The Intersection of the World: Exploring the Significance of the Prime Meridian and the Equator
Related Articles: The Intersection of the World: Exploring the Significance of the Prime Meridian and the Equator
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Intersection of the World: Exploring the Significance of the Prime Meridian and the Equator. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Intersection of the World: Exploring the Significance of the Prime Meridian and the Equator
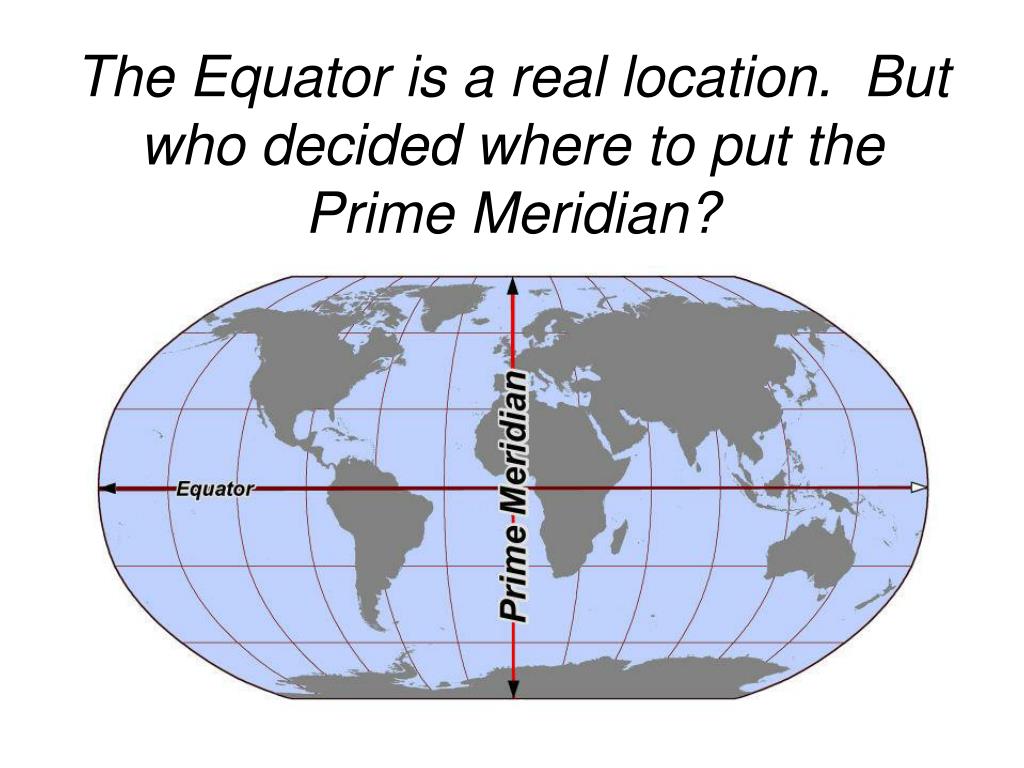
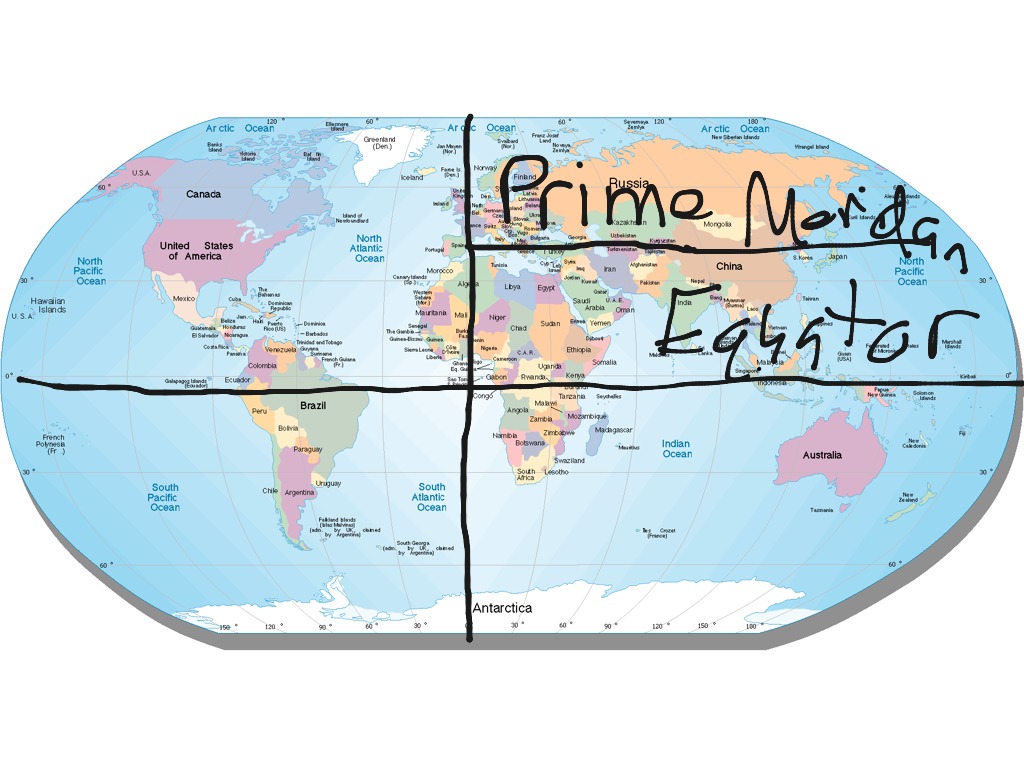
The Earth, a vast and intricate sphere, is divided into an invisible grid of lines, a framework that allows us to pinpoint any location on its surface. At the heart of this grid lies a unique point, the intersection of two fundamental lines: the prime meridian and the equator. While this point, often referred to as the "zero point" of the Earth’s coordinate system, may appear unremarkable on a map, its significance extends far beyond its seemingly simple location.
