The Equator’s Embrace: A Journey Through Africa’s Diverse Landscapes
Related Articles: The Equator’s Embrace: A Journey Through Africa’s Diverse Landscapes
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Equator’s Embrace: A Journey Through Africa’s Diverse Landscapes. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Equator’s Embrace: A Journey Through Africa’s Diverse Landscapes

The equator, an imaginary line circling the Earth at zero degrees latitude, bisects the African continent, carving a path through a tapestry of diverse landscapes, cultures, and ecosystems. This invisible line, a marker of the Earth’s rotational axis, serves as a vital geographical reference point, highlighting the continent’s immense geographical and ecological diversity.
The Equator’s Path: A Cross-Section of Africa’s Geography
The equator’s journey across Africa begins in the west, touching the Atlantic coast in Gabon. From there, it cuts through the heart of the continent, traversing a diverse range of geographical features:
-
The Equatorial Rainforest: The equator’s passage through the Congo Basin, the world’s second largest rainforest, creates a vibrant and biodiverse ecosystem. This region, characterized by dense vegetation, heavy rainfall, and a rich tapestry of flora and fauna, serves as a vital carbon sink and a haven for numerous endangered species.
-
The Great Rift Valley: As the equator traverses eastwards, it intersects with the Great Rift Valley, a geological wonder stretching over 6,000 kilometers. This vast, fractured landscape is home to a diverse range of wildlife, including the iconic African Great Lakes and the towering volcanoes of Mount Kilimanjaro and Mount Kenya.
-
The Ethiopian Highlands: The equator’s journey continues through the Ethiopian Highlands, a plateau region characterized by rugged mountains, deep gorges, and fertile valleys. This area is known for its unique biodiversity, including endemic plant and animal species, and its rich cultural heritage.
-
The Somali Peninsula: Further east, the equator passes through the Somali Peninsula, a region marked by arid landscapes, rugged mountains, and a diverse cultural tapestry. This area is home to the world’s largest concentration of camels and is known for its unique Somali culture and traditions.
-
The Indian Ocean Coast: Finally, the equator reaches the Indian Ocean coast in Somalia, concluding its journey through Africa. This region is characterized by warm, tropical waters, pristine beaches, and a diverse marine ecosystem.
The Equator’s Influence: A Tapestry of Climate, Ecosystems, and Culture
The equator’s influence on Africa’s geography is profound, shaping the continent’s climate, ecosystems, and cultural landscapes.
-
Climate: The equator is a zone of intense solar radiation, resulting in high temperatures and consistent rainfall. This tropical climate supports the growth of lush rainforests, fertile agricultural lands, and diverse ecosystems.
-
Ecosystems: The equator’s passage through Africa creates a variety of ecosystems, ranging from dense rainforests to arid savannas, from fertile highlands to diverse coastal regions. This ecological diversity is a testament to the continent’s rich biodiversity and its unique geographical features.
-
Culture: The equator’s path through Africa intersects with a multitude of cultures, each with its own distinct traditions, languages, and beliefs. This cultural diversity is a reflection of the continent’s long history, its diverse population, and its unique geographical features.
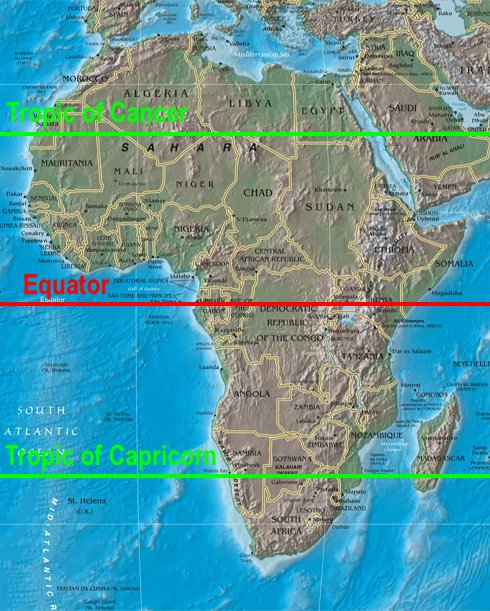
Understanding the Equator’s Significance: A Map as a Tool for Exploration
A map depicting the equator’s path through Africa serves as a powerful tool for understanding the continent’s geographical and cultural diversity. It provides a visual representation of the equator’s influence on the continent’s climate, ecosystems, and cultural landscapes.
