The Significance of Wyoming’s Snowpack in 2024: A Vital Resource for the State
Related Articles: The Significance of Wyoming’s Snowpack in 2024: A Vital Resource for the State
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Significance of Wyoming’s Snowpack in 2024: A Vital Resource for the State. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Significance of Wyoming’s Snowpack in 2024: A Vital Resource for the State
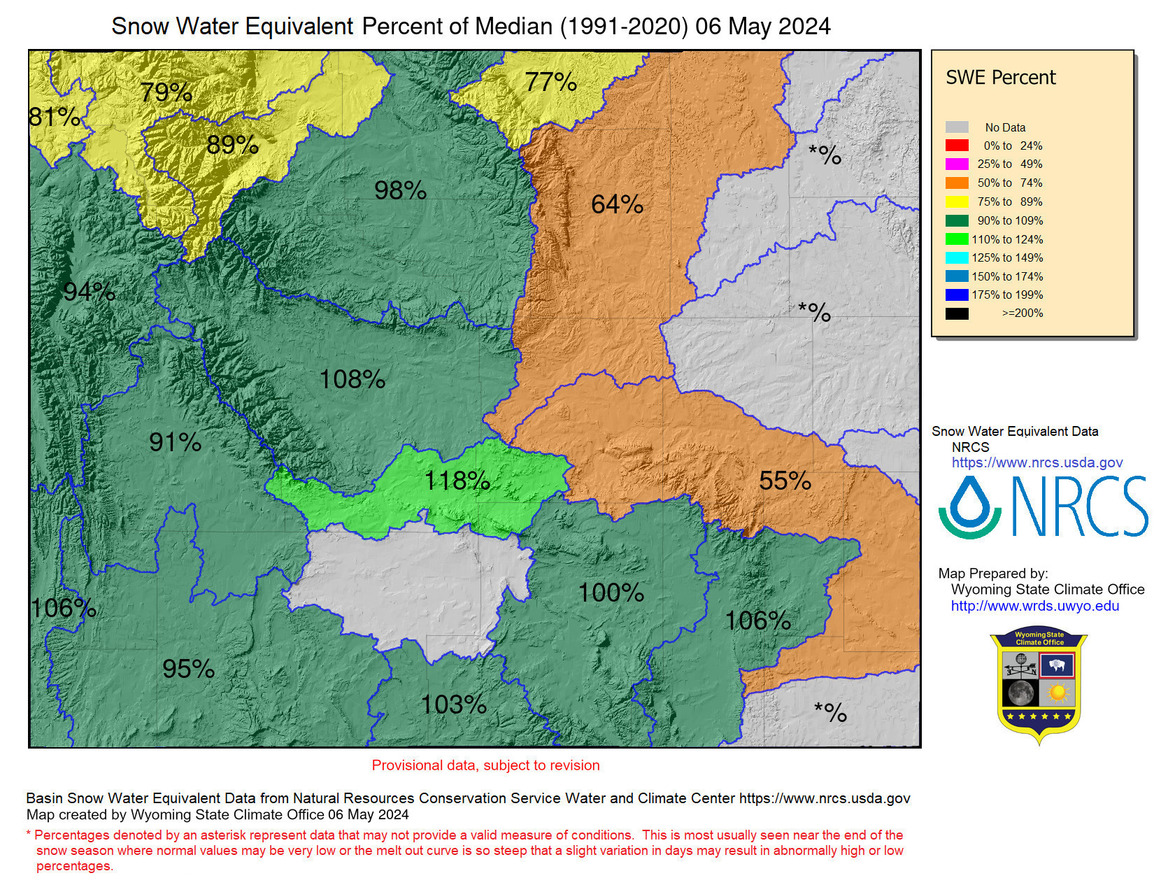
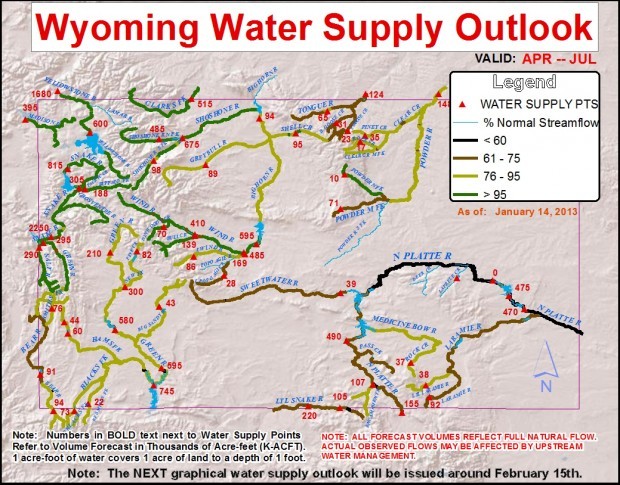
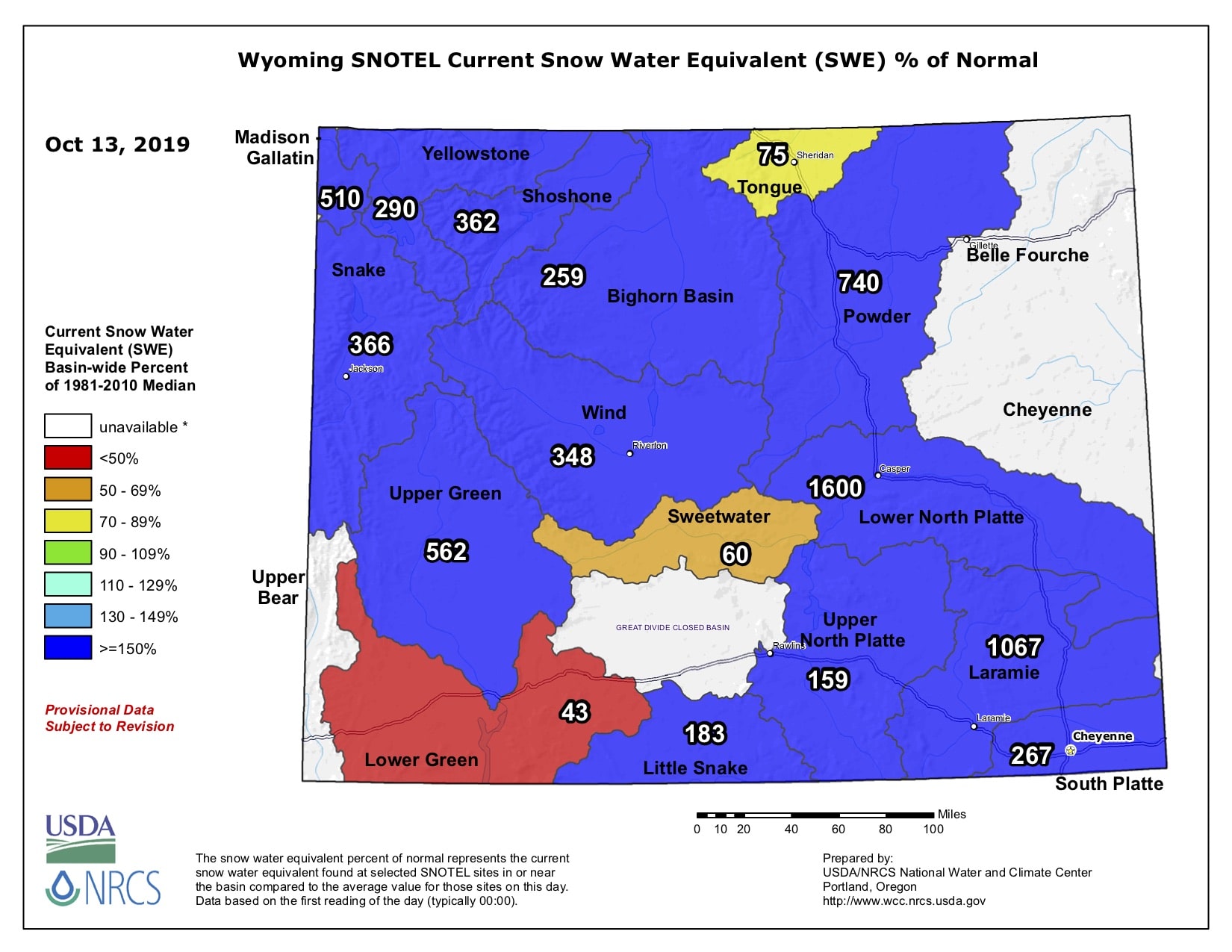
Wyoming, a state renowned for its rugged beauty and vast landscapes, relies heavily on a crucial resource: snowpack. This accumulation of snow in the mountains serves as a natural reservoir, providing water for a multitude of uses throughout the year. The Wyoming Snowpack 2024 Map, a visual representation of snowpack distribution and depth across the state, offers valuable insights into this essential resource and its implications for various sectors.
Understanding the Importance of Snowpack
Snowpack plays a pivotal role in Wyoming’s ecological and economic well-being. It acts as a natural water storage system, slowly releasing meltwater throughout the spring and summer months, replenishing rivers, streams, and groundwater aquifers. This water sustains diverse ecosystems, supports agriculture, provides drinking water for communities, and fuels hydropower generation.
