The Equator: A Line of Significance on the Global Map
Related Articles: The Equator: A Line of Significance on the Global Map
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Equator: A Line of Significance on the Global Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Equator: A Line of Significance on the Global Map

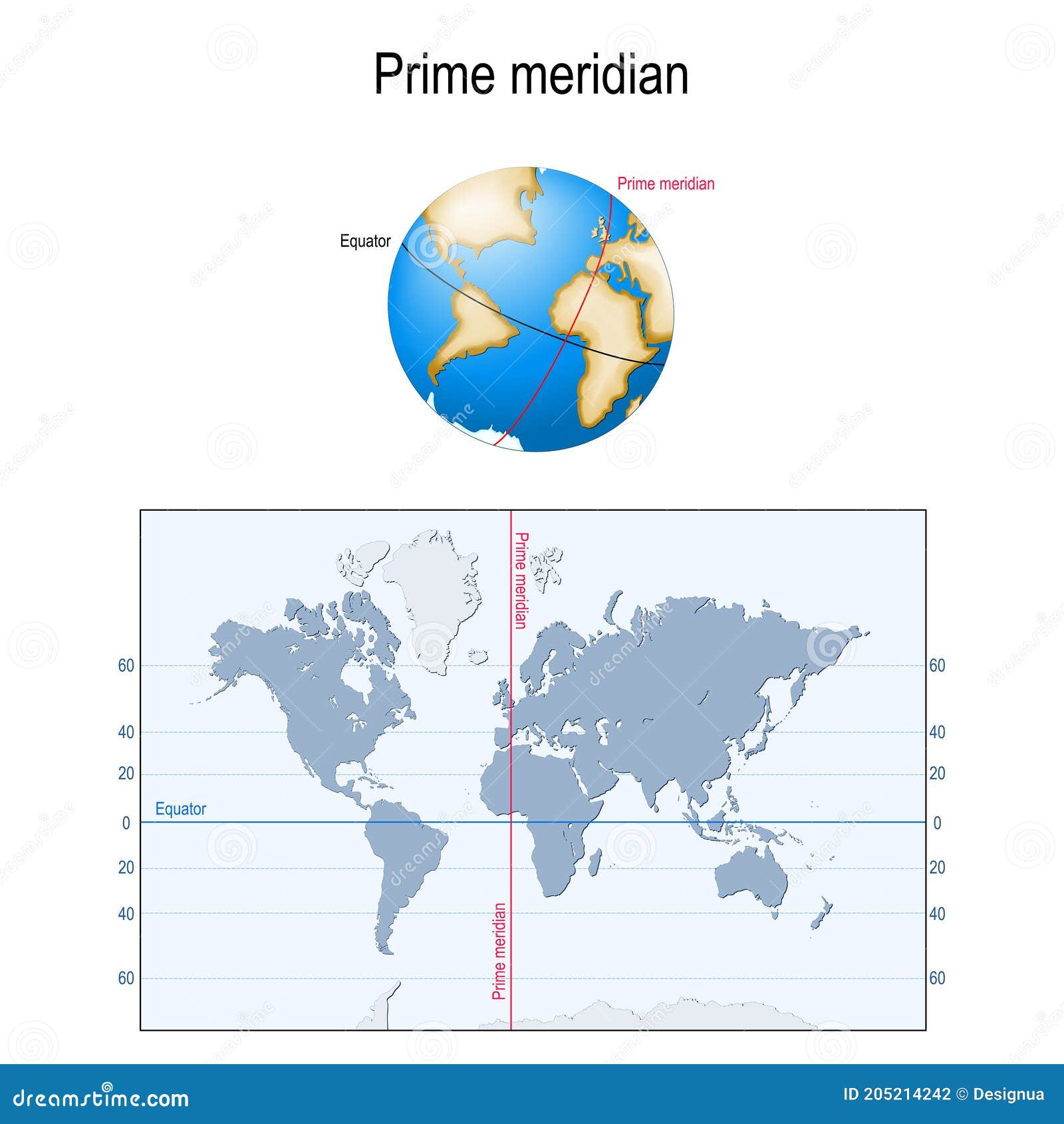
