Unraveling the Geography of Russia: A Comprehensive Look at Latitude, Longitude, and Their Significance
Related Articles: Unraveling the Geography of Russia: A Comprehensive Look at Latitude, Longitude, and Their Significance
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unraveling the Geography of Russia: A Comprehensive Look at Latitude, Longitude, and Their Significance. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unraveling the Geography of Russia: A Comprehensive Look at Latitude, Longitude, and Their Significance

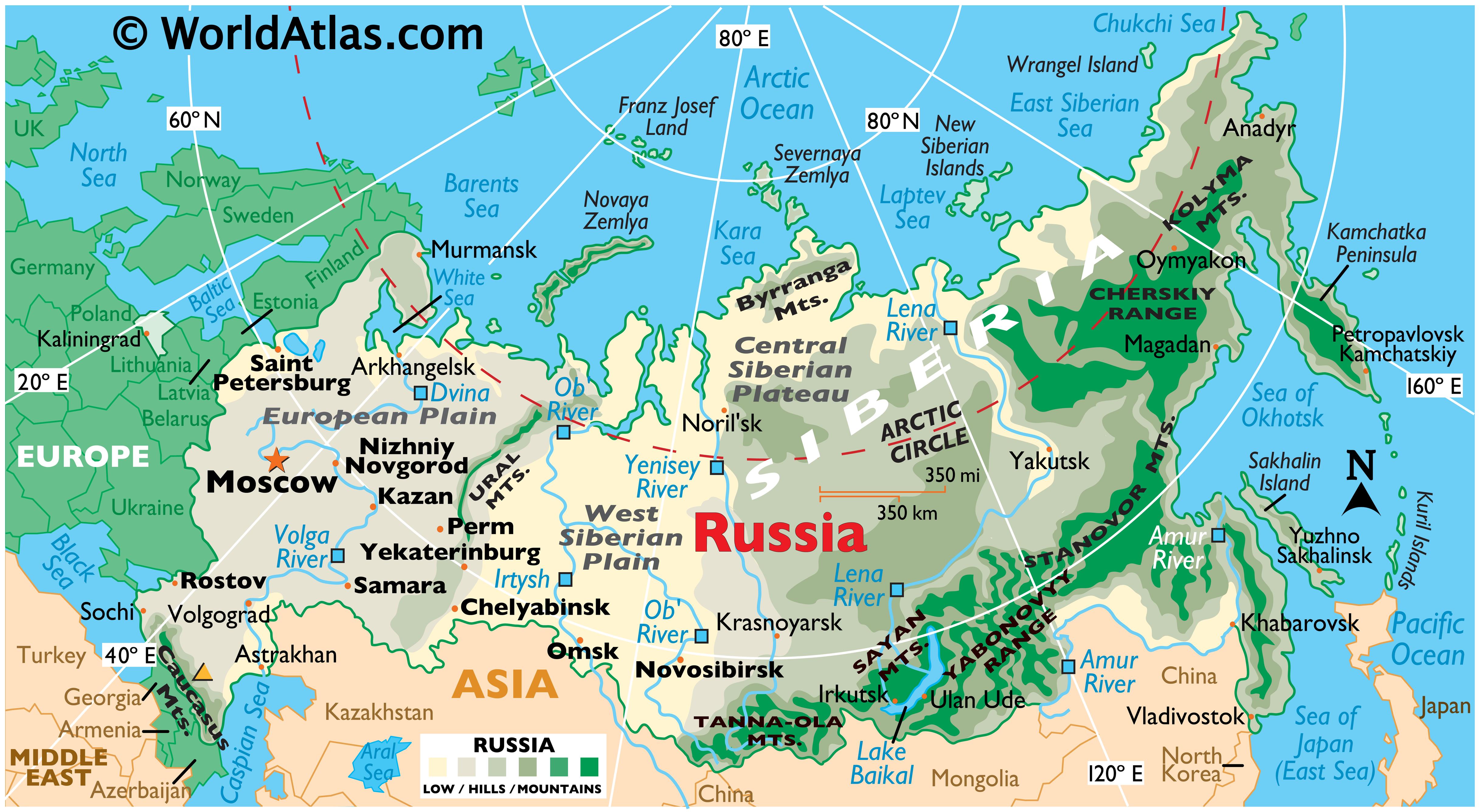
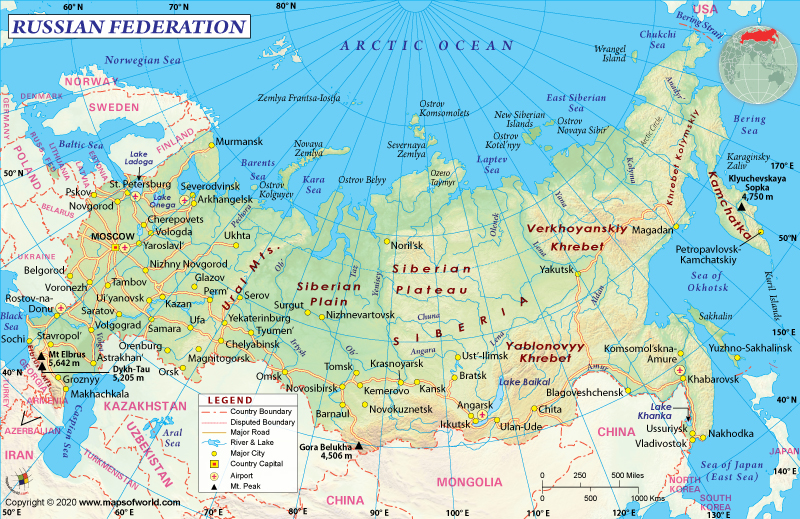
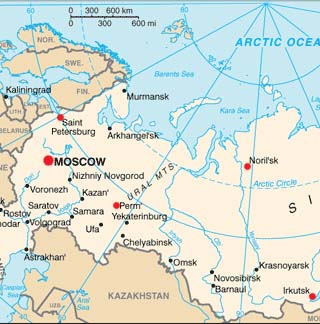
Russia, the largest country in the world by landmass, sprawls across a vast expanse of the Northern Hemisphere. Its geographical position, defined by latitude and longitude, plays a crucial role in shaping its climate, natural resources, and geopolitical landscape. Understanding