The Prime Meridian: Defining the Starting Point
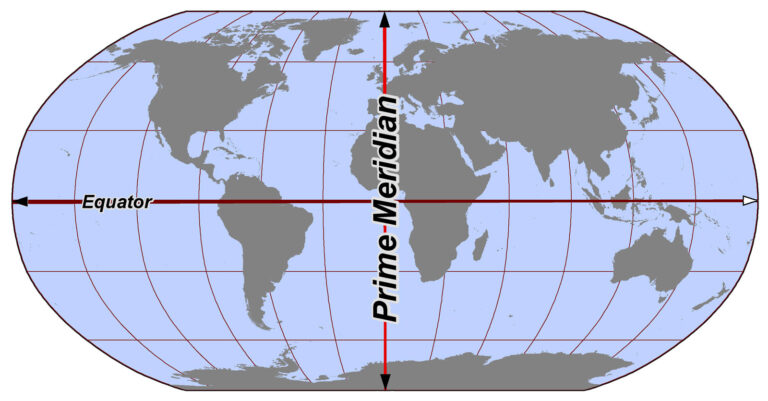
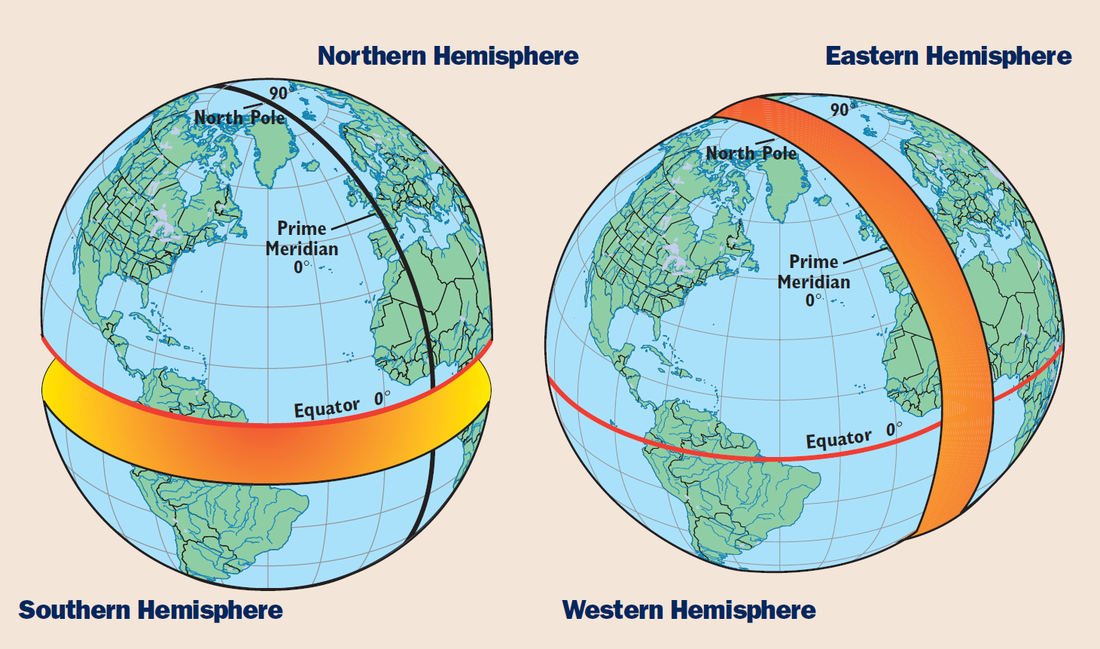
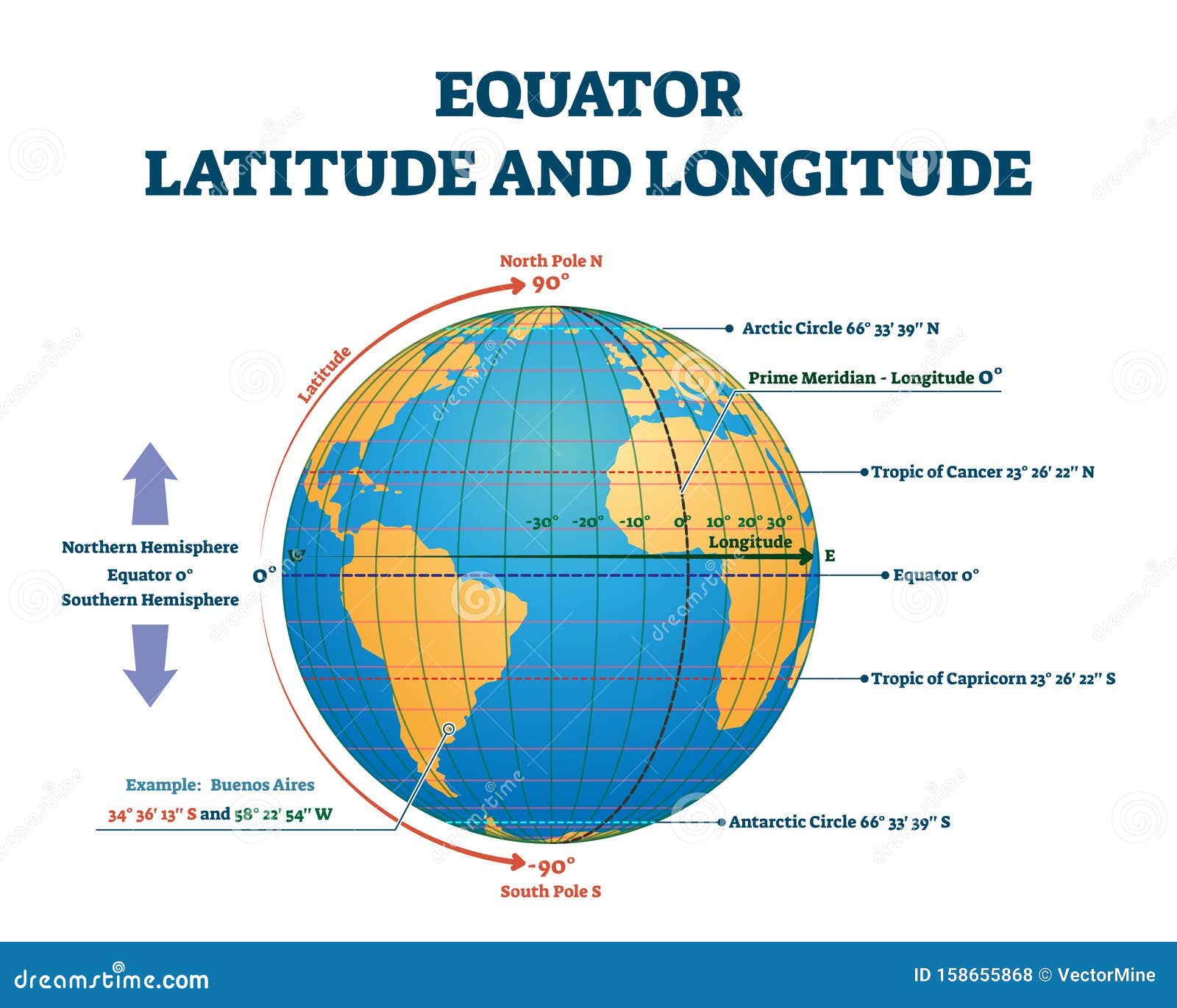
The prime meridian, an imaginary line that runs from the North Pole to the South Pole, serves as the zero point for measuring longitude. It divides the Earth into the Eastern and Western Hemispheres, with locations east of the prime meridian having positive longitudes and locations west of it having negative longitudes.
The choice of the prime meridian was not arbitrary. Initially, various countries used different meridians as their reference point. However, in 1884, an international conference established the Greenwich meridian, passing through the Royal Observatory in Greenwich, England, as the standard prime meridian. This decision, adopted by most countries, unified the global system of longitude measurement and facilitated international communication and navigation.
The Equator: Dividing the Earth into Hemispheres