The Wyoming Snowpack 2024 Map: A Visual Guide
The Wyoming Snowpack 2024 Map, typically published by the Natural Resources Conservation Service (NRCS), provides a detailed overview of snowpack conditions across the state. It uses a color-coded system to represent snow water equivalent (SWE), a measurement of the amount of water contained within the snowpack. The map highlights areas with high, average, and low SWE, allowing for a clear understanding of snowpack distribution and potential water availability.
Benefits of Monitoring Snowpack
Monitoring snowpack through maps like this provides several benefits:
- Water Resource Management: The map allows water managers to anticipate water availability for irrigation, municipal use, and hydropower generation. This enables them to make informed decisions regarding water allocation and conservation efforts.
- Agricultural Planning: Farmers and ranchers rely on snowmelt for irrigation. The map helps them plan planting schedules, adjust water usage, and prepare for potential water shortages.
- Flood Forecasting: In areas with heavy snowpack, the map can assist in predicting potential flood risks. This information allows communities to prepare for and mitigate potential flood damage.
- Ecosystem Health: Snowpack is crucial for maintaining healthy ecosystems, particularly in arid regions. The map assists in understanding the impact of snowpack variations on wildlife habitats and plant communities.
- Climate Change Research: Snowpack is sensitive to climate change, with variations in snowfall and melt patterns impacting water resources. The map provides valuable data for studying these changes and their implications.
Factors Influencing Snowpack
Snowpack accumulation and melt are influenced by various factors, including:
- Elevation: Higher elevations typically receive more snowfall and have deeper snowpacks.
- Latitude: Northern latitudes generally experience heavier snowfall than southern latitudes.
- Topography: Mountain ranges and valleys can significantly influence snow distribution.
- Climate Patterns: Weather patterns, such as El Niño and La Niña, can impact snowfall amounts and timing.
- Climate Change: Rising temperatures and altered precipitation patterns are impacting snowpack accumulation and melt rates.
Implications of Low Snowpack
Low snowpack can have severe consequences for Wyoming:
- Water Shortages: Reduced snowpack leads to lower water availability, potentially impacting agriculture, municipal water supplies, and hydropower production.
- Drought Conditions: Persistent low snowpack can contribute to drought conditions, impacting vegetation, wildlife, and human communities.
- Wildfire Risk: Dry vegetation resulting from low snowpack increases the risk of wildfires, potentially causing damage to ecosystems and property.
- Ecosystem Disruptions: Reduced snowpack can alter habitat conditions for wildlife, impacting populations and biodiversity.
- Economic Impacts: Water shortages can negatively impact industries reliant on water resources, such as agriculture, tourism, and energy production.
Addressing Snowpack Concerns
Addressing snowpack concerns requires a multi-faceted approach:
- Climate Change Mitigation: Reducing greenhouse gas emissions to slow climate change is crucial for preserving snowpack.
- Water Conservation: Implementing water-saving measures in agriculture, municipalities, and industries can reduce water demand.
- Sustainable Water Management: Developing and implementing water management plans that prioritize conservation and equitable distribution.
- Land Management Practices: Promoting sustainable land management practices to protect watersheds and improve snowpack accumulation.
- Public Awareness: Educating the public about the importance of snowpack and the need for responsible water use.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: How is snowpack measured?
A: Snowpack is typically measured using snow depth and snow water equivalent (SWE). Snow depth is the vertical distance from the ground to the snow surface. SWE represents the amount of water contained within the snowpack.
Q: How often is snowpack data collected?
A: Snowpack data is collected regularly throughout the winter and spring months. The NRCS operates a network of snow survey sites across Wyoming, where measurements are taken manually or using automated sensors.
Q: What is the role of the Natural Resources Conservation Service (NRCS) in snowpack monitoring?
A: The NRCS plays a vital role in snowpack monitoring and forecasting. They operate snow survey sites, collect data, and develop snowpack maps and reports. These resources provide valuable information for water resource management, agricultural planning, and disaster preparedness.
Q: How can I access the Wyoming Snowpack 2024 Map?
A: The Wyoming Snowpack 2024 Map is typically available on the NRCS website, along with other snowpack data and resources.
Tips for Water Conservation
- Water your lawn efficiently: Use a watering timer to avoid overwatering. Water early in the morning to minimize evaporation.
- Fix leaks promptly: Even small leaks can waste significant amounts of water.
- Install low-flow showerheads and faucets: These fixtures can reduce water consumption without compromising performance.