Russia’s location through the lens of these coordinates provides a deeper insight into its unique characteristics and the challenges it faces.
Latitude and Longitude: Defining Russia’s Position
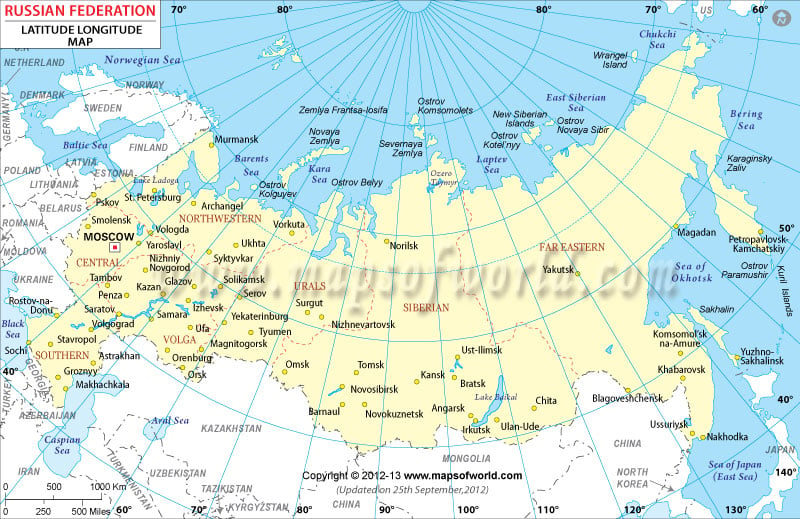
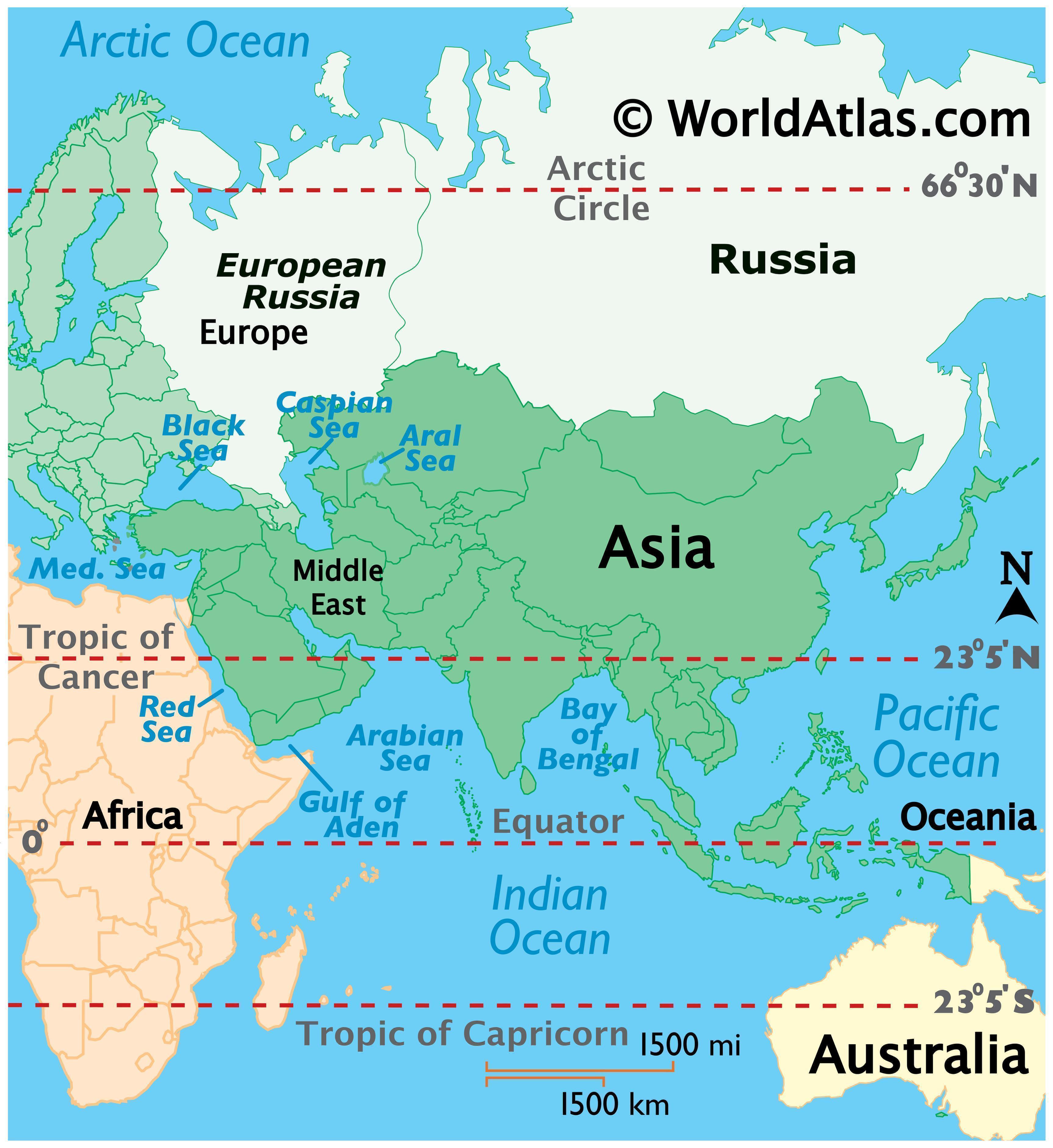
Latitude, measured in degrees north or south of the equator, dictates a region’s distance from the tropics and poles. Russia’s vast expanse stretches from the Arctic Circle in the north (approximately 66.5° N) to the Caucasus Mountains in the south (around 40° N). This significant latitudinal spread results in a wide range of climates, from the frigid tundra and taiga in the north to the temperate steppes and semi-arid deserts in the south.
Longitude, measured in degrees east or west of the prime meridian, indicates a location’s position relative to the Greenwich meridian. Russia’s longitudinal range extends from the Baltic Sea in the west (approximately 20° E) to the Bering Strait in the east (around 170° W). This immense longitudinal span places Russia across multiple time zones, impacting its communication and economic activities.
The Impact of Latitude and Longitude on Russia’s Geography
1. Climate: Russia’s latitudinal range directly influences its diverse climates. The northern regions experience long, cold winters and short, cool summers, characterized by permafrost and limited vegetation. The southern regions, closer to the equator, enjoy longer growing seasons and warmer temperatures, supporting agriculture and diverse ecosystems.
2. Natural Resources: Russia’s vast territory encompasses abundant natural resources, influenced by its geographical location. The Arctic region holds vast reserves of oil, natural gas, and minerals. The Siberian forests are a source of timber and valuable resources. The southern regions are rich in agricultural land and mineral deposits.