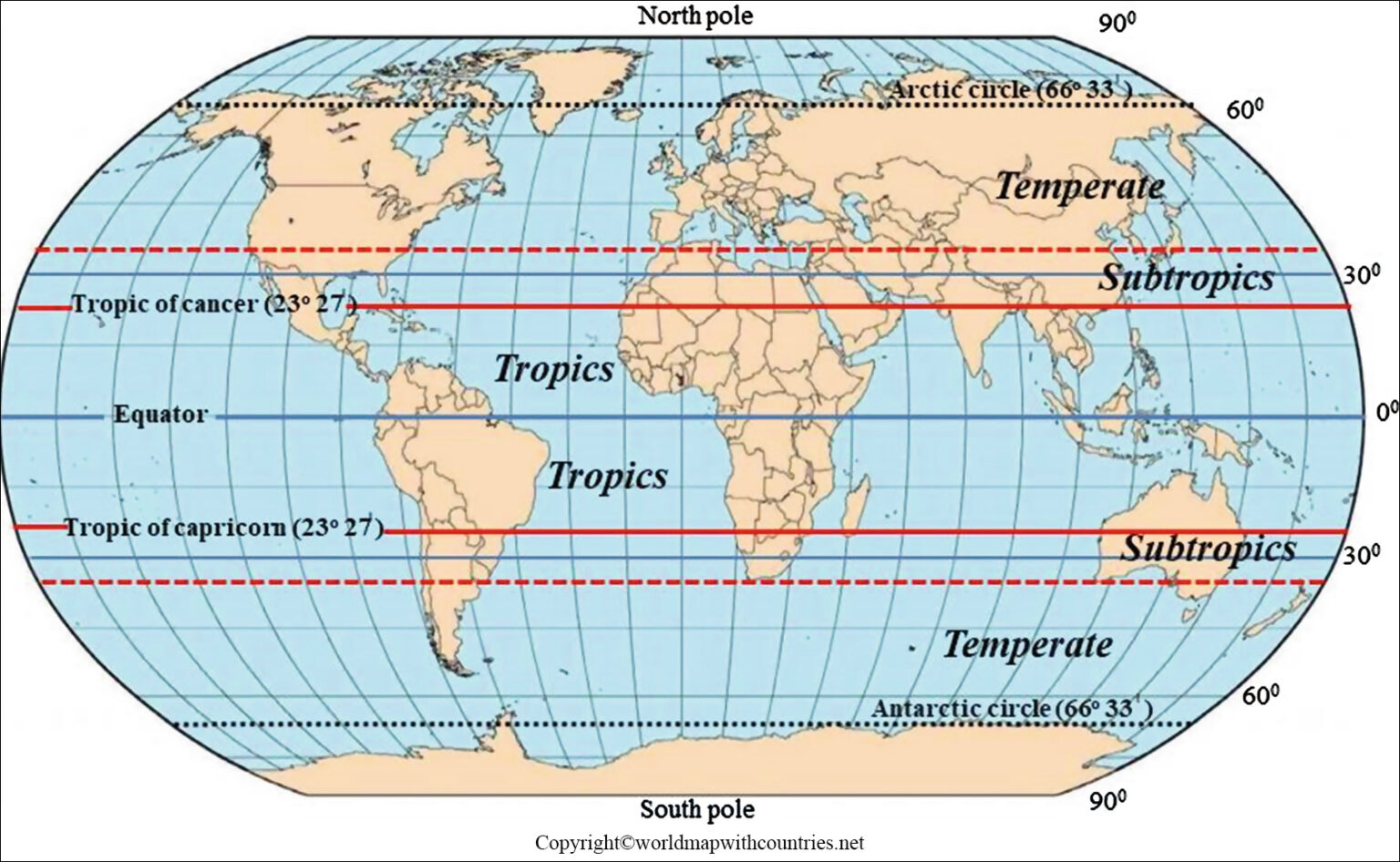
The equator, an imaginary line circling the Earth at 0 degrees latitude, is a fundamental element in understanding our planet’s geography and its influence on various aspects of life. This invisible line divides the Earth into the Northern and Southern Hemispheres, serving as a point of reference for numerous geographical, climatic, and cultural phenomena.
