Understanding India’s Geographic Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Latitude, Longitude, and the Outline Map
Related Articles: Understanding India’s Geographic Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Latitude, Longitude, and the Outline Map
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Understanding India’s Geographic Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Latitude, Longitude, and the Outline Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding India’s Geographic Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Latitude, Longitude, and the Outline Map
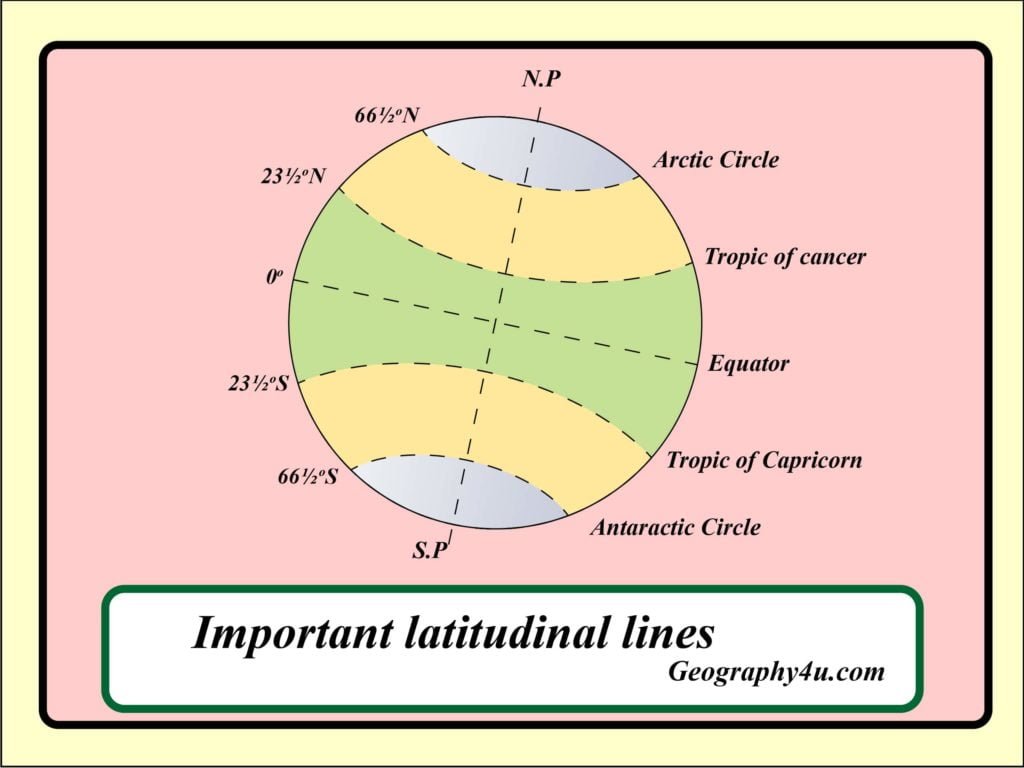
India, a vast and diverse nation, boasts a rich tapestry of cultures, languages, and landscapes. Understanding its geographic position and spatial dimensions is crucial for comprehending its unique characteristics and the influences that shape its people and environment. This article delves into the significance of India’s outline map, highlighting the role of latitude and longitude in defining its location and boundaries.
The Importance of Latitude and Longitude
Latitude and longitude form the foundation of geographical mapping, providing a universal system for pinpointing locations on Earth’s surface. Latitude lines run horizontally, parallel to the equator, measuring distance north or south of the equator in degrees. Longitude lines run vertically, converging at the poles, measuring distance east or west of the prime meridian in degrees.
India’s Geographic Coordinates
India’s geographical position is defined by its latitude and longitude:
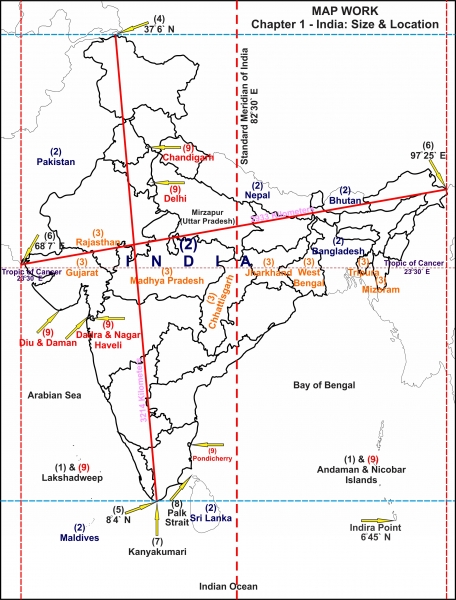
- Latitude: India lies between 8°4′ N and 37°6′ N latitude, extending from the tropical to the subtropical regions. This latitudinal range contributes to India’s diverse climatic zones, ranging from the scorching deserts of Rajasthan to the snow-capped Himalayas in the north.