3. Transportation and Infrastructure: Russia’s vast size and diverse terrain pose challenges for transportation and infrastructure development. The Trans-Siberian Railway, spanning over 9,000 kilometers, connects the European and Asian parts of the country, highlighting the importance of rail infrastructure in traversing the vast distances.
4. Political and Economic Implications: Russia’s geographical position has significant geopolitical implications. Its vast landmass borders numerous countries, making it a key player in regional and global affairs. Its natural resources have attracted international interest, leading to economic partnerships and geopolitical tensions.
5. Cultural Diversity: Russia’s vast geographical expanse has fostered a diverse cultural landscape. Different ethnic groups, languages, and traditions have evolved across the country, reflecting the influence of its unique geographical position.
Understanding Russia’s Latitude and Longitude: A Deeper Dive
1. The Arctic Circle and its Significance: The Arctic Circle, passing through northern Russia, marks the region where the sun remains above the horizon for 24 hours during the summer solstice and below the horizon for 24 hours during the winter solstice. This unique phenomenon influences the region’s climate, wildlife, and human settlements.
2. The Ural Mountains: A Geographical Divide: The Ural Mountains, running north-south through western Russia, form a natural boundary between the European and Asian parts of the country. This geological feature influences climate patterns and the distribution of natural resources.
3. The Trans-Siberian Railway: Connecting East and West: The Trans-Siberian Railway, spanning over 9,000 kilometers, connects Moscow in the west to Vladivostok in the east. It serves as a vital artery for transportation, trade, and cultural exchange, highlighting the importance of infrastructure in bridging the vast distances within Russia.
4. The Caspian Sea: A Vital Resource: The Caspian Sea, located in the south of Russia, is the world’s largest inland body of water. It serves as a source of energy resources, fisheries, and transportation routes, playing a significant role in the regional economy.
5. The Bering Strait: Connecting Continents: The Bering Strait, separating Russia from the United States, is a narrow body of water connecting the Arctic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean. It has historical significance as a possible land bridge between Asia and North America, and continues to play a role in international relations and maritime trade.
FAQs about Russia’s Latitude and Longitude:
1. Why is Russia’s latitude so important?
Russia’s latitude directly influences its climate, vegetation, and natural resources. The northern regions experience harsh winters and limited vegetation, while the southern regions enjoy warmer temperatures and longer growing seasons.
2. How does Russia’s longitude affect its time zones?
Russia’s vast longitudinal span necessitates multiple time zones to accommodate the difference in sunrise and sunset times across the country. This impacts communication and economic activities, requiring coordination across different time zones.
3. What are the challenges of governing a country spanning multiple latitudes and longitudes?
Governing a country with such a vast geographical expanse presents challenges in terms of infrastructure development, transportation, communication, and managing diverse cultures and climates.
4. How does Russia’s geographical location impact its international relations?
Russia’s vast landmass and strategic location make it a significant player in regional and global affairs. Its borders with numerous countries and access to vital resources influence its international relations and geopolitical dynamics.
5. What are the economic opportunities presented by Russia’s geographical position?
Russia’s vast natural resources, including oil, gas, minerals, and forests, offer significant economic opportunities. Its strategic location also provides access to key trade routes and markets, impacting its economic development.
Tips for Understanding Russia’s Geography:
1. Utilize maps and online resources: Explore detailed maps of Russia, including latitude and longitude lines, to visualize its geographical position and understand the spatial relationships between different regions.
2. Explore satellite imagery: Utilize online platforms offering satellite imagery to gain a visual perspective on Russia’s landscape, including its diverse ecosystems, urban areas, and infrastructure.
3. Research the impact of latitude and longitude on various aspects: Investigate how latitude and longitude influence Russia’s climate, natural resources, transportation, and cultural diversity.
4. Engage with experts and publications: Consult with geographers, historians, and political analysts specializing in Russia to gain deeper insights into the country’s geography and its influence on its history, culture, and economy.
Conclusion:
Russia’s geographical position, defined by its latitude and longitude, plays a crucial role in shaping its diverse climate, abundant natural resources, and geopolitical landscape. Understanding the impact of these coordinates provides a deeper appreciation for the country’s unique characteristics, challenges, and opportunities. From the frigid Arctic Circle to the temperate steppes, Russia’s vast expanse offers a fascinating study in the interplay between geography and human society. By exploring Russia’s location through the lens of latitude and longitude, we gain a greater understanding of its complex and multifaceted nature.


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unraveling the Geography of Russia: A Comprehensive Look at Latitude, Longitude, and Their Significance. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!