The Equator: A Line of Significance Dividing the Globe
Related Articles: The Equator: A Line of Significance Dividing the Globe
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Equator: A Line of Significance Dividing the Globe. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Equator: A Line of Significance Dividing the Globe

The Earth, our home planet, is a vast and complex sphere, a blue marble suspended in the vastness of space. To navigate this complex sphere, we rely on various tools, one of the most fundamental being the map. Maps are visual representations of the Earth’s surface, and one crucial element that guides our understanding of the planet’s geography is the Equator.
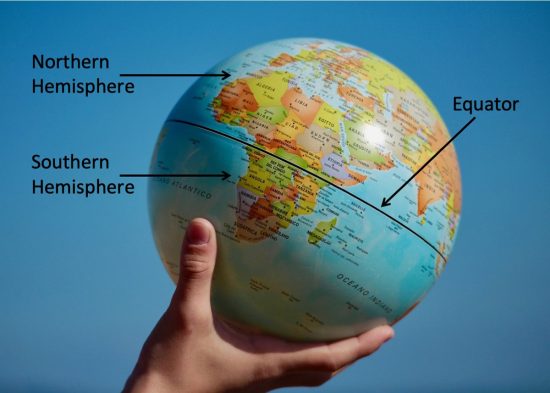
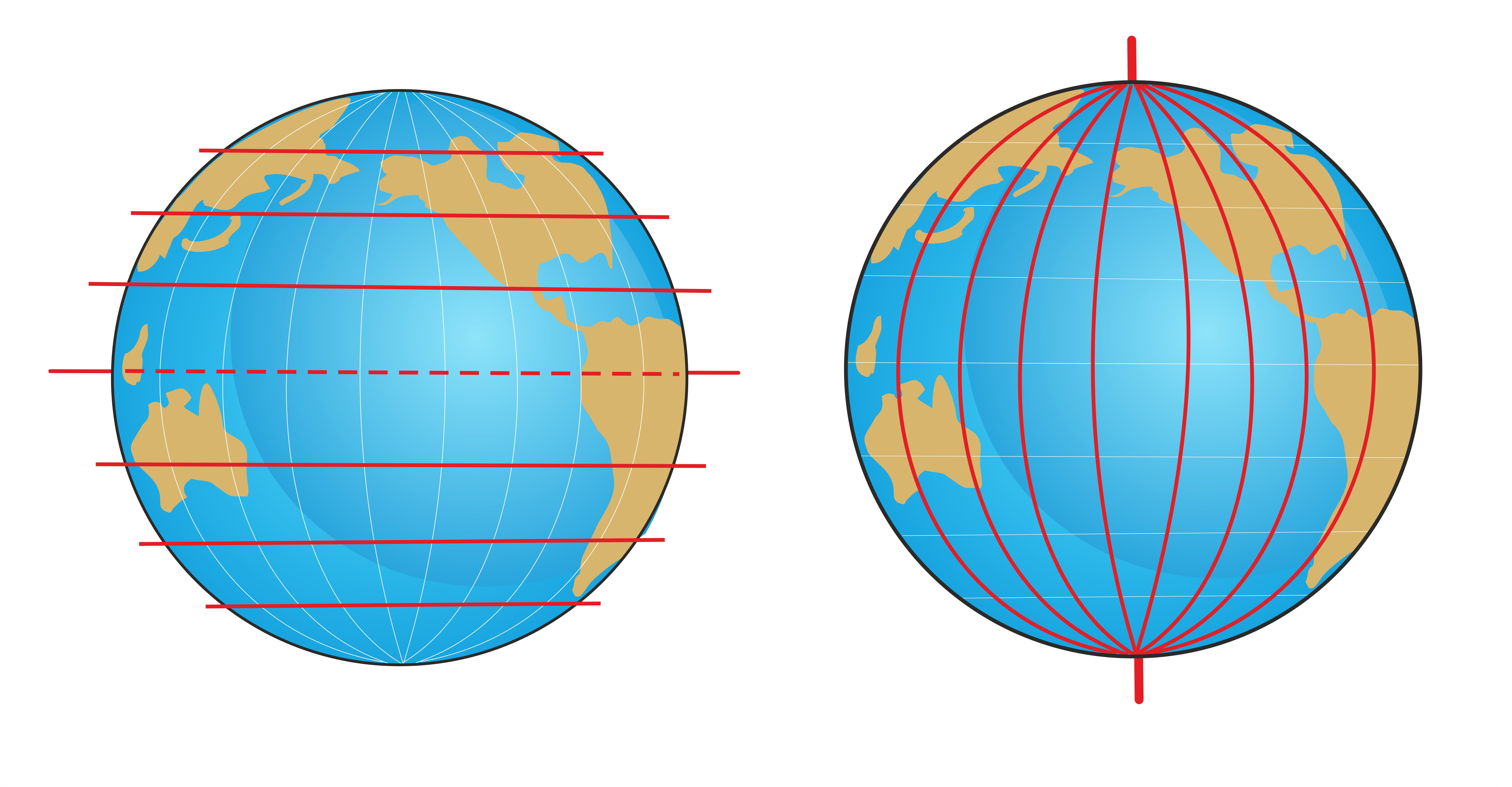
The Equator is an imaginary line that circles the Earth at 0 degrees latitude, equidistant from the North and South Poles. It divides the globe into two hemispheres: the Northern Hemisphere and the Southern Hemisphere. This seemingly simple line holds immense significance, impacting various aspects of our planet, from climate and weather patterns to cultural and political landscapes.
