Ukraine’s Political Landscape: A Nation in Transition
Related Articles: Ukraine’s Political Landscape: A Nation in Transition
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Ukraine’s Political Landscape: A Nation in Transition. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Ukraine’s Political Landscape: A Nation in Transition
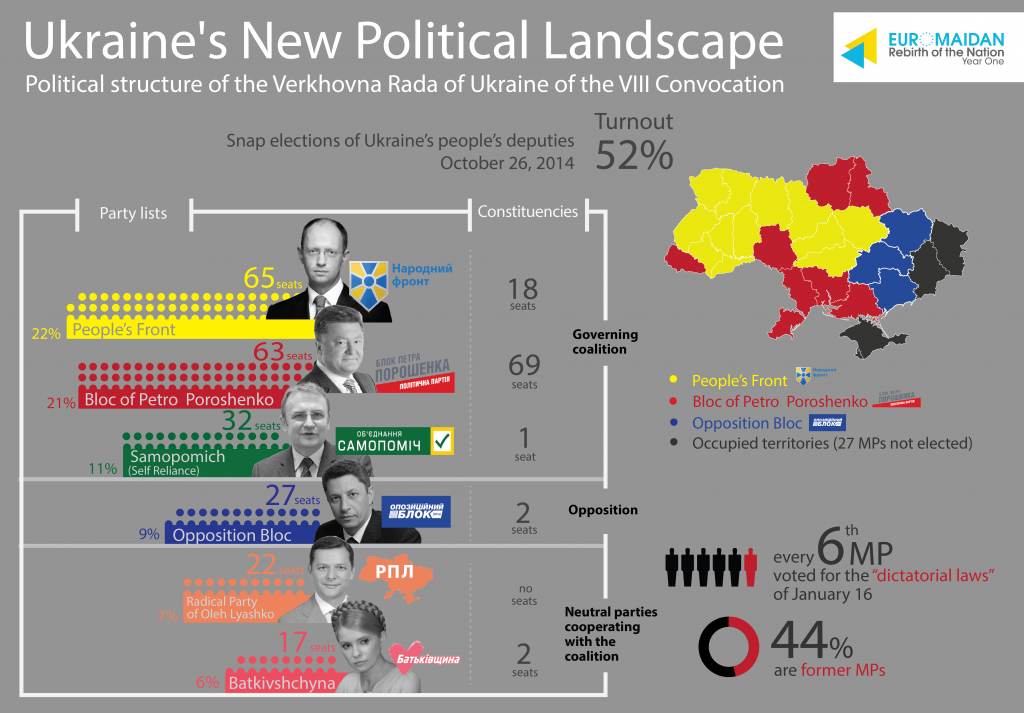
The political map of Ukraine is a complex tapestry woven from a rich history, diverse cultural influences, and the ongoing struggle for self-determination. Understanding this map, its evolution, and its contemporary significance is crucial for grasping the intricacies of the nation’s present and its potential future.
Historical Context: From Empire to Independence
Ukraine’s political landscape has been shaped by centuries of external forces. For much of its history, it was incorporated into larger empires, experiencing periods of autonomy and oppression. The Russian Empire, the Austro-Hungarian Empire, and the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth all exerted influence over different parts of the territory that constitutes modern-day Ukraine.
The 20th century witnessed a dramatic shift in Ukraine’s political status. After the Russian Revolution, Ukraine briefly declared independence in 1917, only to be absorbed into the Soviet Union as the Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic. This period saw the imposition of a centralized political system, the promotion of Russian language and culture, and the suppression of Ukrainian national identity.
The collapse of the Soviet Union in 1991 finally brought about Ukraine’s independence. This momentous event marked the beginning of a new era, one characterized by the transition to a democratic system and the establishment of a sovereign state.
The Political Map of Modern Ukraine
Post-independence, Ukraine adopted a presidential-parliamentary republic system. The country is divided into 24 oblasts (regions), each with its own elected governor and regional council. The capital city, Kyiv, has a special status as a separate entity with its own elected mayor and city council.
The Ukrainian political system has evolved significantly since independence. The 1996 Constitution, the current governing document, established a strong presidency, with the president holding significant power over the executive branch. The Verkhovna Rada (parliament) is responsible for legislative functions, with members elected through a proportional representation system.
Key Political Developments and Challenges
Ukraine’s political landscape has been marked by several key developments and persistent challenges:
- The Orange Revolution (2004): This popular uprising, sparked by allegations of election fraud, led to the cancellation of a rigged presidential election and the eventual victory of Viktor Yushchenko, a pro-Western candidate. The Orange Revolution demonstrated the power of civil society and highlighted the importance of democratic values in Ukraine.