- Use a rain barrel: Collect rainwater for watering plants and lawns.
- Choose drought-tolerant plants: Opt for plants that require less water.
Conclusion
Wyoming’s snowpack is a vital resource, providing water for multiple uses and sustaining the state’s economy and environment. The Wyoming Snowpack 2024 Map provides valuable information for understanding snowpack conditions and their implications. By monitoring snowpack, promoting water conservation, and addressing climate change, Wyoming can ensure the long-term sustainability of this crucial resource for future generations.

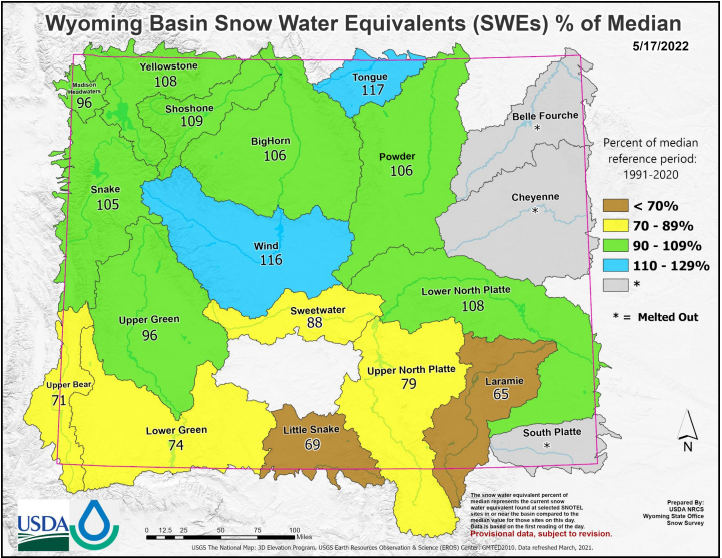

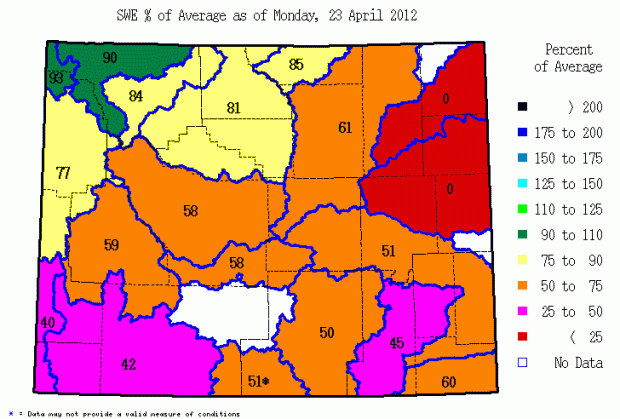
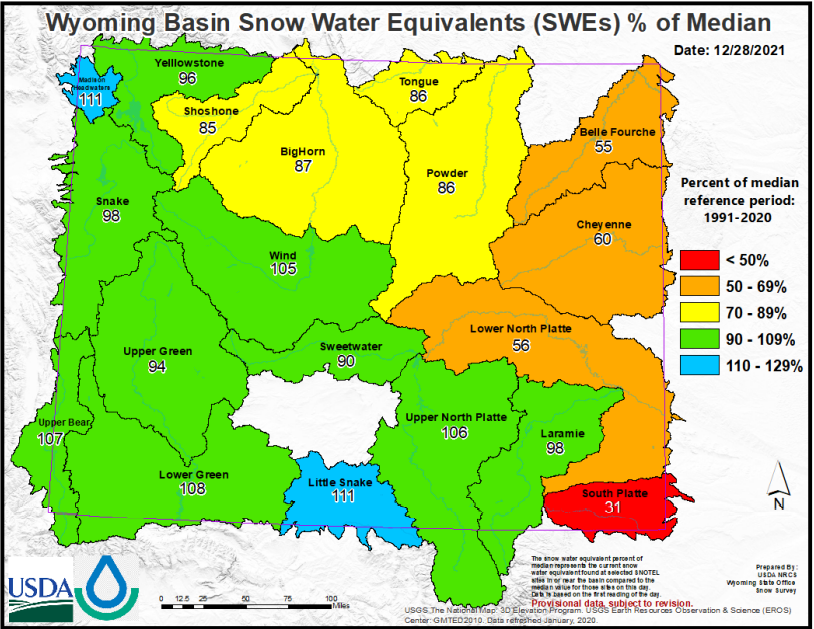

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Significance of Wyoming’s Snowpack in 2024: A Vital Resource for the State. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!