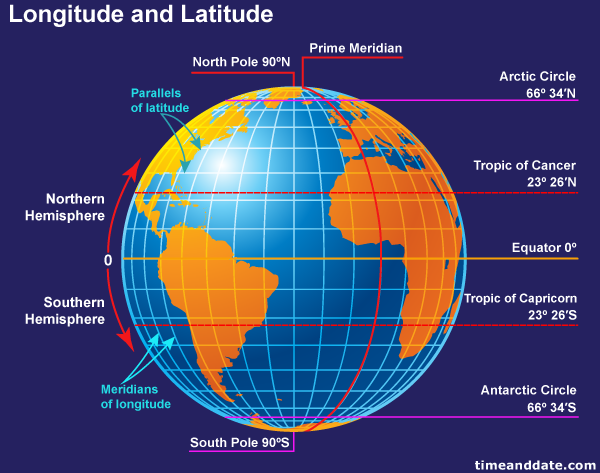
Longitude: Measuring East and West
Longitude lines are like the vertical slices of our orange. They are all semi-circles that converge at the North and South Poles. Each line of longitude is measured in degrees, with the Prime Meridian, a line running through Greenwich, England, serving as the starting point.
- East of the Prime Meridian: Locations to the east of the Prime Meridian are assigned positive degrees of longitude.
- West of the Prime Meridian: Locations to the west of the Prime Meridian are assigned negative degrees of longitude.
Think of it like a clock: the Prime Meridian is like the 12 o’clock mark, and the degrees of longitude represent the hours.
Latitude: Measuring North and South
Latitude lines are like the horizontal cuts of our orange. They are circles that run parallel to the equator, an imaginary line that circles the Earth at 0 degrees latitude.
- North of the Equator: Locations north of the equator are assigned positive degrees of latitude.
- South of the Equator: Locations south of the equator are assigned negative degrees of latitude.
The equator is like the middle point of the orange, and the degrees of latitude represent the distance from that middle point.
The Power of the Grid
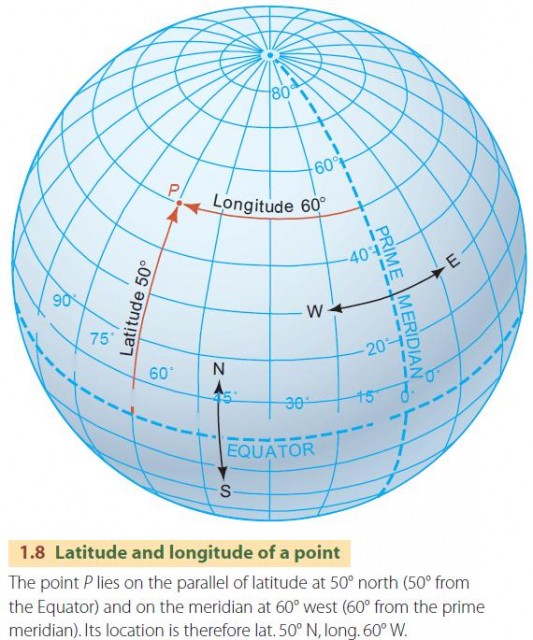
This grid system, created by the intersection of lines of longitude and latitude, allows us to assign unique coordinates to every location on Earth. These coordinates, expressed as a pair of numbers (longitude, latitude), are like the address of a place on the globe.
For example, the Eiffel Tower in Paris has coordinates of 2°29’28.8" E, 48°51’29.2" N. This means it is located 2 degrees, 29 minutes, and 28.8 seconds east of the Prime Meridian and 48 degrees, 51 minutes, and 29.2 seconds north of the equator.
The Importance of Longitude and Latitude
The use of longitude and latitude is crucial in various aspects of our lives:
- Navigation: Sailors, pilots, and even your GPS system rely on these coordinates to navigate across the globe.
- Mapping: Maps use lines of longitude and latitude to accurately represent the location of features like mountains, rivers, and cities.
- Geography: Understanding the grid system helps us study the Earth’s surface, its climate zones, and the distribution of resources.
- Technology: Satellites use longitude and latitude to pinpoint locations for communication, weather forecasting, and even search and rescue operations.
FAQs about Longitude and Latitude
1. Why is the Prime Meridian located in Greenwich, England?
The Prime Meridian was chosen as a reference point for longitude during the 19th century. At that time, England was a major maritime power, and Greenwich Observatory was a leading center for astronomical observation.
2. How are degrees of longitude and latitude further divided?
Each degree of longitude and latitude is further divided into 60 minutes (‘) and each minute into 60 seconds ("). This allows for even greater precision in pinpointing locations.
3. What are the coordinates of the North Pole and the South Pole?
The North Pole has coordinates of 90° N and 0° E, while the South Pole has coordinates of 90° S and 0° E.
4. What is the difference between longitude and latitude?
Longitude measures a location’s position east or west of the Prime Meridian, while latitude measures a location’s position north or south of the equator.
5. Can longitude and latitude be used to locate places in space?
While longitude and latitude are used to pinpoint locations on Earth, they are not used for locations in space. Space coordinates use different systems based on celestial objects and their distances.
Tips for Understanding Longitude and Latitude
- Visualize the grid: Use a globe or an online map to visualize the lines of longitude and latitude.
- Practice with examples: Find the coordinates of familiar places and try to locate them on a map.
- Use online tools: There are many websites and apps that allow you to find the coordinates of any location.
- Connect it to real-world applications: Think about how longitude and latitude are used in navigation, mapping, and other fields.
Conclusion
Longitude and latitude are fundamental tools for understanding and navigating our world. By understanding this grid system, we gain a deeper appreciation for the Earth’s geography and the technology that allows us to connect with places across the globe. Whether you are exploring a map, using a GPS system, or simply learning about the world around you, the concept of longitude and latitude is an essential foundation for understanding our planet.



![[DIAGRAM] Earthguide Diagram Latitude And Longitude - MYDIAGRAM.ONLINE](https://4.bp.blogspot.com/-aCD_3rc7x3U/WILkv1nbm2I/AAAAAAAAb4M/b3M_5TxKXa8OXAtIl4OOsyLbbUIAYRi9ACEw/s1600/latlong.jpg)
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unraveling the Grid: Understanding Longitude and Latitude. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!