The Equator: A Line of Significance on Maps
Related Articles: The Equator: A Line of Significance on Maps
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Equator: A Line of Significance on Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Equator: A Line of Significance on Maps

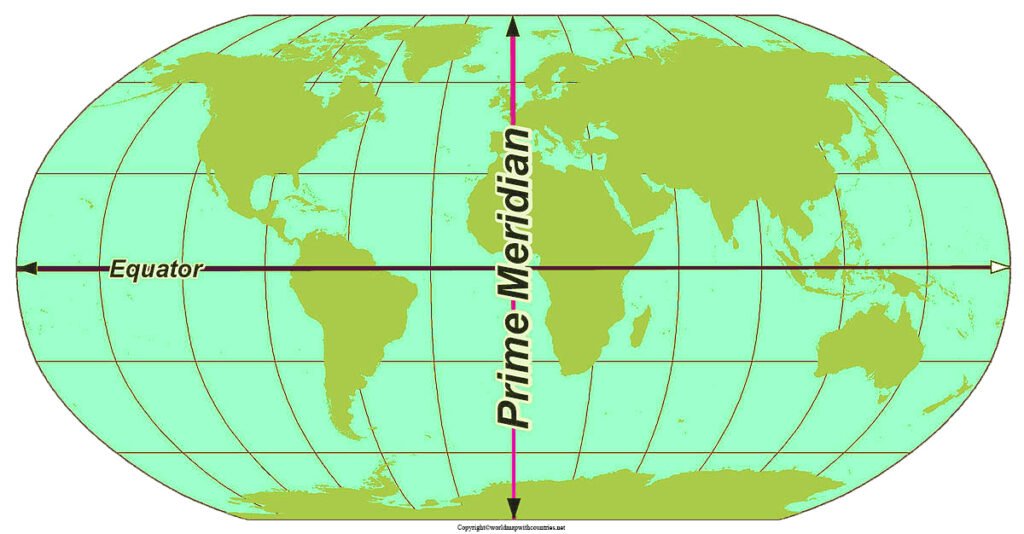
The equator, a prominent line on many maps, holds more than just cartographic significance. It is a crucial geographical feature that divides the Earth into two hemispheres, the Northern and Southern Hemispheres, and serves as a fundamental reference point for understanding global geography, climate, and various other aspects of our planet.
Understanding the Equator
The equator is an imaginary circle that encircles the Earth at zero degrees latitude. It is the largest circle of latitude on the Earth, equidistant from the North and South Poles. This imaginary line is not a physical feature but a conceptual one, crucial for mapping and understanding the Earth’s geometry.
Significance of the Equator
The equator’s importance stems from its unique position on the Earth, influencing various aspects:
1. Climate and Weather:
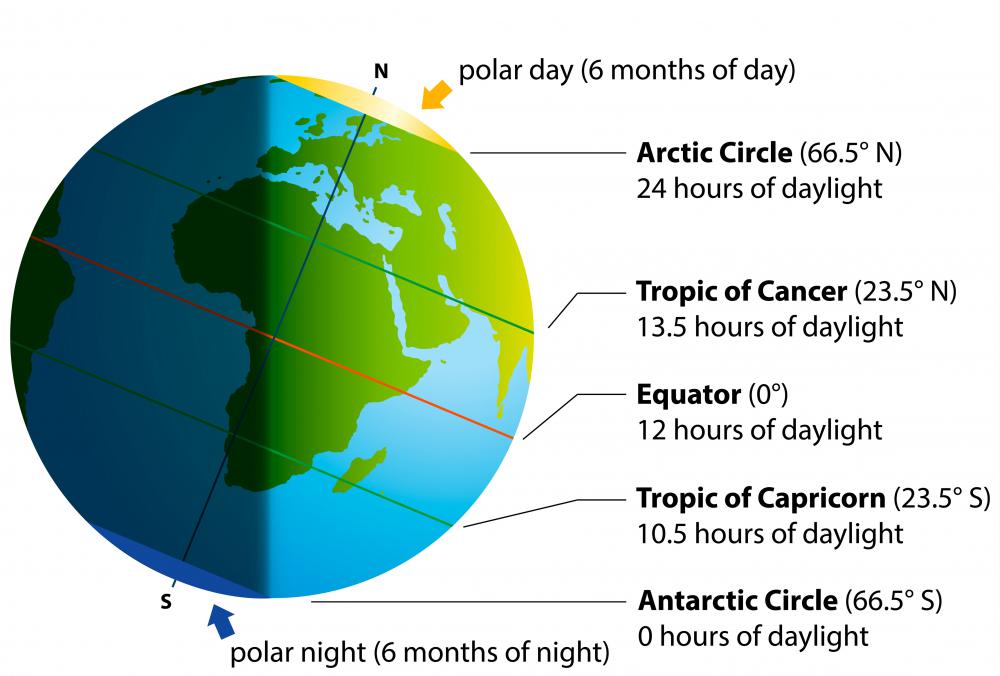
The equator receives the most direct sunlight throughout the year, leading to consistent warm temperatures and high humidity. This region experiences a tropical climate characterized by heavy rainfall, lush vegetation, and a distinct lack of pronounced seasons. The equator’s position directly influences the global circulation of air, creating prevailing wind patterns and influencing the distribution of rainfall across the globe.
