The Equator: A Line of Division and Significance
Related Articles: The Equator: A Line of Division and Significance
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Equator: A Line of Division and Significance. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Equator: A Line of Division and Significance

The Earth, our planet, is a sphere, and like any sphere, it can be divided into imaginary lines that help us understand its shape and orientation. One of the most important of these lines is the equator, a crucial reference point in geography and a fundamental aspect of understanding our world.
Defining the Equator
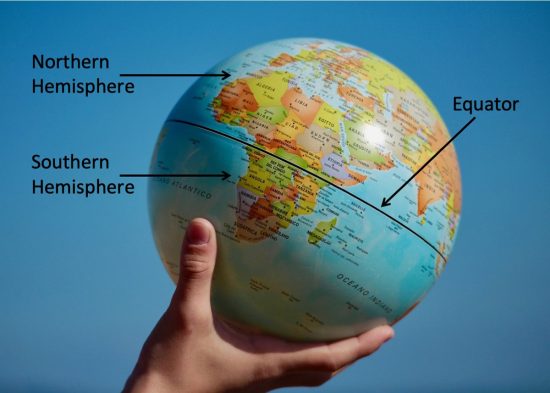
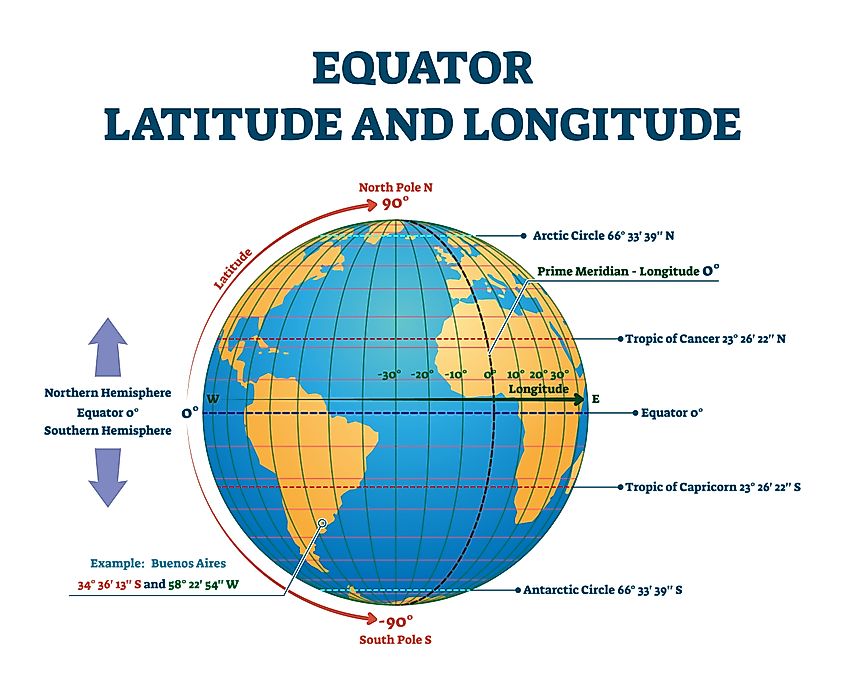
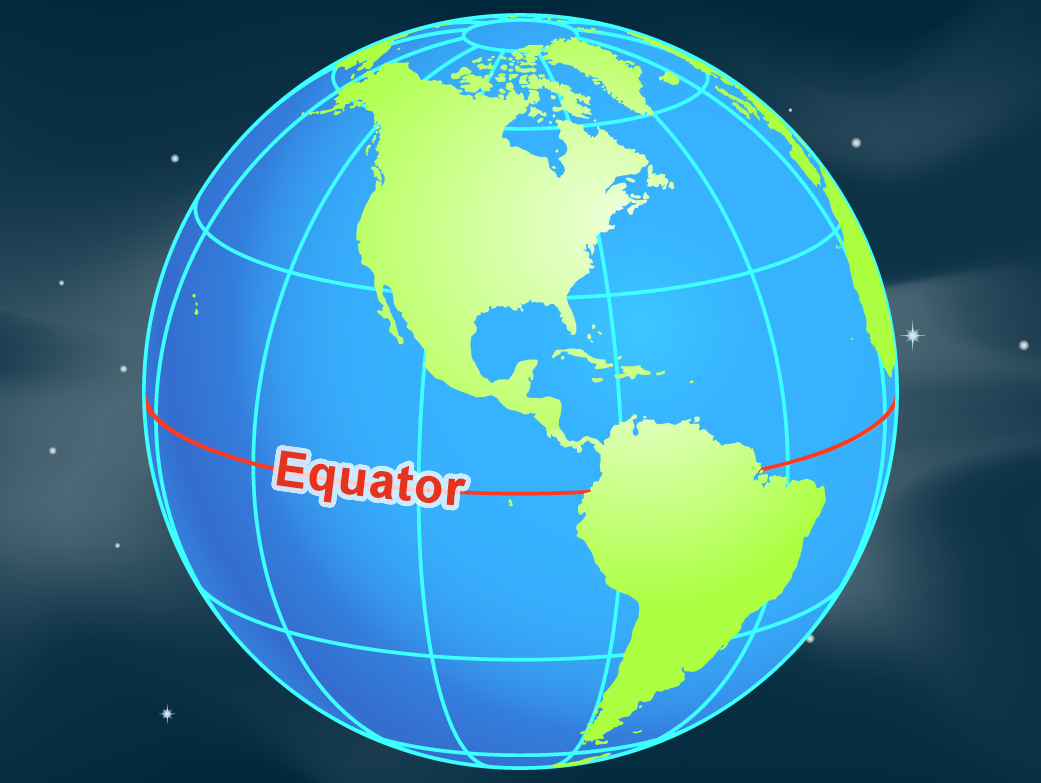
The equator is an imaginary circle that runs around the Earth, dividing it into the Northern and Southern Hemispheres. It is the largest of the