- Longitude: India lies between 68°7′ E and 97°25′ E longitude, spanning over 30 degrees. This vast longitudinal spread influences the duration of daylight hours and the timing of sunrise and sunset across the country.
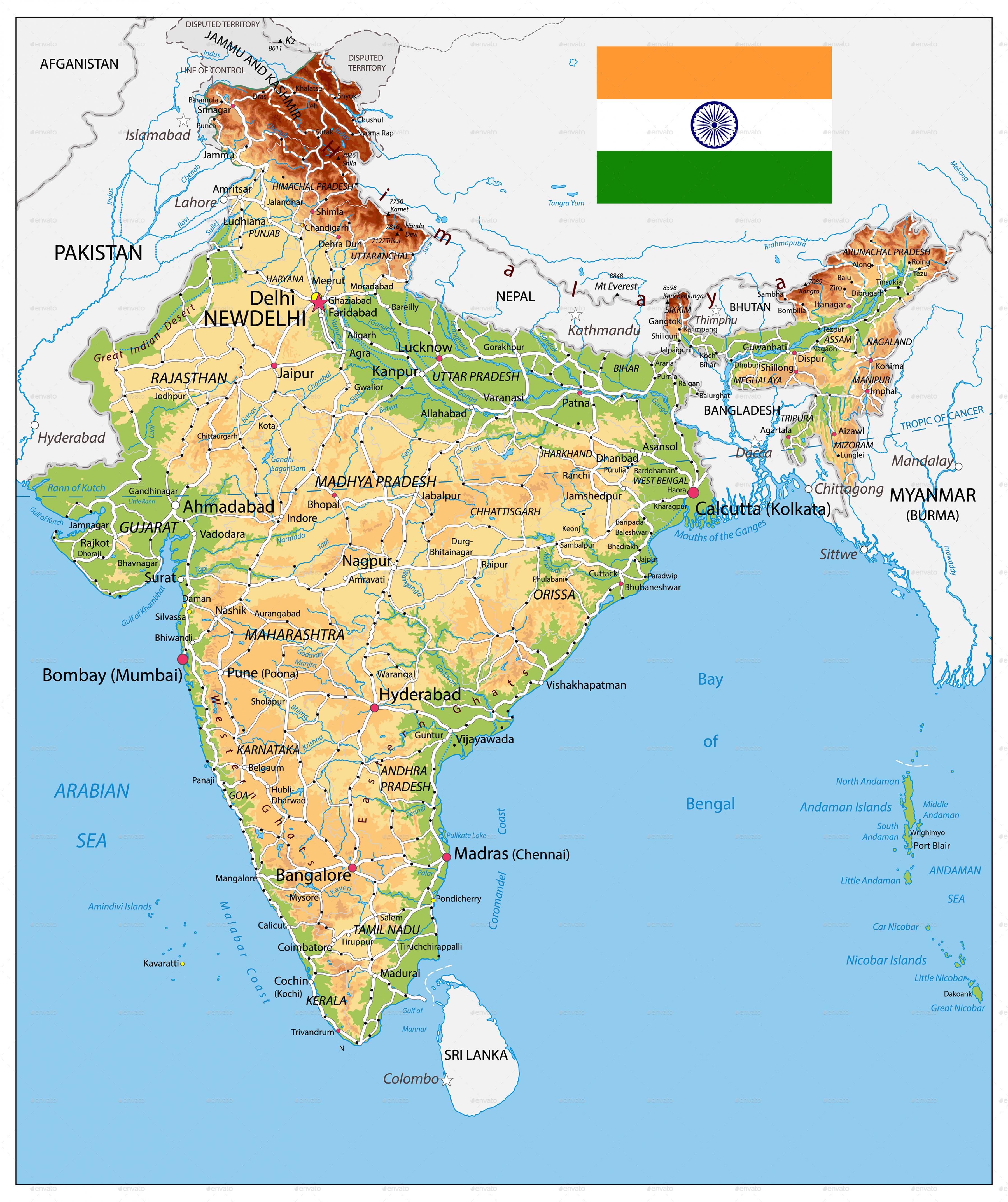
The Outline Map: A Visual Representation of India’s Boundaries
The outline map of India, marked with latitude and longitude lines, serves as a visual tool for understanding its geographical extent and key features. It depicts the country’s shape, size, and relative positions of its states and union territories. This map provides a framework for:
- Understanding the country’s physical features: Mountains, rivers, plains, and coastal regions are visually represented, highlighting the diverse landscape of India.
