The Equator: A Line of Significance
Related Articles: The Equator: A Line of Significance
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Equator: A Line of Significance. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Equator: A Line of Significance

The equator, an imaginary line circling the Earth at zero degrees latitude, serves as a fundamental reference point in geography and a vital element in understanding our planet’s climate, ecosystems, and cultural diversity. Its position on a map, a horizontal line bisecting the globe, holds immense significance for various scientific, cultural, and social aspects of human life.
The Equator’s Position and Importance
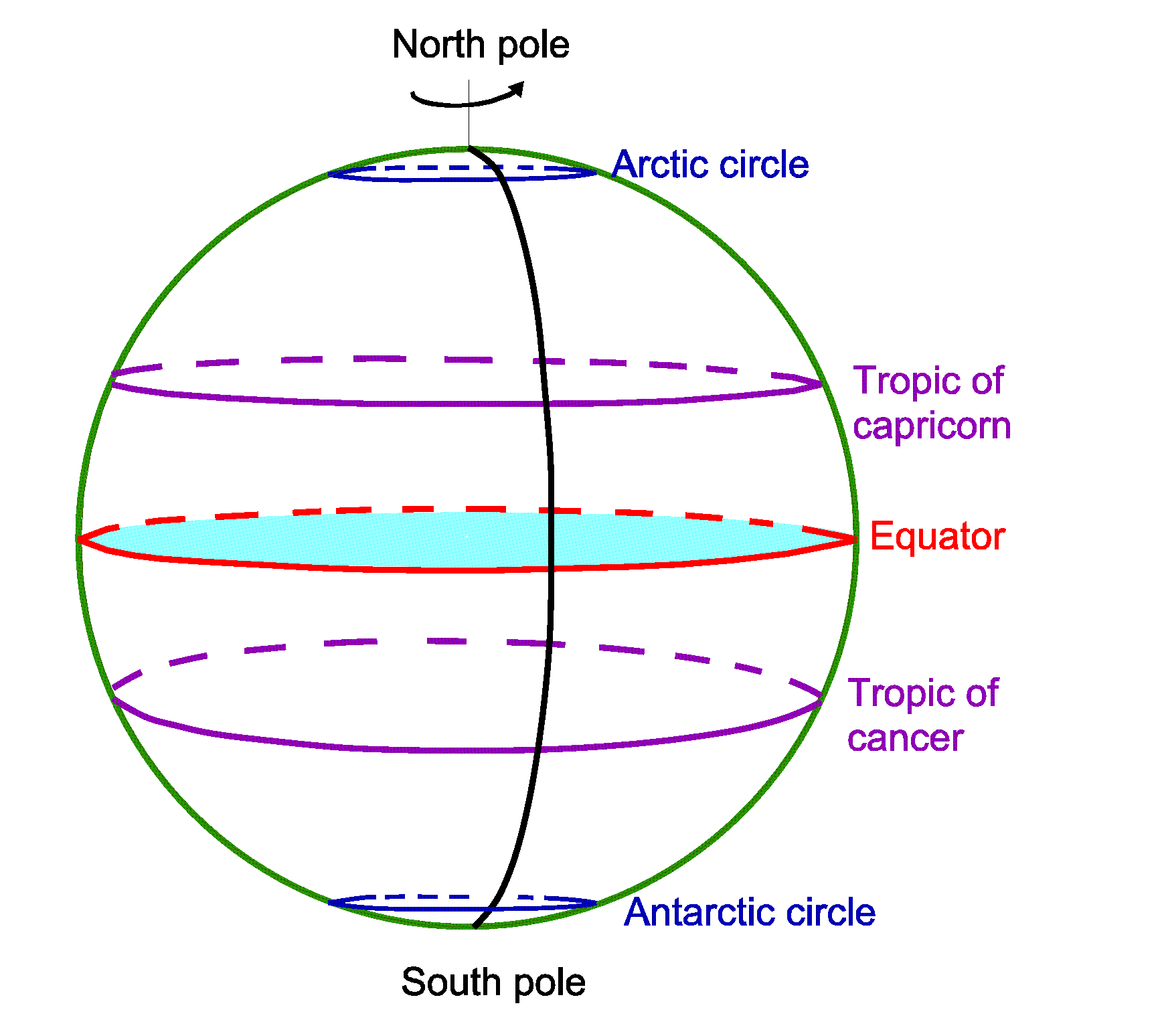
The equator’s location is determined by its relationship to the Earth’s axis of rotation. This axis, an imaginary line passing through the North and South poles, creates a perpendicular plane that intersects the Earth’s surface at zero degrees latitude. This intersection forms the equator, the longest line of latitude, dividing the Earth into the Northern and Southern Hemispheres.
