The Shifting Landscape of Communism: A Map of the Cold War
Related Articles: The Shifting Landscape of Communism: A Map of the Cold War
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Shifting Landscape of Communism: A Map of the Cold War. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Shifting Landscape of Communism: A Map of the Cold War
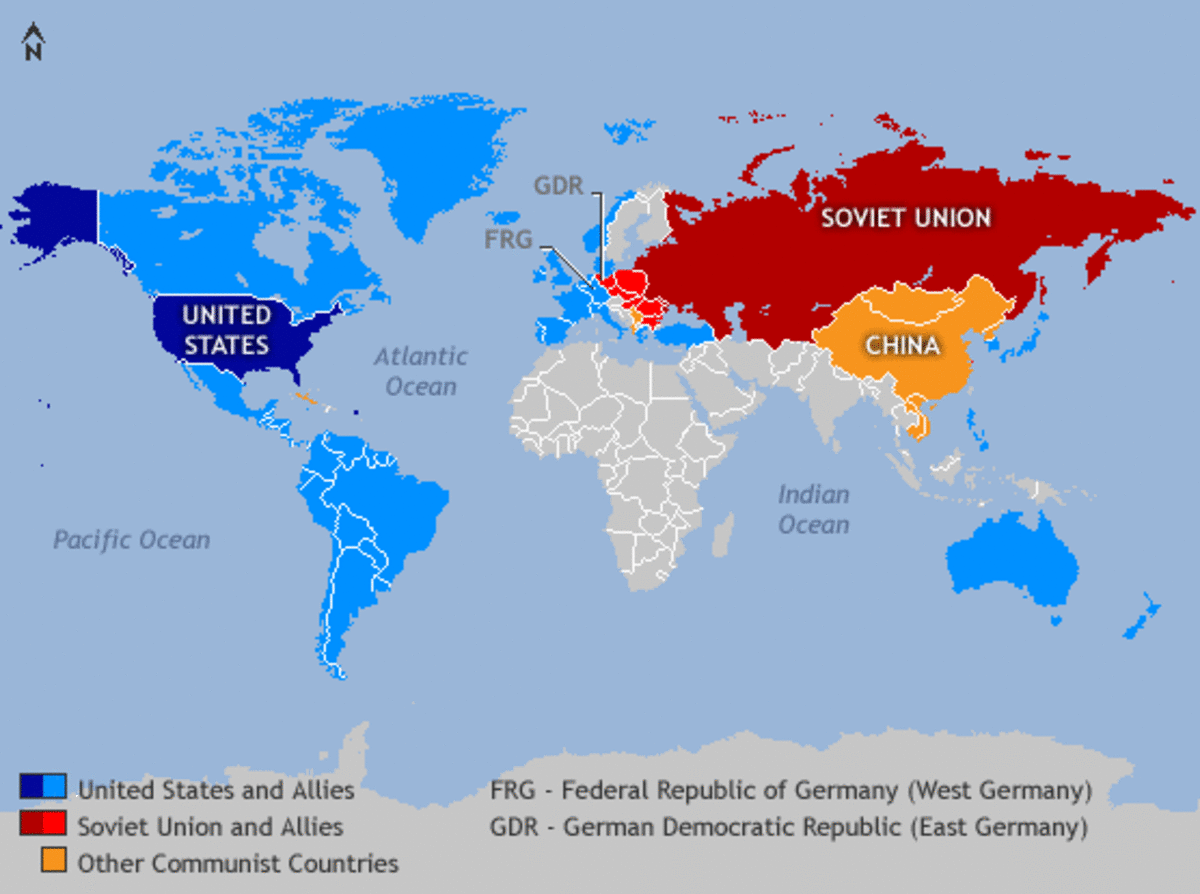
The Cold War, a period of geopolitical tension between the United States and the Soviet Union, was characterized by a stark ideological divide: capitalism versus communism. This division was reflected in the geographical distribution of communist regimes, which fluctuated throughout the Cold War, leaving a lasting impact on the world map.
Understanding the Map:
The map of communist countries during the Cold War reveals a complex and dynamic picture. It is not a static image but rather a constantly evolving landscape, shaped by political upheavals, revolutions, and ideological shifts.
-
The Core: The Soviet Union, the birthplace of communism, served as the heart of the communist bloc. Its vast territory, spanning Eastern Europe and Central Asia, formed the foundation of the communist world.
