Transforming Geographic Data: Mapping Zip Codes to a Hex Grid
Related Articles: Transforming Geographic Data: Mapping Zip Codes to a Hex Grid
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Transforming Geographic Data: Mapping Zip Codes to a Hex Grid. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Transforming Geographic Data: Mapping Zip Codes to a Hex Grid
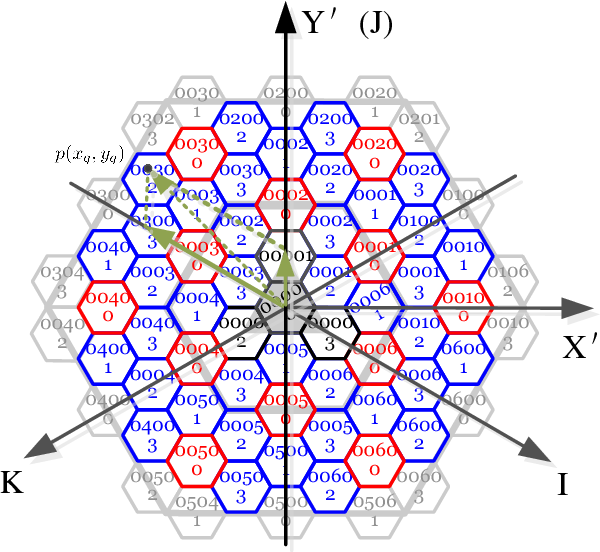
The visualization and analysis of geographic data play a crucial role in various fields, including urban planning, market research, epidemiology, and environmental studies. While traditional geographic representations often utilize square grids or latitude-longitude coordinates, an alternative approach – mapping zip codes to a hexagonal grid – offers several advantages. This method provides a unique perspective on spatial data, enabling more efficient analysis and visualization, particularly for applications where geographic proximity and spatial relationships are paramount.
Understanding the Hex Grid
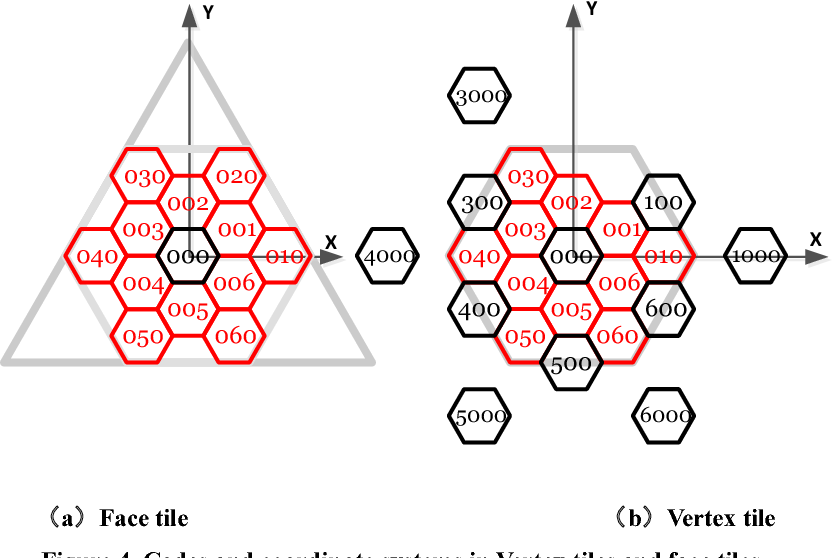
A hexagonal grid, also known as a honeycomb grid, is a geometric arrangement of hexagons that tessellate – meaning they fit together seamlessly without gaps or overlaps – to cover a plane. This structure offers several benefits over traditional square grids:
- Uniformity: Hexagons provide a consistent and symmetrical shape, ensuring that each cell within the grid has the same area and perimeter. This uniformity simplifies analysis and reduces the impact of edge effects, which can occur in square grids where cells at the edges are smaller than those in the center.
- Spatial Proximity: Hexagons possess a unique property where every cell shares a side with its six neighboring cells, facilitating the analysis of spatial relationships and proximity. This is particularly valuable for applications where geographic proximity is a key factor, such as analyzing disease spread or evaluating the impact of local businesses.
- Efficient Data Storage: The hexagonal grid’s efficient packing structure minimizes the amount of data required to represent a given area, leading to reduced storage requirements and faster processing times.
Mapping Zip Codes to a Hex Grid: The Process
Mapping zip codes to a hexagonal grid involves a series of steps that transform raw zip code data into a spatially meaningful representation. The process typically involves:
- Defining the Grid: First, a hexagonal grid is superimposed over the geographic area of interest. The size and density of the hexagons are determined based on the scale of analysis and the desired level of detail.
- Geocoding Zip Codes: Each zip code is assigned a geographic centroid, which represents the center point of the geographic area associated with that zip code. This process can be achieved using various geocoding services or databases.