Navigational and Geographical Significance
- Reference Point for Latitude: The equator serves as the starting point for measuring latitude, with all points north of it having positive latitude values and those south of it having negative values. This system facilitates precise location identification on a global scale.
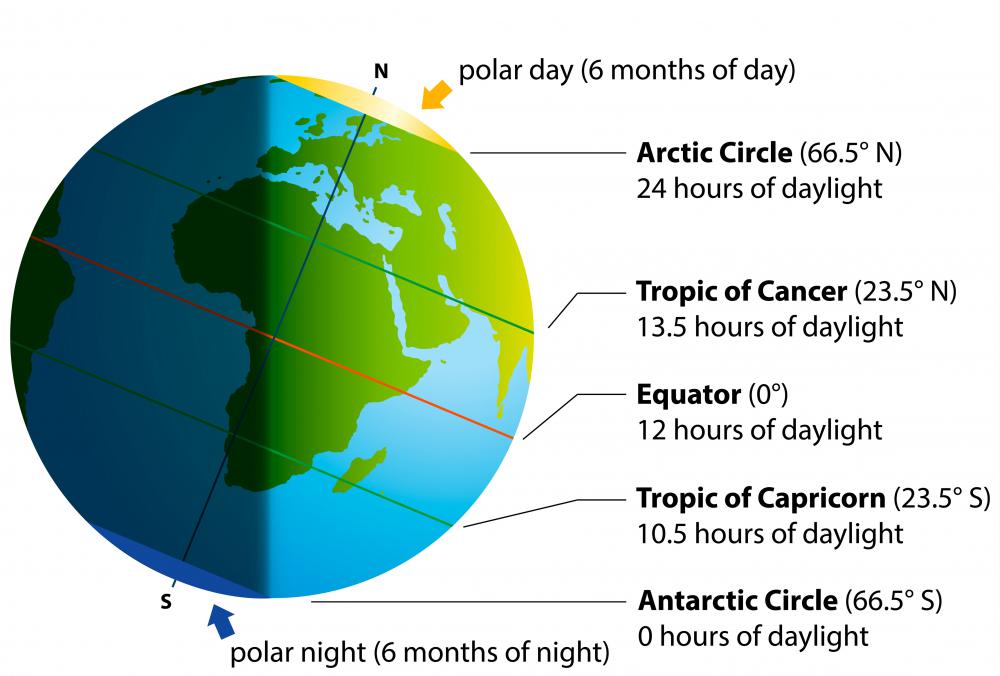
- Understanding Climate Zones: The equator’s position significantly influences global climate patterns. The region receives direct sunlight throughout the year, resulting in consistently warm temperatures and high humidity. This leads to the formation of tropical rainforests and other unique ecosystems.
- Defining Time Zones: The equator plays a crucial role in defining time zones. As the Earth rotates, different longitudes experience sunrise and sunset at different times. The equator, with its constant daylight hours, serves as a reference point for establishing time zones, ensuring consistent timekeeping across the globe.
Cultural and Social Significance
- Cultural Diversity: The equator traverses a diverse range of cultures, languages, and ethnicities. Its position within tropical regions has fostered unique traditions, customs, and beliefs, contributing to the rich tapestry of human civilization.
- Economic Importance: The equatorial regions are rich in natural resources, including fertile land, abundant rainfall, and diverse flora and fauna. This abundance has led to significant agricultural, forestry, and fishing industries, contributing to the economic prosperity of many nations.