-
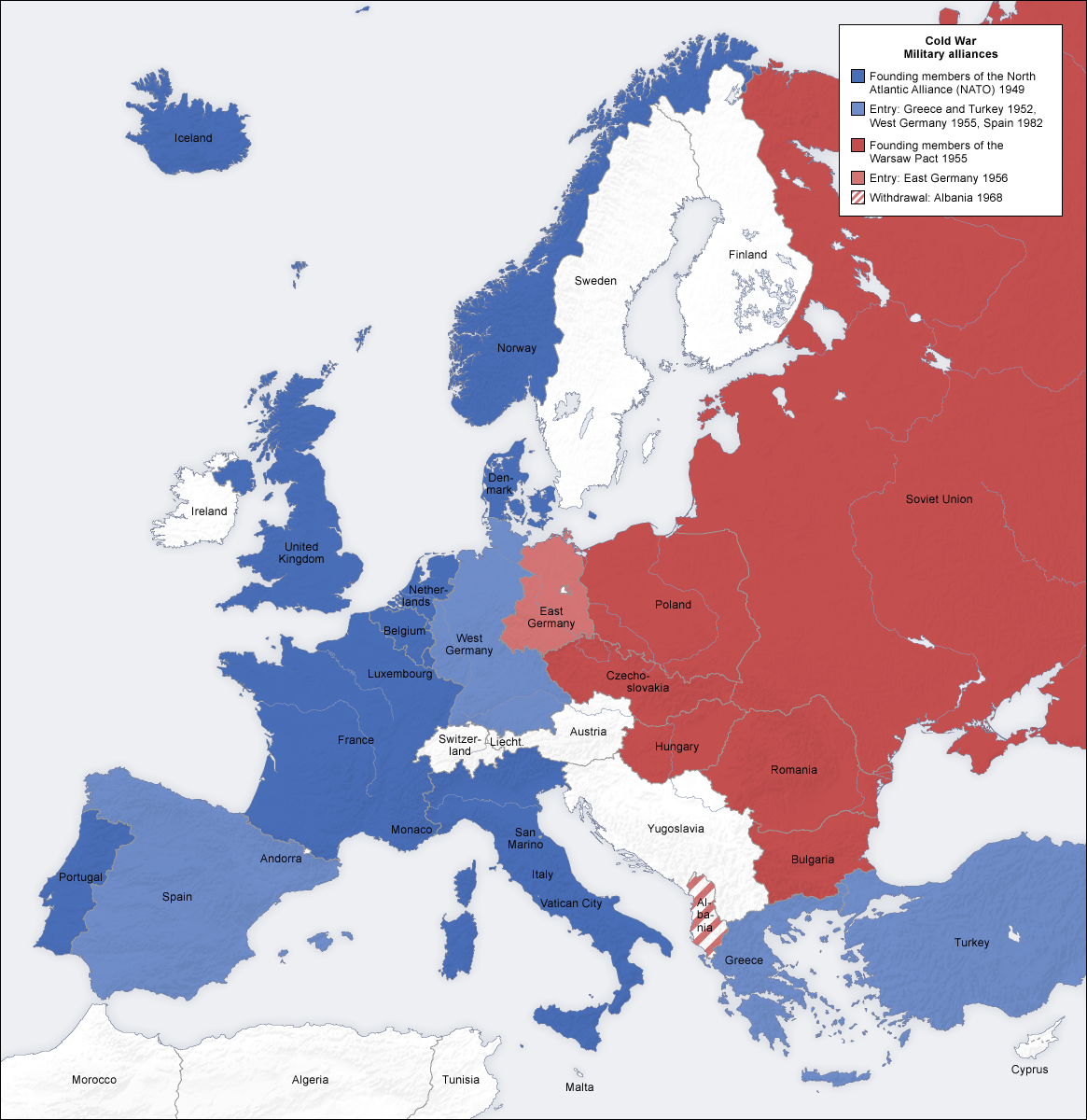
The Satellites: A constellation of Eastern European nations, including Poland, East Germany, Czechoslovakia, Hungary, Romania, and Bulgaria, fell under Soviet influence following World War II. These countries, often referred to as "satellite states," were tightly integrated into the Soviet system through political and economic control.
-
Expansion and Contraction: The communist map expanded beyond Europe. In Asia, China, Vietnam, Laos, North Korea, and Mongolia embraced communist ideologies. Cuba, under the leadership of Fidel Castro, became a communist stronghold in the Caribbean.