Earth’s circles of latitude, situated at 0 degrees latitude. This means that all points along the equator are equidistant from the North and South Poles, and the equator is the only line of latitude that forms a perfect circle.
Understanding the Importance of the Equator
The equator holds immense significance in various fields, including:
- Geography: The equator serves as a fundamental reference point for understanding global locations and mapping the Earth’s surface. It is used to define the location of any point on the planet, with latitude measured in degrees north or south of the equator.
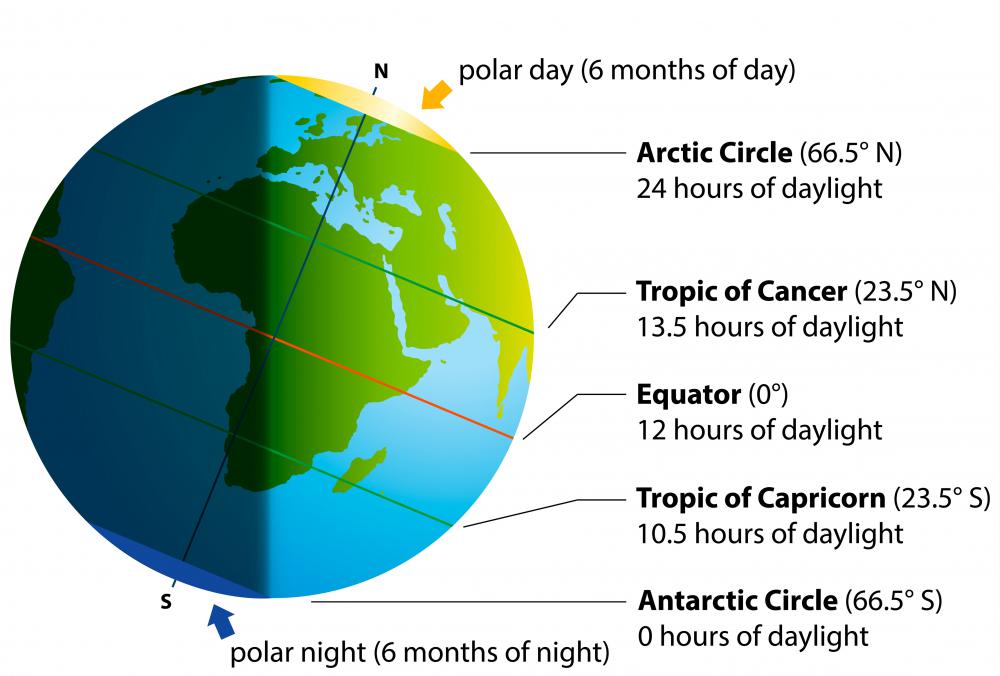
- Climate: The equator experiences a tropical climate characterized by consistently high temperatures and abundant rainfall. This is due to the intense solar radiation received at the equator, which drives atmospheric circulation and influences weather patterns.