-
Visualizing Geographic Diversity: The map highlights the equator’s passage through a variety of geographical features, including rainforests, mountains, valleys, and coastal regions. This visual representation helps to understand the continent’s diverse landscapes and their interconnectedness.
-
Understanding Climate Patterns: The map showcases the equator’s role in shaping Africa’s climate, highlighting the zones of high rainfall and consistent temperatures. This visual understanding aids in comprehending the continent’s climate patterns and their impact on ecosystems and human life.
-
Exploring Cultural Diversity: The map reveals the equator’s intersection with various cultures, showcasing the diversity of languages, traditions, and beliefs across the continent. This visual representation facilitates the exploration of Africa’s rich cultural heritage and its interconnectedness.
FAQs About the Equator’s Path Through Africa
1. Does the equator pass through any major cities in Africa?
The equator passes through several major cities in Africa, including:
- Mbandaka, Democratic Republic of Congo: A major river port and trading center in the Congo Basin.
- Kisumu, Kenya: A major city on the shores of Lake Victoria, known for its vibrant culture and its role as a regional economic hub.
- Kampala, Uganda: The capital city of Uganda, located on a hill overlooking Lake Victoria.
- Mombasa, Kenya: A major port city on the Indian Ocean coast, known for its historical significance and its vibrant culture.
2. What are some of the unique species found in the equatorial rainforests of Africa?
The equatorial rainforests of Africa are home to a remarkable array of unique species, including:
- Gorillas: Two species of gorillas, the western lowland gorilla and the eastern gorilla, are found in the rainforests of Central Africa.
- Chimpanzees: These highly intelligent primates are found in the rainforests of Central and West Africa.
- Okapis: Also known as the "forest giraffe," this elusive mammal is found only in the rainforests of the Democratic Republic of Congo.
- African Forest Elephants: These elephants are smaller than their savanna counterparts and are adapted to life in the rainforest.
3. What are some of the cultural traditions associated with the equator’s path through Africa?
The equator’s path through Africa intersects with a multitude of cultures, each with its own unique traditions and beliefs. Some examples include:
- The Maasai of East Africa: Known for their distinctive red clothing and their cattle-herding traditions.
- The Pygmies of Central Africa: A group of indigenous peoples known for their hunting and gathering lifestyle and their intimate connection to the rainforest.
- The Yoruba of West Africa: A large ethnic group known for their vibrant culture, their traditional music and dance, and their belief in the power of the ancestors.
Tips for Exploring the Equator’s Path Through Africa
- Plan your itinerary carefully: The equator’s path through Africa encompasses a vast area with diverse landscapes and climates. Plan your itinerary to maximize your exploration of the region’s unique features.
- Respect local cultures: Be mindful of local customs and traditions, and avoid behaviors that may be considered disrespectful.
- Pack appropriately: The climate along the equator’s path can be hot and humid, so pack lightweight, breathable clothing.
- Consider a guided tour: A guided tour can provide valuable insights into the region’s history, culture, and wildlife.
Conclusion: The Equator’s Journey Through Africa’s Heart
The equator’s journey through Africa is a testament to the continent’s immense geographical and cultural diversity. This invisible line, a marker of the Earth’s rotational axis, serves as a vital reference point, highlighting the continent’s rich biodiversity, its unique climate patterns, and its vibrant cultural tapestry. By studying the equator’s path through Africa, we gain a deeper understanding of the continent’s complex and fascinating history, its diverse ecosystems, and its rich cultural heritage.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Equator’s Embrace: A Journey Through Africa’s Diverse Landscapes. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!