- Global Connectivity: The equator acts as a vital link between continents, facilitating trade, communication, and cultural exchange. Its position within major shipping routes and air corridors has fostered global connectivity and interdependence.
Understanding the Equator’s Impact on Earth’s Systems
- Global Atmospheric Circulation: The equator’s position influences the circulation of air masses. The warm, moist air rising at the equator creates low-pressure zones, leading to the formation of trade winds and other weather patterns.
- Ocean Currents: The equator’s location significantly impacts ocean currents. The warm, equatorial waters contribute to the formation of major ocean currents, influencing global climate and marine ecosystems.
- Biodiversity Hotspots: The equator’s tropical climate and abundant rainfall create ideal conditions for a diverse range of plant and animal life. These regions are considered biodiversity hotspots, harboring a significant proportion of the world’s species.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What is the exact length of the equator? The equator’s circumference is approximately 40,075 kilometers (24,901 miles).
- What countries does the equator pass through? The equator crosses through 14 countries, including Ecuador, Colombia, Brazil, Indonesia, and Kenya.
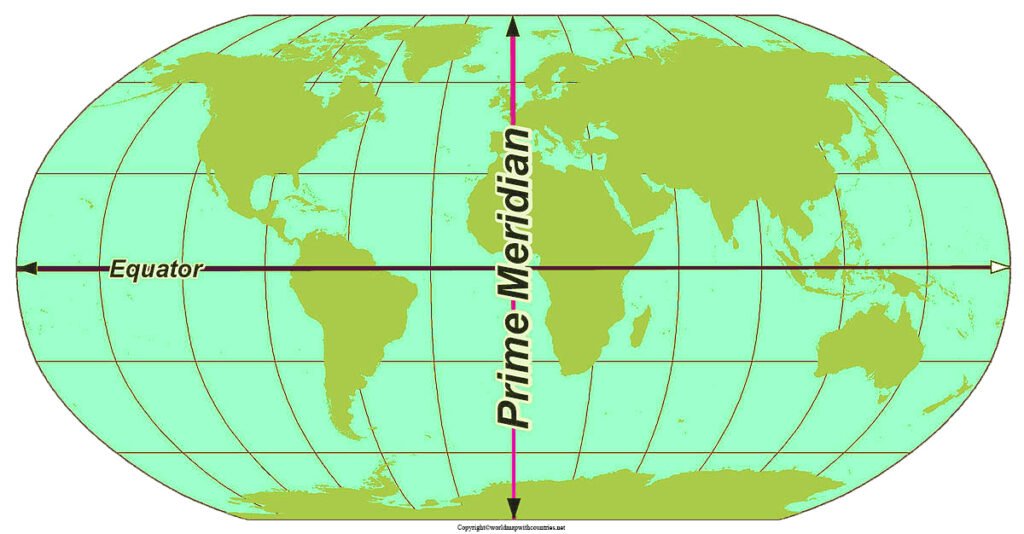
- What is the difference between the equator and the prime meridian? The equator is a line of latitude at zero degrees, while the prime meridian is a line of longitude at zero degrees. They intersect at the equator’s midpoint.
Tips for Understanding the Equator
- Use a Globe: A globe provides a visual representation of the Earth’s curvature and the equator’s position in relation to other geographical features.
- Explore Online Maps: Interactive maps allow you to zoom in and out, providing a detailed view of the equator and its surrounding regions.
- Read about Equatorial Cultures: Explore books, documentaries, and articles that highlight the unique cultures, traditions, and lifestyles of people living along the equator.
Conclusion
The equator, a seemingly simple line on a map, holds immense significance in shaping our planet’s geography, climate, and cultural diversity. Its position as a reference point for latitude, its influence on global weather patterns, and its role in connecting continents make it a vital element in understanding our world. By appreciating the equator’s importance, we can gain a deeper understanding of the interconnectedness of our planet and the diverse cultures that thrive within its boundaries.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Equator: A Line of Significance. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!