2. Day and Night:
The equator experiences an almost equal duration of daylight and darkness throughout the year. This is due to its position relative to the Earth’s tilt, resulting in a consistent 12-hour day and 12-hour night cycle, with minimal variation.
3. Time Zones:
The equator plays a vital role in the establishment of time zones. The Greenwich Meridian, which passes through Greenwich, England, serves as the prime meridian, dividing the Earth into the Eastern and Western Hemispheres. The equator helps define the boundaries between time zones, as each time zone spans 15 degrees of longitude.
4. Global Navigation and Location:
The equator is a critical reference point for global navigation and location systems. It serves as the base line for latitude measurements, with all locations north of the equator having positive latitude values and those south having negative values. This system allows for precise identification of any location on Earth.
5. Biological Diversity:
The equatorial region is known for its exceptional biodiversity, hosting a wide range of plant and animal species. The consistent warmth, high humidity, and abundant rainfall create ideal conditions for thriving ecosystems, making the equator a hotspot for biodiversity.
6. Cultural and Historical Significance:
The equator has played a significant role in human history and culture. Many ancient civilizations recognized the equator’s importance, integrating it into their astronomical observations and calendar systems. The equator has also served as a boundary between different cultures and empires, influencing trade routes and political dynamics throughout history.
Maps with the Equator Marked: A Visual Representation of Global Significance
Maps with the equator marked serve as powerful visual tools for understanding the Earth’s geography and its various features. These maps provide a clear representation of the equator’s position, highlighting its importance as a dividing line between hemispheres and its influence on global climate, time zones, and navigation.
Benefits of Maps with the Equator Marked:
- Enhanced Understanding of Global Geography: Maps with the equator marked provide a visual framework for understanding the Earth’s shape, latitude, longitude, and the relationship between different regions.
- Improved Spatial Awareness: These maps help develop spatial awareness and the ability to visualize locations and distances across the globe.
- Facilitating Global Navigation: Maps with the equator marked are essential for global navigation, helping identify locations and plot courses across continents and oceans.
- Understanding Climate Patterns: The equator’s position on maps highlights its influence on global climate, allowing for a better understanding of temperature variations, rainfall patterns, and the distribution of different climate zones.
- Visualizing Time Zones: Maps with the equator marked help visualize the distribution of time zones across the globe, highlighting the impact of the equator on the global timekeeping system.
FAQs Regarding Maps with the Equator Marked:
1. Why is the equator important?
The equator is crucial because it divides the Earth into two hemispheres, influences global climate and weather patterns, serves as a reference point for navigation, and plays a role in defining time zones.
2. What are the characteristics of the equator?
The equator is an imaginary circle that encircles the Earth at zero degrees latitude, experiences consistent warm temperatures and high humidity, receives the most direct sunlight throughout the year, and experiences an almost equal duration of daylight and darkness.
3. How does the equator impact climate?
The equator’s position directly influences global air circulation, creating prevailing wind patterns and influencing the distribution of rainfall. The region experiences a tropical climate characterized by heavy rainfall, lush vegetation, and a distinct lack of pronounced seasons.
4. What is the significance of the equator in navigation?
The equator serves as the base line for latitude measurements, allowing for precise identification of any location on Earth. It is a crucial reference point for global navigation and location systems.
5. How does the equator affect time zones?
The equator helps define the boundaries between time zones, as each time zone spans 15 degrees of longitude. The prime meridian, which passes through Greenwich, England, serves as the base for determining time zones.
Tips for Using Maps with the Equator Marked:
- Use a globe or a map with a clear representation of the equator.
- Identify the equator’s position and its relationship to other geographical features.
- Explore the different aspects of the equator’s influence, such as climate, time zones, and navigation.
- Use the equator as a reference point when studying global geography and climate patterns.
- Engage in interactive map exercises to enhance your understanding of the equator’s significance.
Conclusion:
The equator, a seemingly simple line on a map, holds immense significance in understanding our planet’s geography, climate, and history. It serves as a crucial reference point for navigation, influences global weather patterns, and plays a vital role in defining time zones. Maps with the equator marked provide a powerful visual representation of this fundamental geographical feature, allowing for a deeper understanding of the Earth’s complexities and the interconnectedness of its various systems. By studying and appreciating the equator’s importance, we gain a greater appreciation for the intricate workings of our planet and the interconnectedness of all its components.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Equator: A Line of Significance on Maps. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!