Unraveling the Grid: A Comprehensive Look at Longitude and Latitude Lines on World Maps
Related Articles: Unraveling the Grid: A Comprehensive Look at Longitude and Latitude Lines on World Maps
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unraveling the Grid: A Comprehensive Look at Longitude and Latitude Lines on World Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unraveling the Grid: A Comprehensive Look at Longitude and Latitude Lines on World Maps
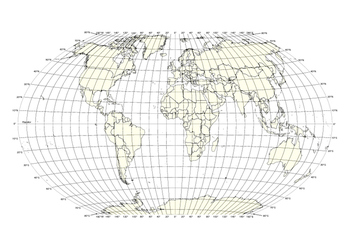
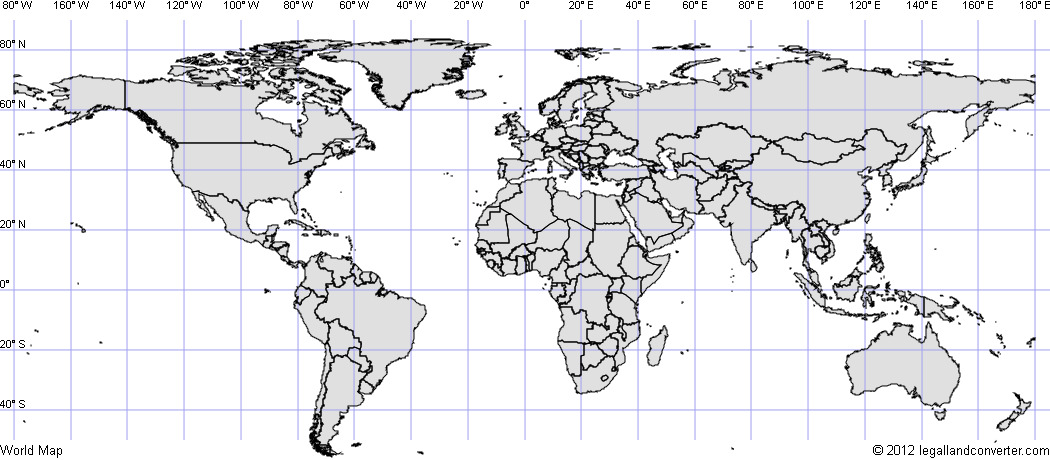
The world map, a familiar visual representation of our planet, is more than just a colorful depiction of continents and oceans. Embedded within its surface lies a complex grid system of longitude and latitude lines, a fundamental tool for navigation, geographical analysis, and understanding the Earth’s spatial relationships. This grid, a testament to human ingenuity, transforms the map into a powerful instrument for exploration and knowledge.
The Foundation: Longitude and Latitude Lines
Imagine the Earth as a sphere, sliced through its center by an imaginary line called the equator. This line divides the Earth into two equal hemispheres: the Northern Hemisphere and the Southern Hemisphere. Perpendicular to the equator, running from the North Pole to the South Pole, are lines called meridians. These meridians, unlike the equator, are not all equal in length.
Longitude: Measuring East to West
Longitude lines are semicircles that run from pole to pole, measuring the angular distance, in degrees, east or west of the Prime Meridian. The Prime Meridian, designated as 0° longitude, passes through Greenwich, England, and serves as the reference point for measuring longitude. Each meridian is assigned a unique longitude value, ranging from 0° to 180°, with values increasing eastward from the Prime Meridian and westward from the International Date Line, which is located at 180° longitude.
Latitude: Measuring North to South
Latitude lines are circles parallel to the equator, measuring the angular distance, in degrees, north or south of the equator. The equator is designated as 0° latitude, with values increasing northward to 90° at the North Pole and southward to 90° at the South Pole.