- Assigning Zip Codes to Hexagons: Once the zip code centroids are determined, each centroid is assigned to the hexagon within the grid that contains it. This process can involve simple geometric intersection calculations, ensuring that each zip code is associated with a single hexagon.
- Data Aggregation: Once zip codes are assigned to hexagons, data associated with each zip code, such as population, demographics, or economic indicators, can be aggregated to the hexagon level. This allows for the analysis of spatial patterns and relationships within the grid.
Benefits of Mapping Zip Codes to a Hex Grid
The transformation of zip code data into a hexagonal grid provides several benefits, particularly for spatial analysis and visualization:
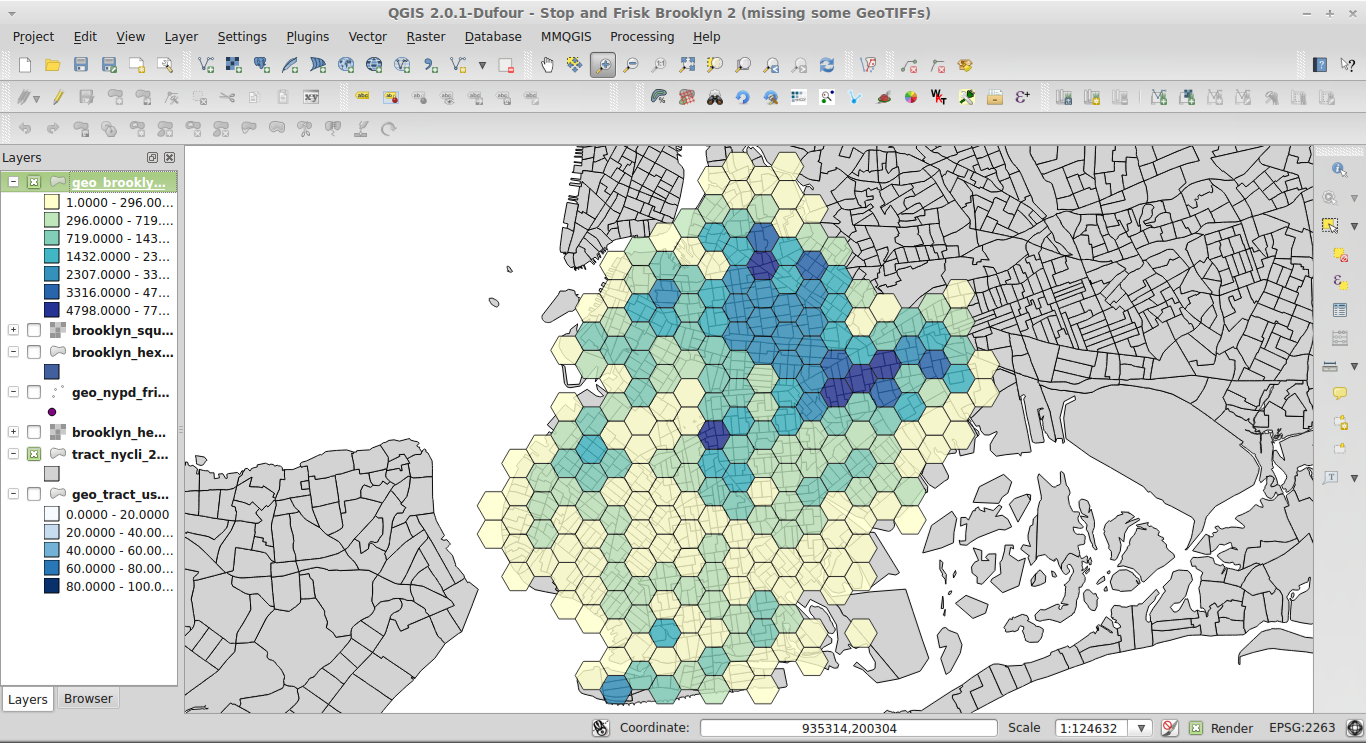
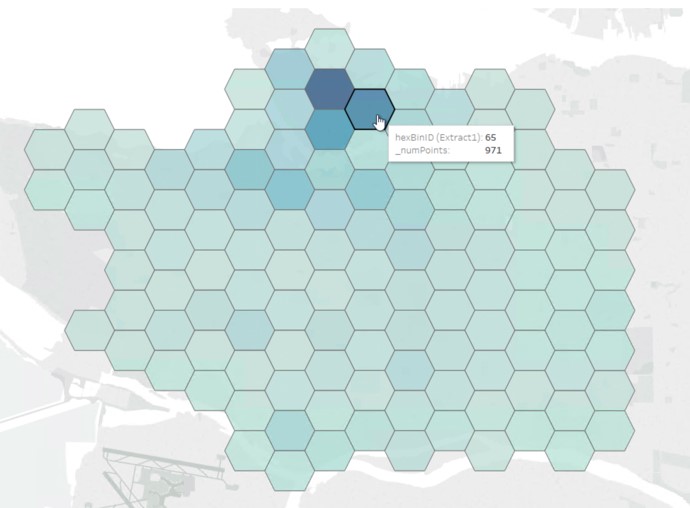
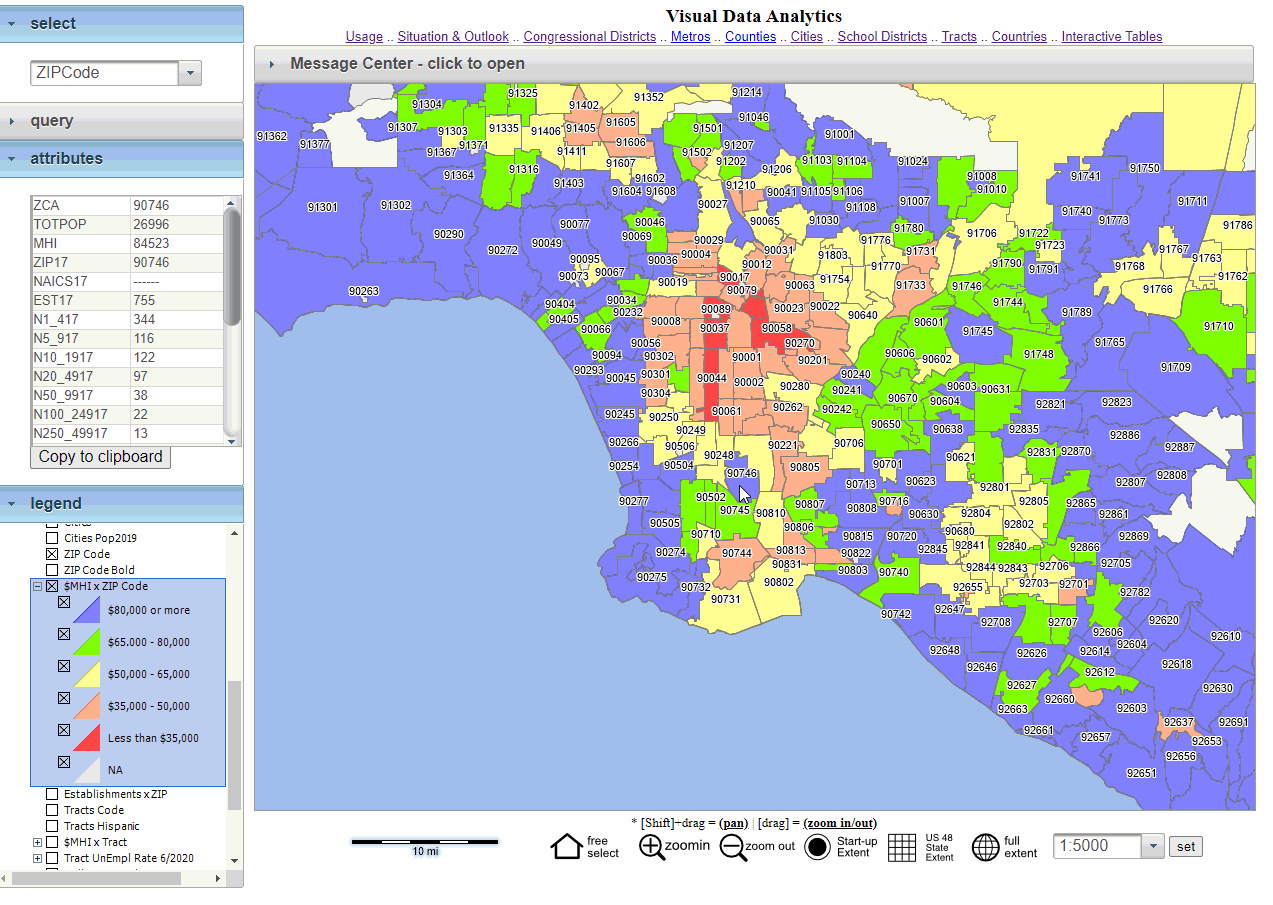
- Enhanced Visualization: Hexagonal grids offer a visually appealing and more informative representation of geographic data compared to traditional square grids. The uniform shape and consistent size of hexagons contribute to a clearer and more intuitive visualization of spatial patterns.
-
Improved Analysis: The hexagonal grid’s spatial proximity and uniformity facilitate more accurate and efficient analysis of geographic data. This is particularly beneficial for applications such as:
- Epidemiological Studies: Analyzing disease outbreaks and identifying areas with higher risk based on spatial proximity and population density.
