Understanding the Reach of a Yellowstone Eruption: Deciphering the Blast Zone Map
Related Articles: Understanding the Reach of a Yellowstone Eruption: Deciphering the Blast Zone Map
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Understanding the Reach of a Yellowstone Eruption: Deciphering the Blast Zone Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding the Reach of a Yellowstone Eruption: Deciphering the Blast Zone Map

The Yellowstone Caldera, a vast volcanic basin in the heart of Wyoming, is a potent reminder of the Earth’s dynamic nature. While eruptions are infrequent, the potential consequences are significant, prompting the creation of detailed blast zone maps. These maps are not predictions of an imminent eruption, but rather a scientific tool for understanding the potential impact of a future eruption, guiding preparedness and mitigation strategies.
Delving into the Blast Zone Map: A Visual Guide to Potential Devastation
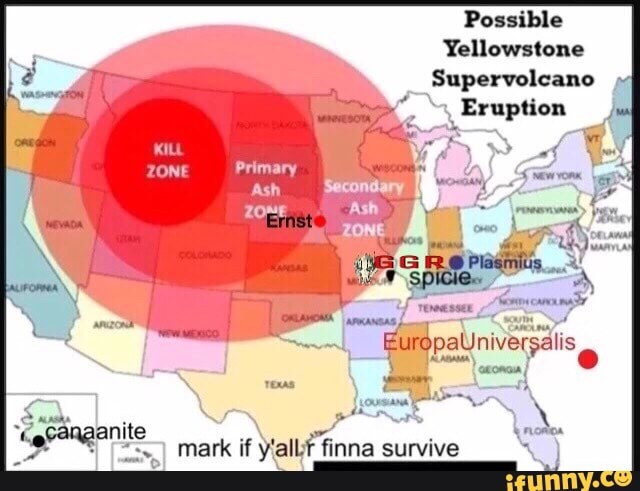
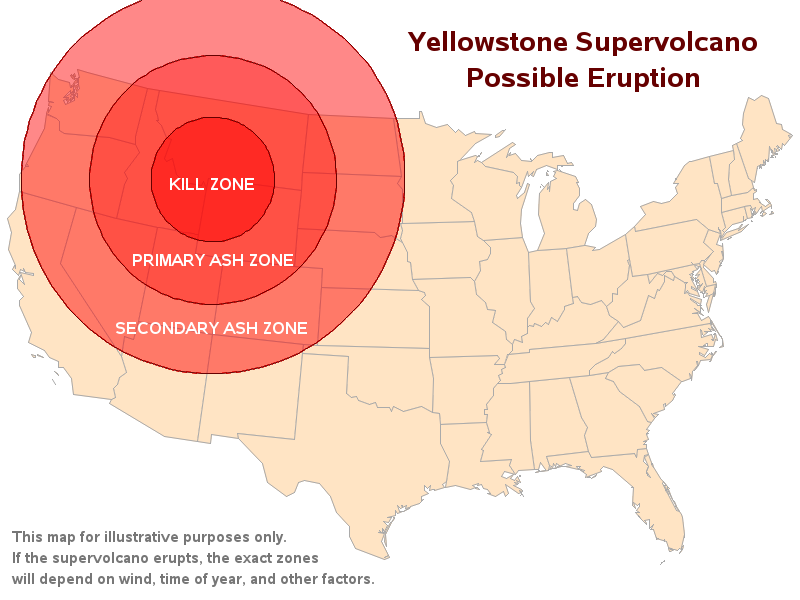
The Yellowstone blast zone map depicts the potential geographic extent of various eruption scenarios, categorized by their intensity and the distance to which volcanic material could be ejected. The map is divided into concentric zones, each representing a distinct level of impact based on the volume of erupted material and its dispersal:
-
Zone 1: The Immediate Impact Zone
This zone encompasses the immediate vicinity of the caldera, potentially experiencing the most severe impact. A major eruption could unleash a pyroclastic flow, a superheated mixture of ash, gas, and rock fragments, capable of traveling at speeds exceeding 400 miles per hour. This zone would be engulfed in this deadly flow, leading to immediate and catastrophic destruction.
-
Zone 2: The Ashfall Zone
Extending outward from the caldera, this zone would experience significant ashfall. The volume and thickness of ash deposited would vary depending on the eruption’s intensity and prevailing winds. The ashfall could disrupt transportation, infrastructure, and agriculture, potentially leading to widespread economic and societal disruption.
-
Zone 3: The Regional Impact Zone
This zone encompasses a wider area surrounding the caldera, experiencing a lesser degree of ashfall and potential for localized volcanic activity. While the impact may be less severe than in Zone 2, it could still pose significant challenges, particularly for transportation, infrastructure, and air quality.