The equator, an imaginary circle that encircles the Earth at zero degrees latitude, divides the Earth into the Northern and Southern Hemispheres. Locations north of the equator have positive latitudes, while those south of it have negative latitudes.
The equator is not just a geographical boundary; it holds significant meteorological and ecological importance. Due to its position, the equator receives the most direct sunlight throughout the year, resulting in consistently warm temperatures and heavy rainfall. This unique climate fosters diverse ecosystems, from lush rainforests to vibrant coral reefs, making the region a biodiversity hotspot.
The Intersection: A Point of Convergence
The intersection of the prime meridian and the equator, the point where longitude and latitude are both zero, is a symbolic location. It marks the convergence of the two fundamental lines that define our planet’s coordinate system, representing a point of origin for the global grid.
While this point is not marked by any physical landmark, its significance lies in its abstract representation. It serves as a reference point for mapping the Earth’s surface, enabling us to locate any place with precision. This point also holds symbolic value, representing the interconnectedness of all locations on Earth and the shared human experience of inhabiting this planet.
The Evolution of Mapping: From Ancient Observations to Modern Technology
The concept of latitude and longitude, and the importance of defining a zero point, have been recognized for centuries. Ancient civilizations, including the Greeks and the Romans, developed rudimentary systems for mapping the Earth, relying on observations of celestial bodies and the position of the sun.
Over time, advancements in technology, particularly the invention of the telescope and the development of more precise instruments, led to more accurate measurements of latitude and longitude. The invention of the chronometer, a highly accurate clock, revolutionized maritime navigation, allowing sailors to determine their longitude with greater precision.