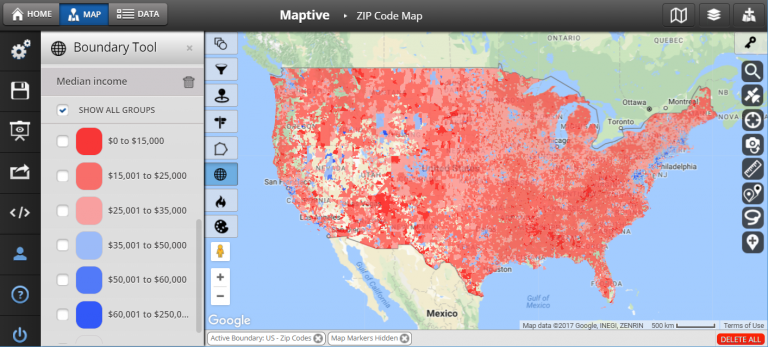
- Market Research: Understanding customer demographics and identifying areas with high potential for business growth based on spending patterns and market segmentation.
- Urban Planning: Identifying areas with high population density, transportation bottlenecks, and potential for development based on infrastructure and demographic data.
- Simplified Data Management: The hexagonal grid’s efficient packing structure reduces the amount of data required to represent a given area, leading to simplified data storage, faster processing times, and more efficient data management.
Challenges and Considerations
While mapping zip codes to a hexagonal grid offers significant advantages, certain challenges and considerations should be addressed:
- Data Accuracy: The accuracy of the analysis relies heavily on the quality of the geocoding process and the availability of accurate zip code centroids. Inaccurate or incomplete data can lead to misinterpretations and misleading results.
- Scale and Resolution: The size and density of the hexagons need to be carefully chosen based on the scale of analysis and the level of detail required. Too small hexagons may lead to excessive data fragmentation, while too large hexagons may obscure important spatial patterns.
- Data Aggregation: Aggregating data to the hexagon level can result in a loss of detail and potentially mask important local variations. It is crucial to balance the need for spatial aggregation with the preservation of individual data points.
FAQs
Q: What are the specific applications of mapping zip codes to a hex grid?
A: This technique finds applications in various fields, including:
- Urban planning: Analyzing population density, transportation patterns, and identifying areas for development.
- Public health: Tracking disease outbreaks and understanding the spread of infectious diseases.
- Market research: Identifying target markets, analyzing consumer behavior, and understanding spatial patterns in consumer spending.
- Environmental studies: Assessing environmental impact, understanding pollution patterns, and monitoring natural resource usage.
- Real estate analysis: Identifying areas with high property values, analyzing market trends, and predicting future property price changes.
Q: What are the advantages of using a hexagonal grid over a square grid?
A: Hexagonal grids offer several advantages over square grids:
- Uniformity: Hexagons have a consistent shape and size, leading to more uniform spatial analysis.
- Spatial Proximity: Each hexagon shares a side with six neighboring hexagons, facilitating the analysis of spatial relationships and proximity.
- Efficient Data Storage: Hexagonal grids require less data to represent a given area compared to square grids, leading to more efficient data management.
Q: What are the challenges associated with mapping zip codes to a hex grid?
A: The challenges include:
- Data Accuracy: The accuracy of the analysis depends on the quality of the geocoding process and the availability of accurate zip code centroids.
- Scale and Resolution: Choosing the appropriate hexagon size and density is crucial for accurate analysis and visualization.
- Data Aggregation: Aggregating data to the hexagon level can lead to a loss of detail and potentially mask local variations.
Tips for Mapping Zip Codes to a Hex Grid
- Choose the appropriate hexagon size and density: Consider the scale of analysis and the desired level of detail.
- Ensure accurate geocoding: Use reliable geocoding services or databases to obtain accurate zip code centroids.
- Address data quality issues: Identify and address any inaccuracies or missing data before mapping zip codes to the grid.
- Visualize data effectively: Utilize color gradients, size variations, and other visual elements to effectively represent data on the hexagonal grid.
Conclusion
Mapping zip codes to a hexagonal grid provides a powerful and versatile approach to visualizing and analyzing geographic data. The hexagonal grid’s unique properties, including its uniformity, spatial proximity, and efficient data storage, offer significant advantages over traditional square grids. By transforming zip code data into a spatially meaningful representation, this method enables more accurate and insightful analyses, supporting informed decision-making across various fields. While challenges associated with data accuracy and scale need to be carefully addressed, the benefits of mapping zip codes to a hexagonal grid outweigh the limitations, making it a valuable tool for spatial analysis and visualization.

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Transforming Geographic Data: Mapping Zip Codes to a Hex Grid. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!