- The Euromaidan Revolution (2013-2014): Protests against the government’s decision to abandon an association agreement with the European Union escalated into a major political crisis, culminating in the ousting of President Viktor Yanukovych. The Euromaidan Revolution further solidified Ukraine’s commitment to European integration and fueled its aspirations for greater political and economic stability.
- The Russian Annexation of Crimea (2014): Following the Euromaidan Revolution, Russia invaded and annexed the Crimean Peninsula, a region with a majority-Russian population. This act of aggression, condemned by the international community, marked a significant escalation in tensions between Russia and Ukraine.
- The War in Donbas (2014-present): Simultaneously with the annexation of Crimea, Russia supported separatists in eastern Ukraine, who launched a war against the Ukrainian government. The conflict in Donbas has resulted in thousands of casualties and a humanitarian crisis, with the region remaining divided and under the control of pro-Russian forces.
- Political Instability and Corruption: Despite the progress made in establishing democratic institutions, Ukraine has faced ongoing challenges related to political instability, corruption, and the influence of oligarchs. These issues have hindered economic development and undermined public trust in the government.
The Importance of Understanding Ukraine’s Political Map
Understanding the political map of Ukraine is crucial for several reasons:
- Geopolitical Significance: Ukraine’s strategic location at the crossroads of Europe and Russia makes it a key player in regional politics. The country’s political stability and its relationship with Russia have significant implications for international security.
- Economic Potential: Ukraine possesses substantial economic potential, particularly in agriculture, energy, and manufacturing. Its political stability and the implementation of reforms are essential for attracting foreign investment and fostering economic growth.
- Humanitarian Crisis: The ongoing conflict in Donbas has created a humanitarian crisis, with millions of people displaced and in need of assistance. Understanding the political landscape is crucial for addressing the humanitarian needs of the affected population.
- European Integration: Ukraine aspires to join the European Union, a process that requires significant political and economic reforms. Understanding the country’s political system and its challenges is crucial for assessing its progress towards European integration.
FAQs
Q: What is the current political situation in Ukraine?
A: Ukraine is currently engaged in a protracted conflict with Russia-backed separatists in the Donbas region. The country is also facing significant challenges related to corruption, economic instability, and the ongoing threat of Russian aggression.
Q: What are the main political parties in Ukraine?
A: Ukraine has a multi-party system with a diverse range of political parties. Some of the major parties include the Servant of the People party, the European Solidarity party, the Opposition Platform – For Life party, and the Fatherland party.
Q: What is the role of the president in Ukraine?
A: The president of Ukraine is the head of state and the commander-in-chief of the armed forces. The president appoints the prime minister and the cabinet, and has the power to veto legislation passed by parliament.
Q: What is the relationship between Ukraine and Russia?
A: The relationship between Ukraine and Russia is complex and characterized by historical ties, cultural similarities, and ongoing tensions. The annexation of Crimea and the war in Donbas have significantly strained relations between the two countries.
Q: What is the future of Ukraine?
A: The future of Ukraine is uncertain, but it is likely to remain a key player in regional politics. The country’s commitment to European integration, its resilience in the face of Russian aggression, and its ongoing efforts to address internal challenges will shape its future trajectory.
Tips
- Stay informed: Follow reputable news sources and analytical reports to stay updated on the political developments in Ukraine.
- Engage in critical thinking: Be wary of biased or misleading information. Analyze different perspectives and form your own informed opinions.
- Support Ukrainian initiatives: Contribute to organizations that provide humanitarian assistance to Ukraine or promote democratic values in the country.
- Advocate for peace and stability: Encourage diplomatic solutions to the conflict in Donbas and support efforts to de-escalate tensions between Ukraine and Russia.
Conclusion
The political map of Ukraine is a dynamic and complex landscape. It reflects the country’s rich history, its ongoing struggle for self-determination, and its aspirations for a brighter future. Understanding this map is essential for appreciating the challenges and opportunities facing Ukraine, and for engaging in informed discussions about the country’s role in the world. As Ukraine continues to navigate its path towards a stable and prosperous future, its political landscape will undoubtedly continue to evolve, shaping the destiny of this resilient nation.