The Equator’s Significance in Geography
The equator’s primary significance lies in its role as the starting point for the latitude system. Latitude lines, which run parallel to the equator, measure distances north or south of this central line. This system allows for precise location identification on the globe, facilitating navigation, cartography, and various scientific studies.
Furthermore, the equator holds particular importance in understanding the Earth’s shape and rotation. Due to the centrifugal force generated by the planet’s rotation, the Earth bulges at the equator and is slightly flattened at the poles. This phenomenon, known as the equatorial bulge, influences the Earth’s gravitational field and contributes to the distribution of landmasses and ocean currents.
Climatic Influence of the Equator
The equator’s location on the Earth’s surface significantly influences global climate patterns. The sun’s rays strike the equator at a near-perpendicular angle, leading to intense solar radiation and high temperatures throughout the year. This results in a tropical climate characterized by consistently warm temperatures, high humidity, and abundant rainfall.
The equator is also home to the Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ), a region where air masses from the Northern and Southern Hemispheres converge. This convergence leads to frequent thunderstorms and heavy rainfall, contributing to the lush vegetation and biodiversity found in equatorial regions.
Cultural and Historical Significance of the Equator
The equator holds cultural and historical significance for various civilizations throughout history. Many ancient cultures, recognizing the equator’s influence on climate and the Earth’s shape, incorporated it into their belief systems and astronomical observations.
For example, the ancient Egyptians, renowned for their astronomical knowledge, understood the equator’s role in determining the solstices and equinoxes. The Inca Empire, located in the Andean region, developed a calendar system based on the sun’s position relative to the equator.
The Equator in Modern Society
The equator continues to play a crucial role in modern society. It serves as a reference point for numerous scientific and technological advancements, including satellite navigation systems, weather forecasting, and climate modeling.
Furthermore, the equator’s unique geographical position has led to the development of diverse ecosystems and cultural practices. Equatorial regions are home to a wide array of plant and animal life, contributing to global biodiversity. The equatorial climate also supports a vibrant agricultural industry, providing food for millions of people worldwide.
FAQs about the Equator
Q: What is the length of the equator?
A: The length of the equator is approximately 40,075 kilometers (24,901 miles).
Q: Is the equator a straight line?
A: No, the equator is a circle that encircles the Earth.
Q: What countries does the equator pass through?
A: The equator passes through 14 countries, including Ecuador, Colombia, Brazil, Indonesia, and Kenya.
Q: What is the time difference between the equator and the poles?
A: The equator experiences 12 hours of daylight and 12 hours of darkness throughout the year. The poles, on the other hand, experience periods of 24-hour daylight and 24-hour darkness depending on the time of year.
Q: Is the equator the only imaginary line on the Earth?
A: No, the Earth is also divided by lines of longitude, which run from pole to pole. The prime meridian, located at 0 degrees longitude, is another important imaginary line that serves as the starting point for the longitude system.
Tips for Understanding the Equator
- Use a globe or map: Visualizing the equator on a globe or map provides a better understanding of its position and significance.
- Learn about latitude and longitude: Understanding the latitude and longitude system helps in interpreting the equator’s role in geographical location.
- Explore equatorial regions: Traveling to or learning about countries that lie on the equator offers firsthand experience with the unique climate and cultural practices associated with this region.
- Research historical and cultural connections: Investigating the historical and cultural significance of the equator in different civilizations provides a deeper understanding of its influence on human history.
Conclusion
The equator, an invisible line on the Earth’s surface, holds immense significance in understanding our planet’s geography, climate, and culture. From its role in the latitude system to its influence on global weather patterns, the equator serves as a crucial reference point for navigating the Earth and comprehending its intricate workings. Recognizing the equator’s importance allows for a deeper appreciation of the interconnectedness of our planet and its diverse ecosystems.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Equator: A Line of Significance on the Global Map. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!