- Analyzing the distribution of resources: The outline map aids in visualizing the location of mineral deposits, forests, and agricultural lands, providing insights into resource management and economic development.
- Mapping population distribution: The map allows for studying the concentration of population in different regions, revealing urban centers and rural areas.
- Identifying key geographical features: Important cities, towns, ports, and historical sites can be easily located and studied using the outline map.
- Understanding geopolitical significance: The map facilitates the analysis of India’s strategic location, its borders with neighboring countries, and its potential for trade and transportation.
Beyond the Outline: Exploring the Significance of India’s Geographic Features
The outline map, with its latitude and longitude lines, provides a foundational understanding of India’s geography. However, it is crucial to delve deeper into the specific features that shape the country’s landscape and influence its people:
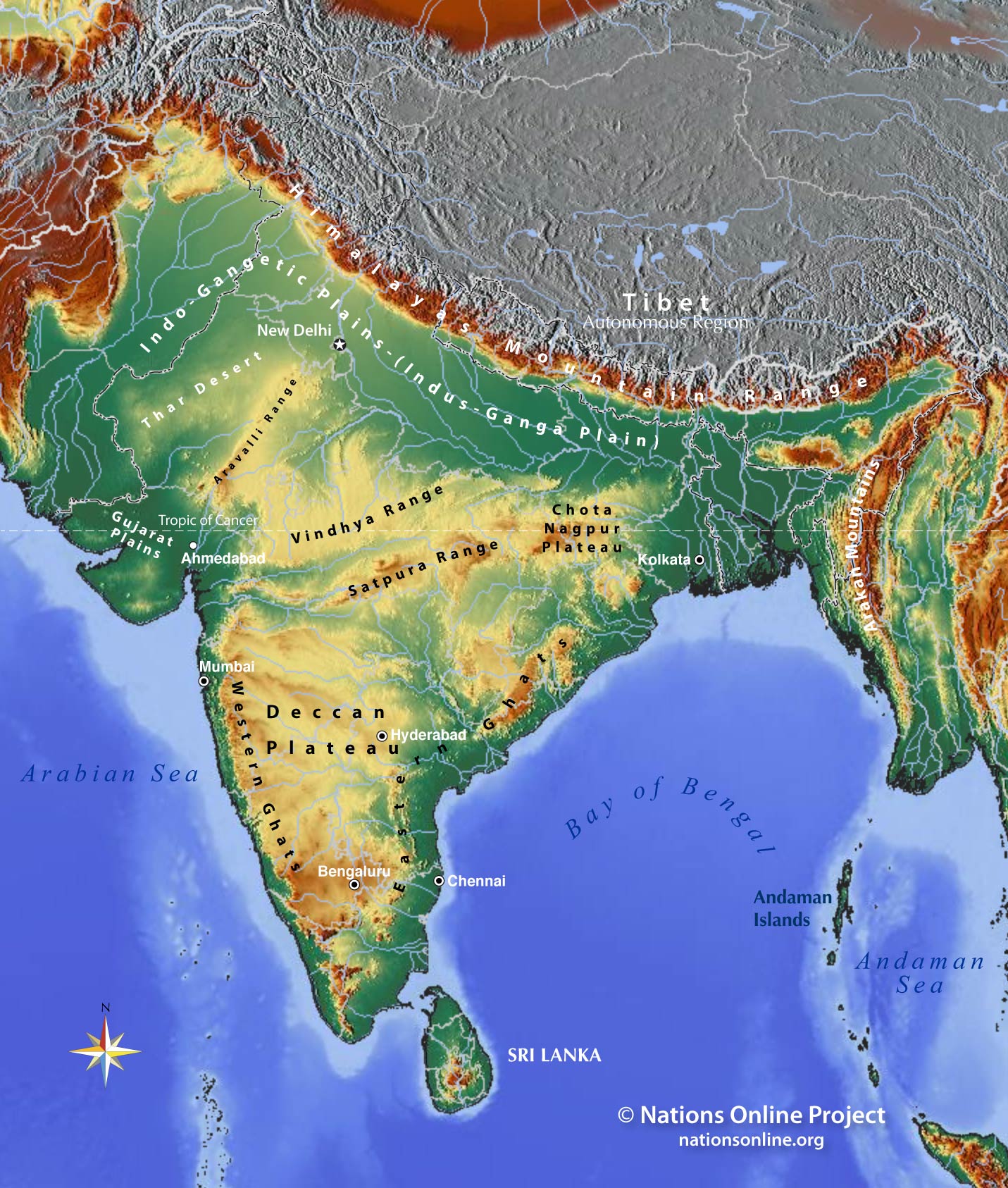
- The Himalayas: The towering Himalayan mountain range, forming the country’s northern border, acts as a natural barrier, impacting weather patterns and influencing the distribution of flora and fauna.
- The Indo-Gangetic Plain: This fertile plain, stretching across northern India, is a major agricultural region, supporting a dense population and contributing significantly to the country’s economy.
- The Deccan Plateau: This vast plateau, located in peninsular India, is characterized by its dry climate and mineral wealth, contributing to the country’s industrial development.
- The Coastal Regions: India’s extensive coastline, bordering the Indian Ocean, Arabian Sea, and Bay of Bengal, provides access to global trade routes and influences the country’s maritime activities.
FAQs
1. Why is the outline map of India with latitude and longitude important?
The outline map with latitude and longitude provides a clear visual representation of India’s geographic boundaries, allowing for a better understanding of its size, shape, and relative positions of its states and union territories. It facilitates analysis of the distribution of resources, population, and key geographical features, contributing to various fields like geography, economics, and social studies.
2. How does latitude and longitude affect India’s climate?
India’s latitudinal range, extending from the tropical to the subtropical regions, contributes to its diverse climatic zones. The Himalayan mountain range acts as a natural barrier, influencing weather patterns and creating distinct climatic zones across the country.