- Astronomy: The equator is also important in astronomy. The celestial equator, an extension of the Earth’s equator projected onto the celestial sphere, is used to define the celestial coordinates of stars and other celestial objects.
- Navigation: The equator is a crucial reference point for navigation, especially for seafaring vessels and aircraft. It helps in determining the location of ships and planes, enabling them to navigate across vast distances.
- Cultural Significance: The equator holds cultural significance in many societies. It is often associated with a sense of diversity, as it passes through numerous countries with distinct cultures and traditions.
Understanding the Equator’s Impact on Earth’s Systems
The equator’s influence extends far beyond its geographical location. It plays a vital role in shaping Earth’s climate, weather patterns, and biological diversity.
- Climate Zones: The equator’s location directly influences global climate patterns. The intense solar radiation at the equator drives the formation of Hadley cells, atmospheric circulation patterns that transport heat and moisture from the tropics towards the poles. This process creates distinct climate zones, with the equator being the heart of the tropical zone.
- Biodiversity: The equatorial regions are renowned for their exceptional biodiversity, hosting a vast array of plant and animal life. The stable tropical climate and abundant rainfall create ideal conditions for a wide range of species to thrive.
- Ocean Currents: The equator also influences ocean currents. The trade winds, driven by the Hadley cells, push surface water westward, creating powerful ocean currents like the Equatorial Current. These currents play a crucial role in regulating global heat distribution and marine ecosystems.
FAQs about the Equator
Q: What are the major countries that lie on the equator?
A: The equator passes through 14 countries, including Ecuador, Colombia, Brazil, Congo, Kenya, and Indonesia.
Q: Is the equator always in the same place?
A: While the equator is a fixed line of latitude, its position relative to the Earth’s surface can shift slightly due to the Earth’s wobble. This wobble, known as precession, causes the Earth’s axis to tilt over thousands of years, resulting in a gradual shift in the equator’s position.
Q: What is the difference between the equator and the prime meridian?
A: The equator is a line of latitude that divides the Earth into the Northern and Southern Hemispheres. The prime meridian is a line of longitude that divides the Earth into the Eastern and Western Hemispheres. The equator is a horizontal line, while the prime meridian is a vertical line.
Q: What is the significance of the equator in relation to the Earth’s rotation?
A: The Earth rotates on its axis, and the equator is the line of latitude that experiences the fastest rotational speed. This is because the Earth’s circumference at the equator is the largest, meaning that points on the equator have to travel a greater distance in the same amount of time.
Tips for Understanding the Equator
- Visualize the Earth as a sphere: Imagine a line circling the Earth at its widest point, dividing it into two equal halves. This line is the equator.
- Use a globe or a map: Examine a globe or a world map to see the equator’s position and how it relates to other geographical features.
- Explore the countries that lie on the equator: Learn about the diverse cultures, landscapes, and ecosystems found along the equator.
- Research the equator’s impact on climate and weather: Understand how the equator’s position influences global climate patterns and weather phenomena.
Conclusion
The equator is more than just an imaginary line on a map. It is a fundamental reference point that shapes our understanding of the Earth’s geography, climate, and even cultural diversity. Recognizing its significance allows us to appreciate the interconnectedness of our planet and the vital role it plays in shaping our world.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Equator: A Line of Division and Significance. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!