Today, we rely on satellite technology and advanced mapping systems, like Google Maps, to provide real-time location data and detailed maps of the Earth. These tools, powered by complex algorithms and vast datasets, have transformed our understanding of the world, enabling us to navigate, explore, and connect with each other in unprecedented ways.
Exploring the Intersection: A Digital Journey
While the intersection of the prime meridian and the equator is a theoretical point, it can be visualized and explored using digital tools. Google Maps, a widely used mapping platform, allows users to zoom into the Earth’s surface and pinpoint the exact location where latitude and longitude are zero.
This digital representation, while not a physical landmark, provides a tangible connection to the abstract concept of the Earth’s coordinate system. It allows us to visualize the convergence of the prime meridian and the equator, gaining a deeper understanding of how this point serves as the foundation for mapping and understanding the world.
Beyond the Intersection: The Importance of Geographic Data
The significance of the intersection of the prime meridian and the equator extends beyond its symbolic representation. The ability to accurately measure latitude and longitude is fundamental to a wide range of activities, including:
- Navigation: Accurate location data is essential for navigation, enabling ships, aircraft, and vehicles to travel efficiently and safely.
- Mapping: Latitude and longitude data are used to create maps, providing visual representations of the Earth’s surface and its features.
- Weather forecasting: Weather patterns are influenced by latitude and longitude, and accurate location data is crucial for predicting and monitoring weather events.
- Environmental monitoring: Satellite imagery and geographic data are used to monitor environmental changes, such as deforestation, pollution, and climate change.
- Resource management: Geographic data is used to manage natural resources, such as water, forests, and minerals.
FAQs: Unraveling the Mysteries of the Intersection
Q: Is there any physical landmark at the intersection of the prime meridian and the equator?
A: The intersection of the prime meridian and the equator is a theoretical point, not marked by any physical landmark. It is a virtual location that serves as the origin of the Earth’s coordinate system.
Q: Why is the prime meridian located at Greenwich, England?
A: The Greenwich meridian was chosen as the standard prime meridian in 1884 at an international conference. The Royal Observatory in Greenwich, England, was a prominent astronomical institution at the time, and its meridian was already used as a reference point by many countries.
Q: Can you visit the intersection of the prime meridian and the equator?
A: While the intersection is a theoretical point, you can visit locations near it. For example, the Equator Monument in Quito, Ecuador, is located close to the equator, and the Greenwich Observatory in London, England, is located on the prime meridian.
Q: What is the importance of the equator in terms of climate and ecology?
A: The equator receives the most direct sunlight throughout the year, resulting in consistently warm temperatures and heavy rainfall. This unique climate fosters diverse ecosystems, making the region a biodiversity hotspot.
Q: How has technology impacted our understanding of latitude and longitude?
A: Advancements in technology, from the invention of the telescope to the development of satellite systems, have enabled us to measure latitude and longitude with greater accuracy, leading to more precise maps and a deeper understanding of the Earth’s geography.
Tips for Understanding the Intersection
- Use digital tools like Google Maps to visualize the intersection of the prime meridian and the equator.
- Explore locations near the equator and the prime meridian to gain a physical understanding of these lines.
- Research the history of mapping and the development of latitude and longitude measurements.
- Consider the impact of geographic data on various fields, such as navigation, weather forecasting, and environmental monitoring.
Conclusion: A Point of Reference, a Symbol of Interconnectedness
The intersection of the prime meridian and the equator, while a theoretical point, holds immense significance in our understanding of the Earth. It serves as a reference point for mapping and navigating our planet, reminding us of the interconnectedness of all locations and the shared human experience of inhabiting this sphere.
As technology continues to advance, our ability to measure and understand latitude and longitude will continue to evolve, providing us with increasingly precise and detailed maps of our world. The intersection of the prime meridian and the equator will remain a fundamental point of reference, a symbol of the Earth’s coordinate system and the intricate web of connections that unite us all.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Intersection of the World: Exploring the Significance of the Prime Meridian and the Equator. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!