The Equator: An Invisible Line Dividing the World
Related Articles: The Equator: An Invisible Line Dividing the World
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Equator: An Invisible Line Dividing the World. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: The Equator: An Invisible Line Dividing the World
- 2 Introduction
- 3 The Equator: An Invisible Line Dividing the World
- 3.1 The Significance of the Equator
- 3.2 Visualizing the Equator: The Importance of Maps
- 3.3 Beyond the Line: Exploring the Equator’s Influence
- 3.4 FAQs: Understanding the Equator
- 3.5 Tips: Exploring the Equator
- 3.6 Conclusion: The Equator – An Invisible Line with a Global Impact
- 4 Closure
The Equator: An Invisible Line Dividing the World

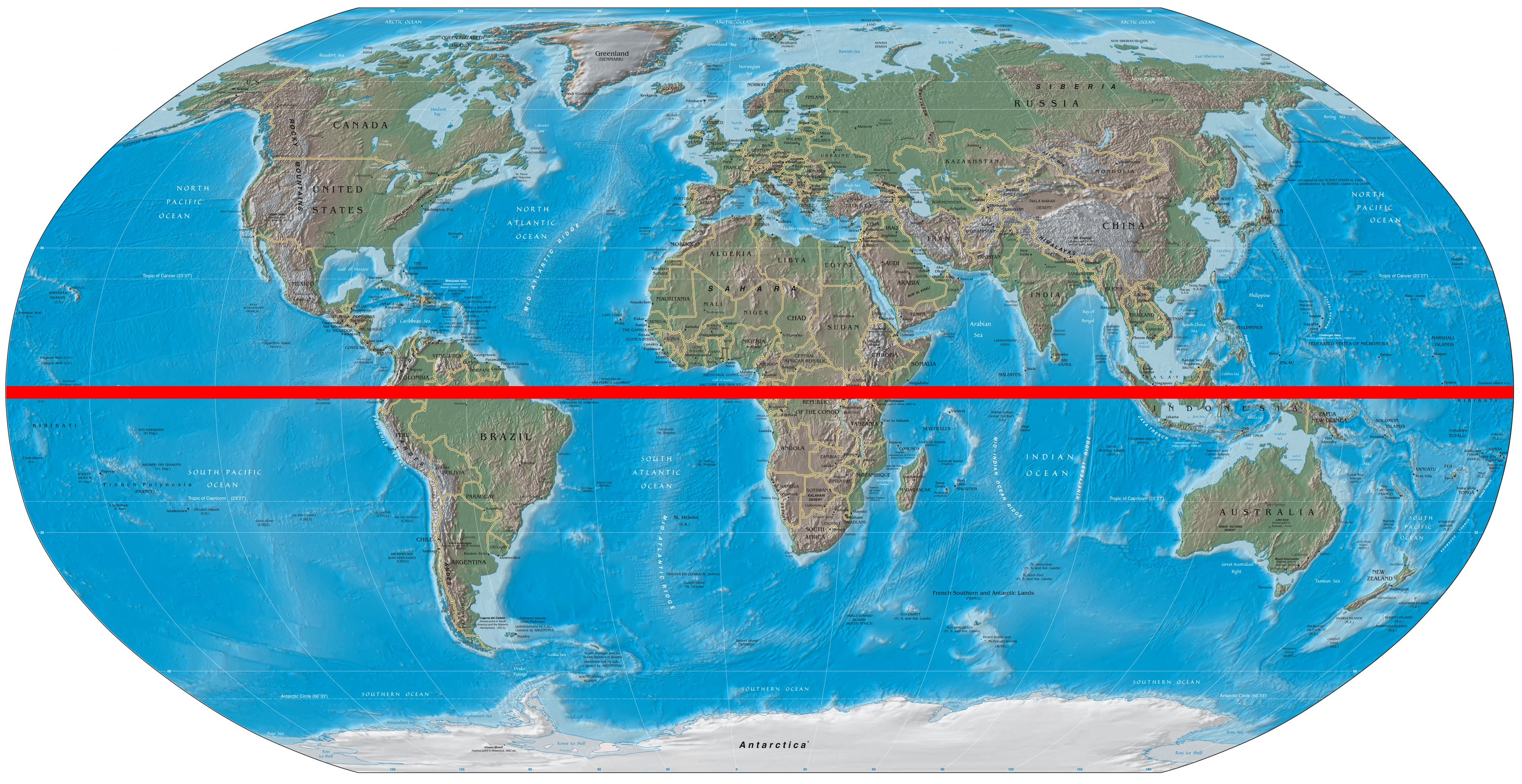
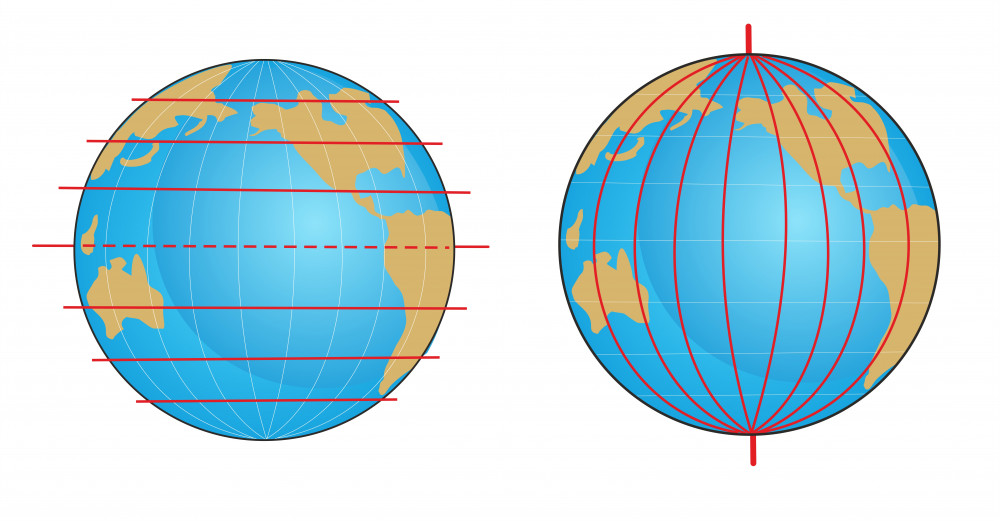
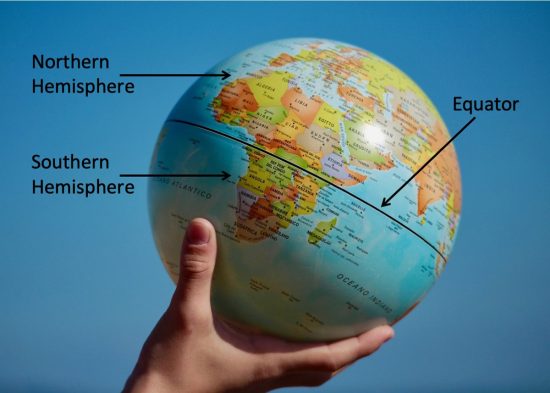
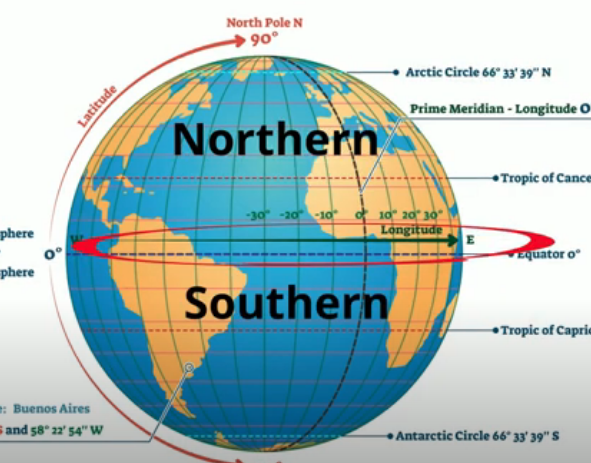
The Earth, a sphere suspended in the vastness of space, is a complex and dynamic entity. Its surface is marked by diverse landscapes, bustling cities, and expansive oceans. But beneath this visible tapestry lies an invisible line of immense significance: the Equator. This imaginary circle, equidistant from the North and South Poles, divides our planet into two hemispheres – the Northern and Southern Hemispheres. While invisible to the naked eye, the Equator plays a crucial role in shaping our world, influencing climate, geography, and even culture.
The Significance of the Equator
The Equator’s significance stems from its unique position on Earth. It is the only line of latitude that experiences equal day and night throughout the year. This occurs due to the Earth’s tilt, which causes the sun’s rays to strike the Equator directly at the solstices. This consistent exposure to sunlight results in the Equator being the warmest region on Earth, influencing its climate and vegetation.
The Equator’s influence on climate is profound. The intense sunlight and consistent temperatures create a tropical climate characterized by high humidity, abundant rainfall, and lush vegetation. This tropical climate supports a diverse array of flora and fauna, resulting in the vibrant biodiversity often associated with equatorial regions.