The Grid’s Significance: A Framework for Understanding the Earth
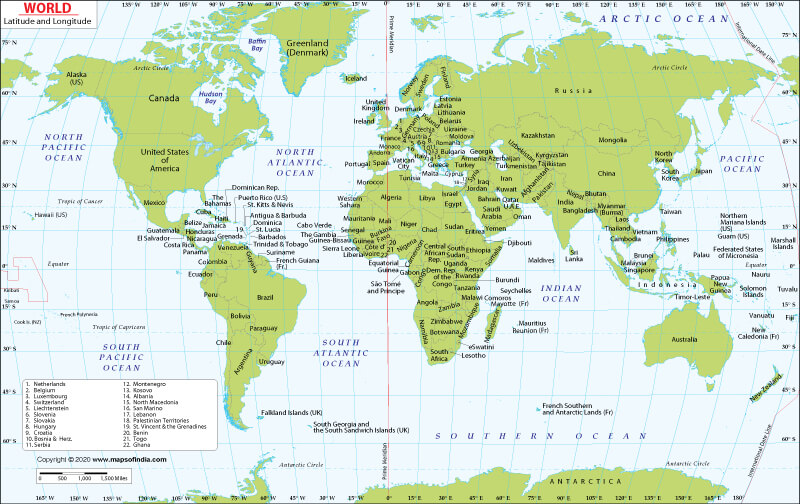
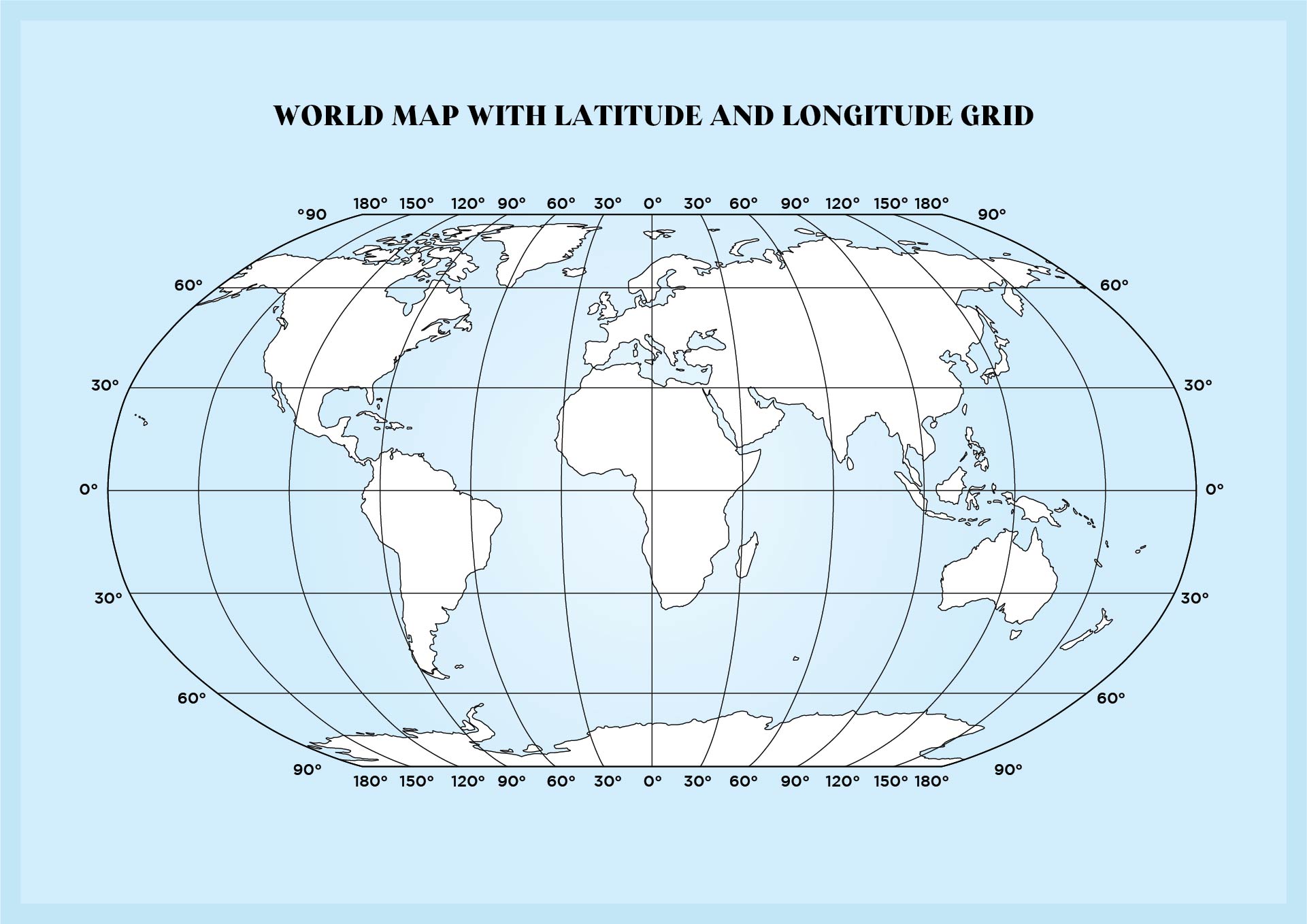
This intricate grid of longitude and latitude lines, known as the geographic coordinate system, provides a standardized framework for locating any point on Earth. Each location can be uniquely identified by its latitude and longitude coordinates, expressed as a pair of numerical values. This system allows for precise communication of locations, facilitating navigation, mapping, and data analysis.
