The Geopolitical Landscape of Ukraine and Russia: A Complex Relationship
Related Articles: The Geopolitical Landscape of Ukraine and Russia: A Complex Relationship
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Geopolitical Landscape of Ukraine and Russia: A Complex Relationship. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Geopolitical Landscape of Ukraine and Russia: A Complex Relationship
The relationship between Ukraine and Russia is a complex and multifaceted one, deeply rooted in shared history, culture, and geography. Understanding this relationship requires examining the historical context, the current political situation, and the implications for the broader global stage.
Historical Context: A Shared Past and a Contested Present
The historical ties between Ukraine and Russia are intertwined, stretching back centuries. Both nations emerged from the collapse of the Kievan Rus’ in the 11th century, a powerful Eastern Slavic state that spanned modern-day Ukraine, Russia, and Belarus. Over the centuries, both regions experienced periods of shared rule under various empires, including the Golden Horde, the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth, and the Russian Empire.
In the 20th century, Ukraine’s fate became intertwined with that of Russia through the Bolshevik Revolution and the subsequent establishment of the Soviet Union. Ukraine was incorporated into the Soviet republic, experiencing periods of forced collectivization, famine (Holodomor), and political repression. However, a distinct Ukrainian national identity persisted, fueled by cultural and linguistic differences from Russia.
The collapse of the Soviet Union in 1991 marked a pivotal moment in the relationship between Ukraine and Russia. Ukraine declared independence, choosing a path toward democratic reforms and closer ties with the West. This move was met with mixed reactions in Russia, which saw the loss of Ukraine as a major blow to its influence and prestige.
The Current Political Landscape: A Deepening Divide
Since independence, the relationship between Ukraine and Russia has been marked by a growing divide. This divide is fueled by a number of factors, including:
- Geopolitical Ambitions: Russia has consistently sought to maintain its influence over Ukraine, viewing it as a crucial buffer zone against the West. This ambition has been evident in Russia’s annexation of Crimea in 2014 and its support for separatist movements in eastern Ukraine.
- National Identity and Language: The question of national identity and language has been a contentious issue, with Russia promoting the idea of a shared "Russian world" that includes Ukraine. This narrative has been met with resistance from Ukraine, which seeks to assert its own distinct identity.
- Economic Dependence: Ukraine’s economy remains heavily reliant on Russia, particularly for energy supplies. This dependence has given Russia leverage in its dealings with Ukraine, creating a situation where Ukraine feels pressured to comply with Russian demands.
- Western Integration: Ukraine’s aspirations to join NATO and the European Union have been met with opposition from Russia, which views these moves as a threat to its security. This has created a situation where Ukraine is caught between the West and Russia, struggling to balance its interests.
The Implications for the Global Stage: A Regional and International Crisis
The conflict in Ukraine has far-reaching implications for the global stage. It has:
- Revived Cold War Tensions: The conflict has rekindled Cold War tensions between Russia and the West, leading to a new era of geopolitical confrontation. This has manifested in increased military spending, sanctions, and diplomatic tensions.
- Undermined International Security: The conflict has undermined the international security order, raising concerns about the effectiveness of existing institutions and the potential for further conflict.
- Exacerbated Global Energy Crisis: The conflict has exacerbated the global energy crisis, as Russia has weaponized its energy exports to exert pressure on Europe.
- Disrupted Global Supply Chains: The conflict has disrupted global supply chains, particularly for wheat and other agricultural products, leading to food shortages and rising prices.
FAQs
1. What is the historical basis for the conflict in Ukraine?
The conflict in Ukraine is rooted in a long history of tension between Russia and Ukraine, stemming from their shared past and divergent aspirations. Russia has long sought to maintain its influence over Ukraine, viewing it as a vital part of its sphere of influence. Ukraine, on the other hand, seeks to assert its independence and forge its own path, often aligning with the West.
2. What is the role of NATO in the conflict?
NATO’s role in the conflict is complex. Ukraine’s aspirations to join NATO have been a source of tension with Russia, which views it as a threat to its security. NATO has provided support to Ukraine in the form of military aid and training, but has stopped short of offering membership. The conflict has raised questions about NATO’s expansion and the effectiveness of its deterrence strategy.
3. What are the economic implications of the conflict?
The conflict has had a significant impact on the global economy, disrupting supply chains, increasing energy prices, and leading to economic instability in both Ukraine and Russia. The conflict has also strained relations between Russia and the West, leading to sanctions and counter-sanctions that have disrupted trade and investment flows.
4. What are the potential solutions to the conflict?
There are no easy solutions to the conflict in Ukraine. Any resolution would likely require a compromise from both sides, involving a commitment to dialogue, a de-escalation of tensions, and a willingness to address the underlying issues that have fueled the conflict.