-
The Breakaway: While the map initially expanded, it later witnessed significant contractions. The collapse of the Soviet Union in 1991 triggered a domino effect, leading to the dismantling of communist regimes in Eastern Europe. This dramatic shift marked the end of the Cold War and reshaped the global political landscape.
The Significance of the Map:
The map of communist countries during the Cold War is more than a mere geographical representation. It symbolizes the power dynamics, ideological conflicts, and geopolitical tensions that defined the era.
-
The Iron Curtain: The division of Europe into communist and non-communist blocs, symbolized by the "Iron Curtain" metaphor coined by Winston Churchill, marked a profound geopolitical divide. This division was not only physical but also ideological, shaping international relations and global alliances.
-
The Proxy Wars: The map highlights the theaters of proxy wars, where the superpowers supported opposing sides in conflicts around the globe. From Korea to Vietnam, the Cold War played out in these proxy battles, fueled by ideological and geopolitical rivalry.
-
The Arms Race: The map reflects the escalating arms race between the US and the USSR. Both sides invested heavily in nuclear weapons and military technology, creating a climate of fear and uncertainty.
-
The Global Impact: The map demonstrates the global reach of the Cold War. The ideological struggle between communism and capitalism extended beyond Europe, influencing political developments in Africa, Latin America, and Asia.
FAQs about the Map of Communist Countries during the Cold War:
-
What countries were communist during the Cold War? The communist bloc during the Cold War included the Soviet Union, Eastern European satellite states, China, Vietnam, Laos, North Korea, Mongolia, and Cuba.
-
Why did some countries become communist? Various factors contributed to the rise of communism in different countries. These included:
- Economic inequalities: The appeal of communist ideology was strong in countries grappling with poverty, unemployment, and economic disparity.
- Social unrest: Revolutions and uprisings often provided fertile ground for communist movements to gain momentum.
- Soviet influence: The Soviet Union actively supported communist movements in various countries, providing financial and military aid.
-
How did the Cold War end? The Cold War ended with the collapse of the Soviet Union in 1991. A combination of factors contributed to the Soviet Union’s demise, including:
- Economic stagnation: The Soviet economic system proved unsustainable, unable to keep pace with the West’s technological advancements.
- Internal dissent: Growing discontent with the Soviet regime led to widespread protests and calls for reform.
- The Berlin Wall: The fall of the Berlin Wall in 1989 symbolized the crumbling of communist control in Eastern Europe and signaled the end of the Cold War.
-
What are the lasting legacies of the Cold War? The Cold War left a lasting impact on the global political landscape. Its legacies include:
- The Nuclear Threat: The arms race left a legacy of nuclear proliferation and the enduring threat of nuclear war.
- The End of the Bipolar World: The collapse of the Soviet Union marked the end of the bipolar world order and ushered in a new era of multipolarity.
- The Rise of New Powers: The Cold War’s end paved the way for the emergence of new global powers, such as China and India.
Tips for Studying the Map of Communist Countries During the Cold War:
-
Historical Context: Understanding the historical context of the Cold War is crucial for interpreting the map. Explore the events that led to the rise of communism, the ideological clash between capitalism and communism, and the key figures involved.
-
Geopolitical Analysis: Examine the map from a geopolitical perspective. Consider the strategic locations of communist countries, their alliances, and their influence on global power dynamics.
-
The Human Element: Remember that the map represents real people and their lives. Explore the experiences of individuals living under communist regimes, their struggles, and their hopes for change.
Conclusion:
The map of communist countries during the Cold War is a powerful visual representation of a complex and turbulent period in world history. It encapsulates the ideological clashes, geopolitical tensions, and human stories that shaped the 20th century. By studying the map, we gain a deeper understanding of the Cold War’s significance, its lasting impact on the global political landscape, and the lessons learned from this pivotal era.
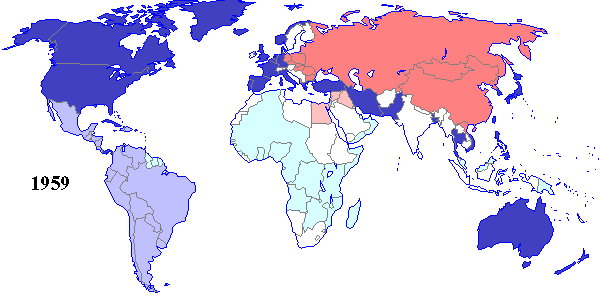



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Shifting Landscape of Communism: A Map of the Cold War. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!