Beyond the Blast: Understanding the Underlying Science
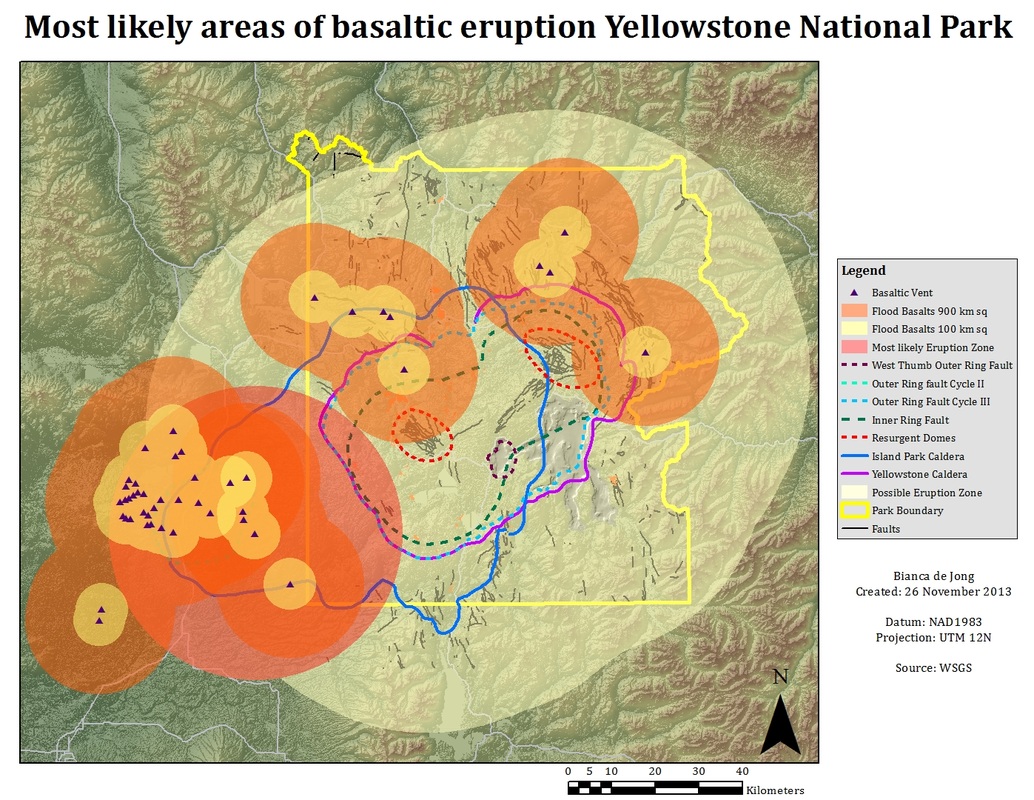
The blast zone map is not a static representation; it evolves as scientific understanding of the Yellowstone system progresses. The map relies on a combination of geological evidence, computer simulations, and expert analysis to depict the potential reach of different eruption scenarios.
-
Geological Evidence: The Past Holds the Key to the Future
Geologists study the remnants of past eruptions, analyzing the layers of ash and volcanic rock deposited over millennia. This information provides valuable insights into the eruption frequency, intensity, and potential impact zones.
-
Computer Simulations: Modeling the Unpredictable
Sophisticated computer models are employed to simulate different eruption scenarios, factoring in variables such as eruption volume, ash particle size, and prevailing wind patterns. These simulations help refine the blast zone map, providing a more accurate representation of the potential impact.
-
Expert Analysis: A Multidisciplinary Approach
Experts from various fields, including volcanology, geology, atmospheric science, and engineering, collaborate to interpret the data and refine the blast zone map. This multidisciplinary approach ensures a comprehensive and informed understanding of the potential risks associated with a Yellowstone eruption.
The Importance of the Blast Zone Map: A Guide for Preparedness
The Yellowstone blast zone map serves as a critical tool for preparing for a potential eruption. It provides a framework for:
-
Emergency Planning: Local, state, and federal agencies utilize the map to develop and refine emergency plans, including evacuation routes, communication strategies, and resource allocation.
-
Infrastructure Resilience: The map assists in assessing the vulnerability of critical infrastructure, such as power grids, transportation networks, and water systems, enabling proactive measures to enhance resilience.
-
Public Awareness: The map plays a crucial role in educating the public about the potential risks associated with a Yellowstone eruption, promoting awareness and encouraging preparedness.
FAQs: Addressing Common Questions about the Yellowstone Blast Zone Map
1. Does the blast zone map predict an imminent eruption?
No, the blast zone map does not predict an imminent eruption. It is a tool for understanding the potential impact of a future eruption, not a prediction of when or if one will occur.
2. How often does Yellowstone erupt?
Yellowstone has experienced major eruptions on average every 600,000 to 800,000 years. The last major eruption occurred about 630,000 years ago, suggesting that a major eruption is not imminent.
3. What are the signs of an impending eruption?
Signs of an impending eruption include increased ground deformation, changes in heat flow, increased seismic activity, and changes in gas emissions. Monitoring these factors allows scientists to track the volcano’s activity and detect potential precursors to an eruption.
4. What can I do to prepare for a potential eruption?
While the likelihood of a major eruption in the near future is low, it is prudent to be prepared. Familiarize yourself with evacuation routes, have an emergency kit ready, and stay informed about official updates and instructions from authorities.
5. Is the blast zone map constantly updated?
Yes, the blast zone map is continually updated as new data becomes available. Scientists are constantly monitoring Yellowstone’s activity and refining their understanding of the volcano’s behavior.
Tips for Staying Informed and Prepared
-
Monitor Official Sources: Stay informed about Yellowstone’s activity by following official sources, such as the U.S. Geological Survey (USGS) and the Yellowstone Volcano Observatory (YVO).
-
Develop a Family Emergency Plan: Create a plan for your family, including evacuation routes, communication strategies, and a designated meeting place.
-
Prepare an Emergency Kit: Assemble a kit with essential supplies, such as food, water, first-aid supplies, and a battery-powered radio.
Conclusion: Living with a Volcano
The Yellowstone blast zone map serves as a reminder of the dynamic forces that shape our planet. While a major eruption is unlikely in the near future, understanding the potential impact and preparing for such an event is essential. By staying informed, developing emergency plans, and taking proactive measures, we can mitigate the risks associated with this extraordinary natural phenomenon. The blast zone map is not a source of fear, but rather a tool for informed decision-making, enabling us to live in harmony with the powerful forces of nature.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding the Reach of a Yellowstone Eruption: Deciphering the Blast Zone Map. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!