Navigational Power: Guiding Ships and Planes
For centuries, sailors have relied on longitude and latitude lines for navigation. By determining their latitude using celestial observations and longitude through chronometers, navigators could pinpoint their position on the vast expanse of the ocean. Today, GPS systems, utilizing satellite technology, rely on the same principles of longitude and latitude to provide real-time location data, guiding ships, planes, and even our smartphones.
Beyond Navigation: Applications in Diverse Fields
The significance of longitude and latitude extends far beyond navigation. These lines play a crucial role in:
- Mapping and Cartography: The grid system forms the basis for creating accurate and detailed maps, enabling the representation of geographical features and their spatial relationships.
- Geographic Information Systems (GIS): GIS software, widely used in fields like urban planning, environmental monitoring, and disaster management, relies on longitude and latitude data to analyze and visualize spatial information.
- Weather Forecasting: Weather patterns and climate models rely on data collected from weather stations around the globe, each identified by its unique longitude and latitude coordinates.
- Earth Sciences: Geologists, oceanographers, and other earth scientists utilize longitude and latitude to study and analyze geological formations, ocean currents, and other Earth processes.
FAQs: Addressing Common Questions
Q: Why is the Prime Meridian located in Greenwich, England?
A: The choice of Greenwich as the location of the Prime Meridian was largely historical. In the 18th century, the Royal Observatory at Greenwich was a leading center for astronomical research, and its meridian was adopted as a standard reference point by various countries.
Q: Why are there 360 degrees in a circle?
A: The division of a circle into 360 degrees is attributed to the ancient Babylonians, who used a sexagesimal number system (base 60). The number 360 is easily divisible by many numbers, making it convenient for calculations and measurements.
Q: How are longitude and latitude lines used in everyday life?
A: While we may not consciously think about them, longitude and latitude are embedded in our daily lives. They power our GPS systems, guide our maps, and inform weather forecasts. They are the invisible grid that connects us to the world around us.
Tips for Understanding Longitude and Latitude
- Visualize the Earth as a sphere: This helps to understand how longitude and latitude lines are formed and how they relate to each other.
- Use a globe or an interactive map: These tools can provide a more realistic representation of the Earth and the grid system.
- Practice locating places using their coordinates: This will help you solidify your understanding of the relationship between coordinates and locations.
Conclusion: A Universal Language for Understanding the Earth
Longitude and latitude lines are not just abstract lines on a map; they are a fundamental tool for understanding the Earth’s spatial relationships and navigating its vast expanse. Their influence extends beyond the realms of navigation, shaping our maps, informing our weather forecasts, and empowering our understanding of the world around us. As we continue to explore and analyze our planet, the grid system of longitude and latitude remains an indispensable tool, a universal language that connects us to the Earth’s intricate geography.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unraveling the Grid: A Comprehensive Look at Longitude and Latitude Lines on World Maps. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!