Beyond climate, the Equator also impacts the Earth’s geography. It acts as a dividing line between the Earth’s two hemispheres, marking the transition from the Northern Hemisphere’s clockwise rotation to the Southern Hemisphere’s counter-clockwise rotation. This distinction influences the direction of ocean currents, wind patterns, and even the movement of celestial bodies as observed from different parts of the globe.
Visualizing the Equator: The Importance of Maps
Understanding the Equator’s impact requires a visual representation. Maps, particularly world maps, serve as essential tools for visualizing this invisible line and its global influence. By incorporating the Equator as a prominent feature, maps allow us to understand its position relative to continents, oceans, and other geographical features.
The Equator’s presence on maps facilitates a deeper understanding of its significance:
- Global Perspective: Maps with the Equator clearly marked provide a global perspective, showcasing the Earth’s interconnectedness. They demonstrate how the Equator acts as a unifying element, connecting different continents and oceans.
- Climate Zones: The Equator’s presence on maps allows for the clear delineation of climate zones. Maps can highlight the tropical regions influenced by the Equator, contrasting them with the temperate and polar regions.
- Geographical Boundaries: Maps with the Equator clearly marked define geographical boundaries. They showcase the transition from the Northern Hemisphere to the Southern Hemisphere, highlighting the contrasting characteristics of each region.
- Navigation: The Equator serves as a crucial reference point for navigation. Sailors and pilots use it to determine their position and course, especially when navigating across large distances.
Beyond the Line: Exploring the Equator’s Influence
The Equator’s influence extends far beyond its geographical location. It shapes cultural practices, economic activities, and even political boundaries.
- Cultural Impact: The Equator’s tropical climate has shaped cultural practices in equatorial regions. Many cultures celebrate the Equator’s unique position with festivals and rituals, acknowledging its impact on their lives. The vibrant colors, music, and dance associated with equatorial cultures often reflect the region’s natural beauty and abundance.
- Economic Significance: The Equator’s fertile land and favorable climate support a thriving agricultural sector. Equatorial regions are known for producing a wide variety of crops, including coffee, cocoa, and rubber, contributing significantly to global trade. Furthermore, the Equator’s natural beauty attracts tourism, providing economic opportunities for local communities.
- Political Implications: The Equator’s position has influenced political boundaries. Many countries straddle the Equator, leading to complex political landscapes and unique challenges. The Equator’s significance in global affairs is undeniable, influencing international relations and diplomatic efforts.
FAQs: Understanding the Equator
1. What is the exact length of the Equator?
The Equator’s circumference is approximately 40,075 kilometers (24,901 miles).
2. Is the Equator a straight line?
No, the Equator is a circle that runs around the Earth, equidistant from the North and South Poles.
3. Why is the Equator important for climate?
The Equator receives the most direct sunlight, leading to consistently high temperatures and abundant rainfall, creating a tropical climate.
4. What are some of the major cities located on the Equator?
Major cities located on or near the Equator include Quito, Ecuador; Kampala, Uganda; and Macapa, Brazil.
5. Does the Equator pass through any countries?
Yes, the Equator passes through 13 countries: Ecuador, Colombia, Brazil, São Tomé and Príncipe, Gabon, Republic of the Congo, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Uganda, Kenya, Somalia, Indonesia, Kiribati, and the Maldives.
Tips: Exploring the Equator
- Visit an Equatorial Monument: Many countries have erected monuments marking the Equator’s position. Visiting these monuments provides a tangible understanding of the Equator’s significance.
- Observe the Sun’s Movement: The Equator experiences equal day and night throughout the year. Observe the sun’s movement and its impact on the length of day and night.
- Explore Equatorial Cultures: Learn about the unique cultural practices, traditions, and art forms influenced by the Equator’s tropical climate.
- Use Online Mapping Tools: Explore interactive online maps to visualize the Equator’s position and its impact on different regions of the world.
Conclusion: The Equator – An Invisible Line with a Global Impact
The Equator, though invisible, is a powerful force shaping our planet. Its unique position influences climate, geography, culture, and even politics. By understanding the Equator’s significance, we gain a deeper appreciation for the interconnectedness of our world and the intricate web of forces that shape our lives. As we navigate the complexities of our globalized world, recognizing the Equator’s influence provides a valuable framework for understanding the diverse challenges and opportunities that lie ahead.

/Latitude-and-Longitude-58b9d1f35f9b58af5ca889f1.jpg)


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Equator: An Invisible Line Dividing the World. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!