Tips
- Stay Informed: It is crucial to stay informed about the conflict through reliable news sources and reputable think tanks.
- Engage in Critical Analysis: Be cautious of information from biased sources and strive to analyze information critically, considering multiple perspectives.
- Support Humanitarian Efforts: There are numerous organizations working to provide humanitarian aid to Ukraine. Consider supporting these efforts through donations or volunteering.
- Advocate for Peace: Raise awareness about the conflict and advocate for peaceful solutions through diplomatic channels.
Conclusion
The relationship between Ukraine and Russia is a complex and multifaceted one, marked by shared history, cultural ties, and deep political divisions. The ongoing conflict has had a profound impact on the region and the world, raising concerns about international security, economic stability, and the future of the global order. Understanding the historical context, the current political landscape, and the implications for the global stage is crucial for navigating this complex and challenging situation.




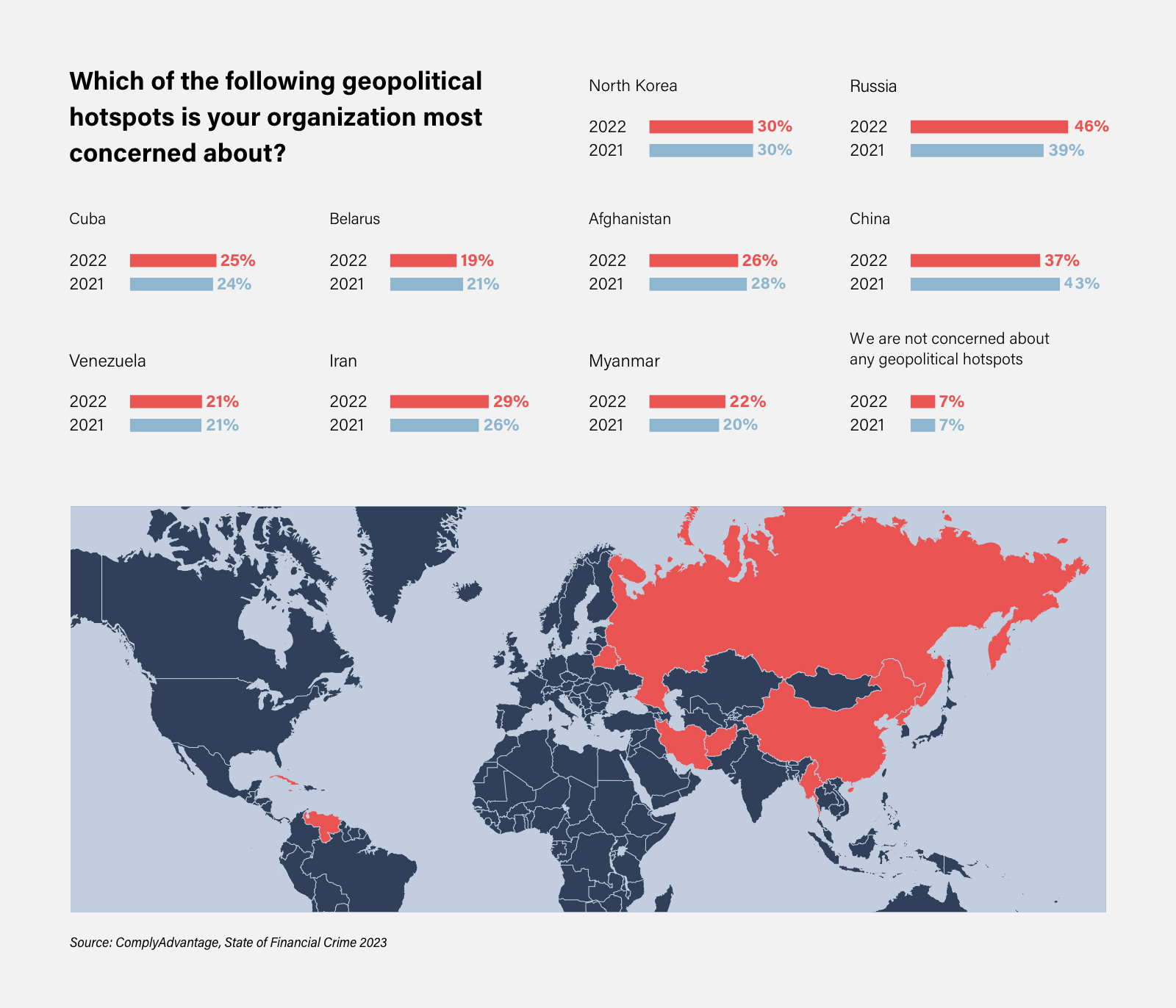
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Geopolitical Landscape of Ukraine and Russia: A Complex Relationship. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!