3. What is the significance of India’s coastal regions?
India’s extensive coastline provides access to global trade routes, fostering maritime trade and economic development. Coastal regions are also important for fishing, tourism, and transportation.
4. How does the outline map help in understanding India’s population distribution?
The map allows for studying the concentration of population in different regions, revealing urban centers and rural areas. This information is crucial for understanding demographic trends, planning infrastructure development, and addressing social issues.
5. What are the key geographical features that influence India’s economy?
India’s diverse geography, including the fertile Indo-Gangetic Plain, the mineral-rich Deccan Plateau, and the coastal regions, contributes significantly to the country’s economy. These features support agriculture, industry, trade, and tourism.
Tips for Understanding India’s Outline Map
- Study the map carefully: Pay attention to the latitude and longitude lines, and note the positions of key geographical features like mountains, rivers, and coastal regions.
- Use different resources: Combine the outline map with other sources of information, such as textbooks, online resources, and documentaries, to gain a deeper understanding of India’s geography.
- Relate geography to other subjects: Connect the geographical features to their impact on India’s history, culture, economy, and social development.
- Engage in hands-on activities: Use maps, globes, and models to visualize India’s geography and explore its different regions.
Conclusion
The outline map of India with latitude and longitude provides a foundational understanding of the country’s geographic extent and key features. It serves as a visual tool for studying the distribution of resources, population, and various geographical features, contributing to a comprehensive understanding of India’s diverse landscape and its influence on the nation’s history, culture, and development. By delving deeper into the specific geographical features and their impact on the country’s people and environment, we gain a richer appreciation for the complexity and beauty of India’s geographic landscape.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding India’s Geographic Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Latitude, Longitude, and the Outline Map. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!