Understanding the Equator’s Impact
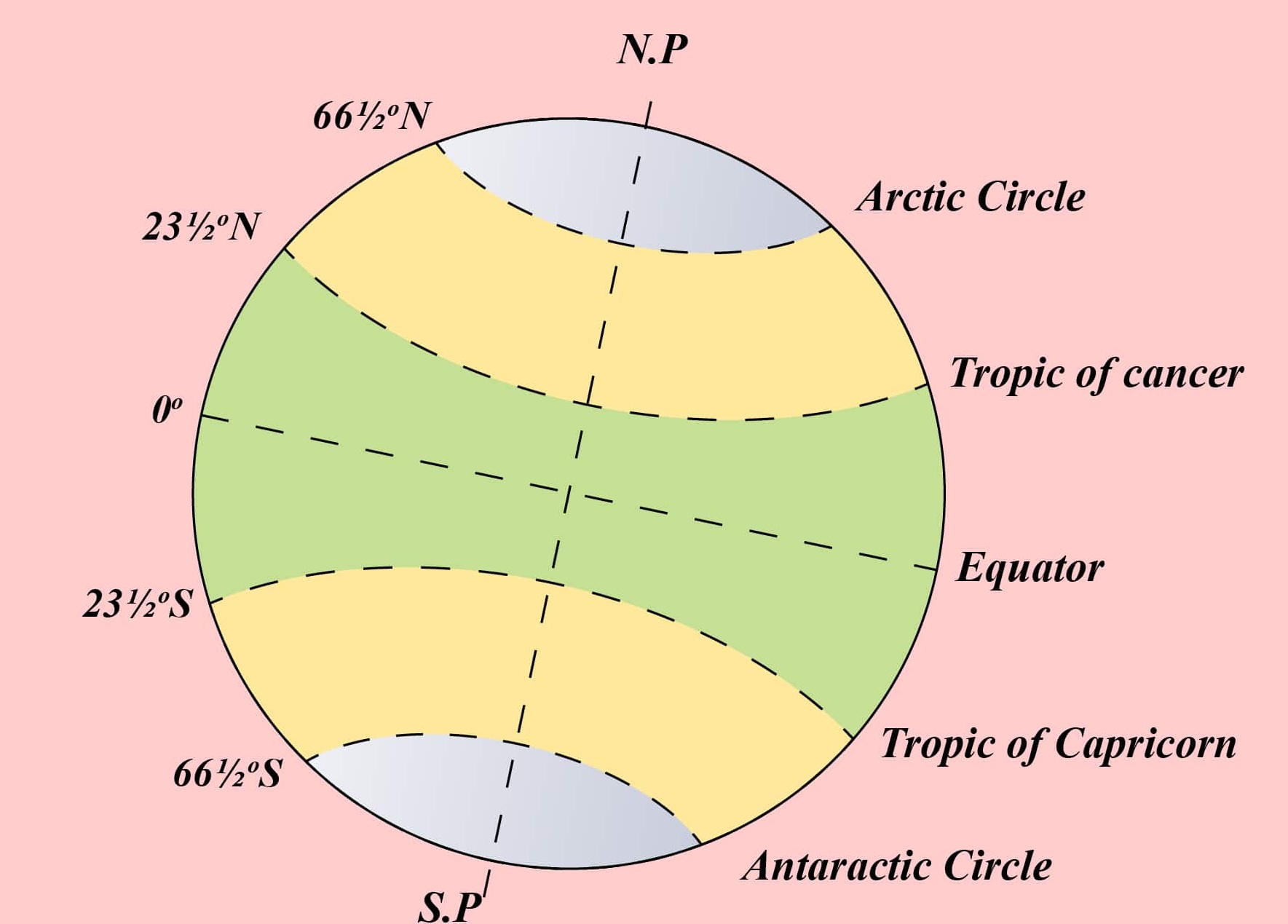
The Equator’s importance stems from its role in shaping the Earth’s climate and weather. The sun’s rays hit the Equator directly, resulting in the highest concentration of solar energy and consistently warm temperatures. This direct sunlight leads to a band of high atmospheric pressure, characterized by low rainfall and stable weather conditions. This region is often referred to as the Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ), a zone of low pressure where air rises, cools, and condenses, leading to heavy rainfall and the formation of tropical rainforests.