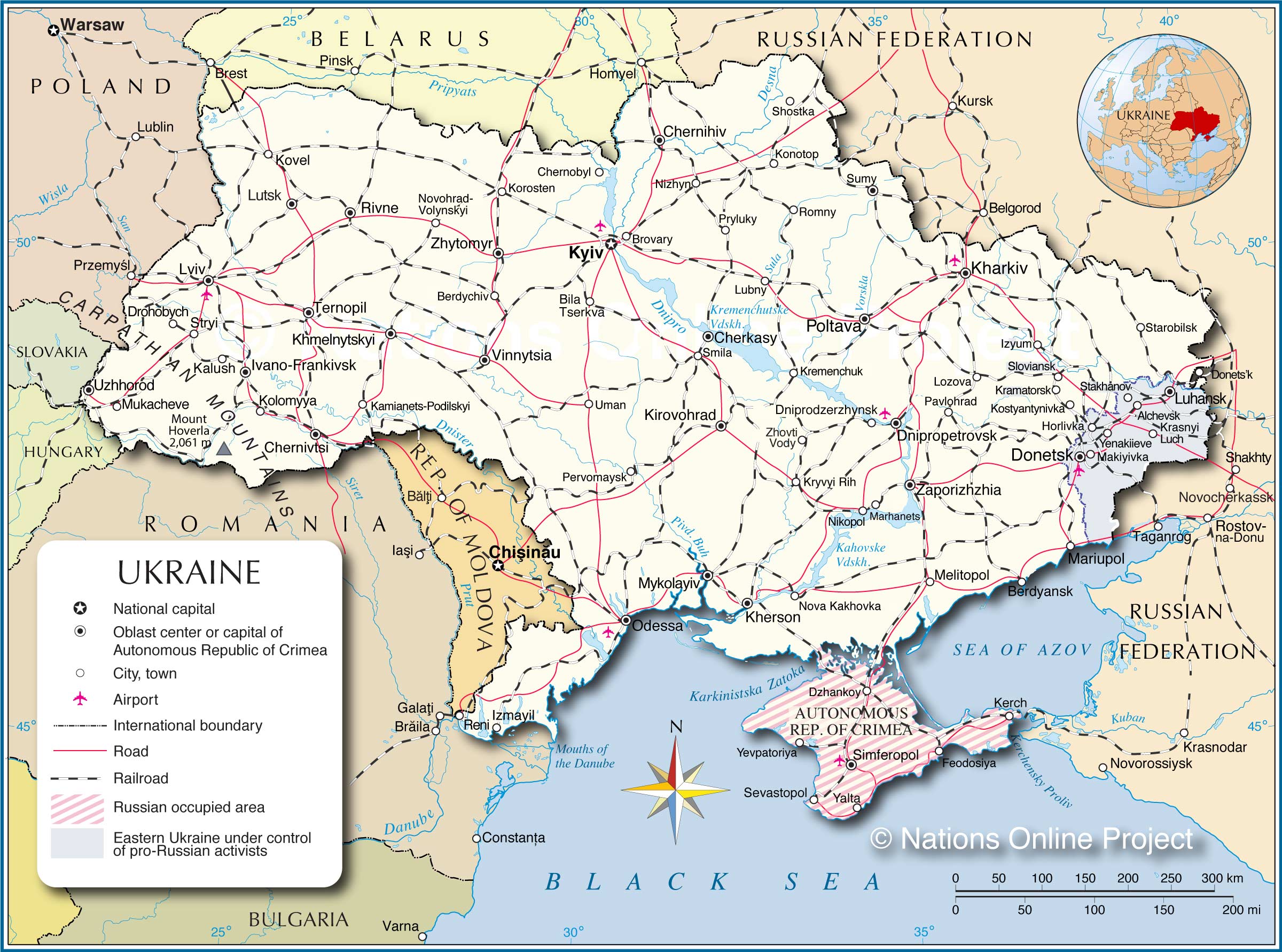



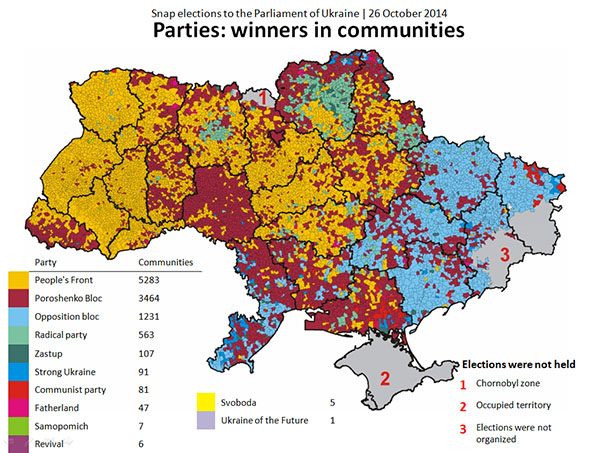
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Ukraine’s Political Landscape: A Nation in Transition. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!