As one moves away from the Equator, the angle of the sun’s rays decreases, leading to a decrease in solar energy and a cooler climate. This creates a pattern of distinct climate zones, with tropical climates dominating near the Equator, temperate climates further away, and polar climates at the poles.
Beyond Climate: The Equator’s Influence on Life and Culture
The Equator’s influence extends beyond climate, impacting life and culture across the globe. The equatorial regions are home to a diverse array of flora and fauna, from lush rainforests teeming with biodiversity to vibrant coral reefs teeming with marine life. The Equator’s unique environment has shaped the evolution of these ecosystems, resulting in the presence of species found nowhere else on Earth.
Human civilizations have also adapted to the Equator’s conditions, developing distinct cultures and traditions. The Equator’s proximity to the sun has influenced architectural styles, with homes designed to maximize ventilation and minimize heat absorption. Traditional clothing often reflects the hot climate, using lightweight and breathable fabrics.
The Equator’s influence on human activity is further evident in the distribution of major cities, trade routes, and global economic activity. Many of the world’s largest cities are located near the Equator, benefiting from its favorable climate and access to transportation routes. The Equator also serves as a major shipping route, connecting continents and facilitating global trade.
The Equator’s Role in Navigation and Mapping
The Equator plays a crucial role in navigation and mapping, providing a fundamental reference point for understanding the Earth’s geography. It serves as the zero-degree line for latitude, with all other latitudes measured north or south of it. This system allows for precise location identification, enabling navigation, mapping, and geographical analysis.
FAQs about the Equator
1. Does the Equator pass through any countries?
Yes, the Equator passes through 13 countries: Ecuador, Colombia, Brazil, São Tomé and Príncipe, Gabon, Republic of the Congo, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Uganda, Kenya, Somalia, Maldives, Indonesia, and Kiribati.
2. Is the Equator a physical feature?
No, the Equator is an imaginary line, not a physical feature. It is a conceptual line that helps us understand the Earth’s geography and its relationship to the sun.
3. What is the significance of the Equator’s length?
The Equator is the Earth’s longest line of latitude, measuring approximately 40,075 kilometers (24,901 miles). This length reflects the Earth’s shape as a sphere and its circumference at its widest point.
4. How does the Equator affect day and night?
The Equator experiences roughly equal day and night throughout the year. This is because the Earth’s axis is tilted at an angle of 23.5 degrees, and the Equator lies directly on the plane of the Earth’s rotation.
5. What are some interesting facts about the Equator?
- The Equator is the only line of latitude that divides the Earth into two equal hemispheres.
- The Equator is the only place on Earth where the sun is directly overhead at noon twice a year, during the equinoxes.
- The Equator is home to the world’s largest rainforest, the Amazon rainforest.
- The Equator is a popular destination for tourists seeking warm weather, exotic wildlife, and unique cultural experiences.
Tips for Understanding the Equator
- Use a globe or a world map to visualize the Equator’s location and its relationship to other lines of latitude and longitude.
- Explore the different climate zones that exist near and away from the Equator.
- Learn about the unique flora and fauna found in equatorial regions.
- Research the cultures and traditions of people living near the Equator.
- Consider visiting the Equator and experiencing its unique environment firsthand.
Conclusion
The Equator, though an imaginary line, is a crucial element in understanding our planet. It shapes climate and weather patterns, influences life and culture, and serves as a fundamental reference point for navigation and mapping. By understanding the Equator’s significance, we gain a deeper appreciation for the Earth’s complex geography and the interconnectedness of life on our planet.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Equator: A Line of Significance Dividing the Globe. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!