The Equator: A Line of Division and Connection
Related Articles: The Equator: A Line of Division and Connection
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Equator: A Line of Division and Connection. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Equator: A Line of Division and Connection

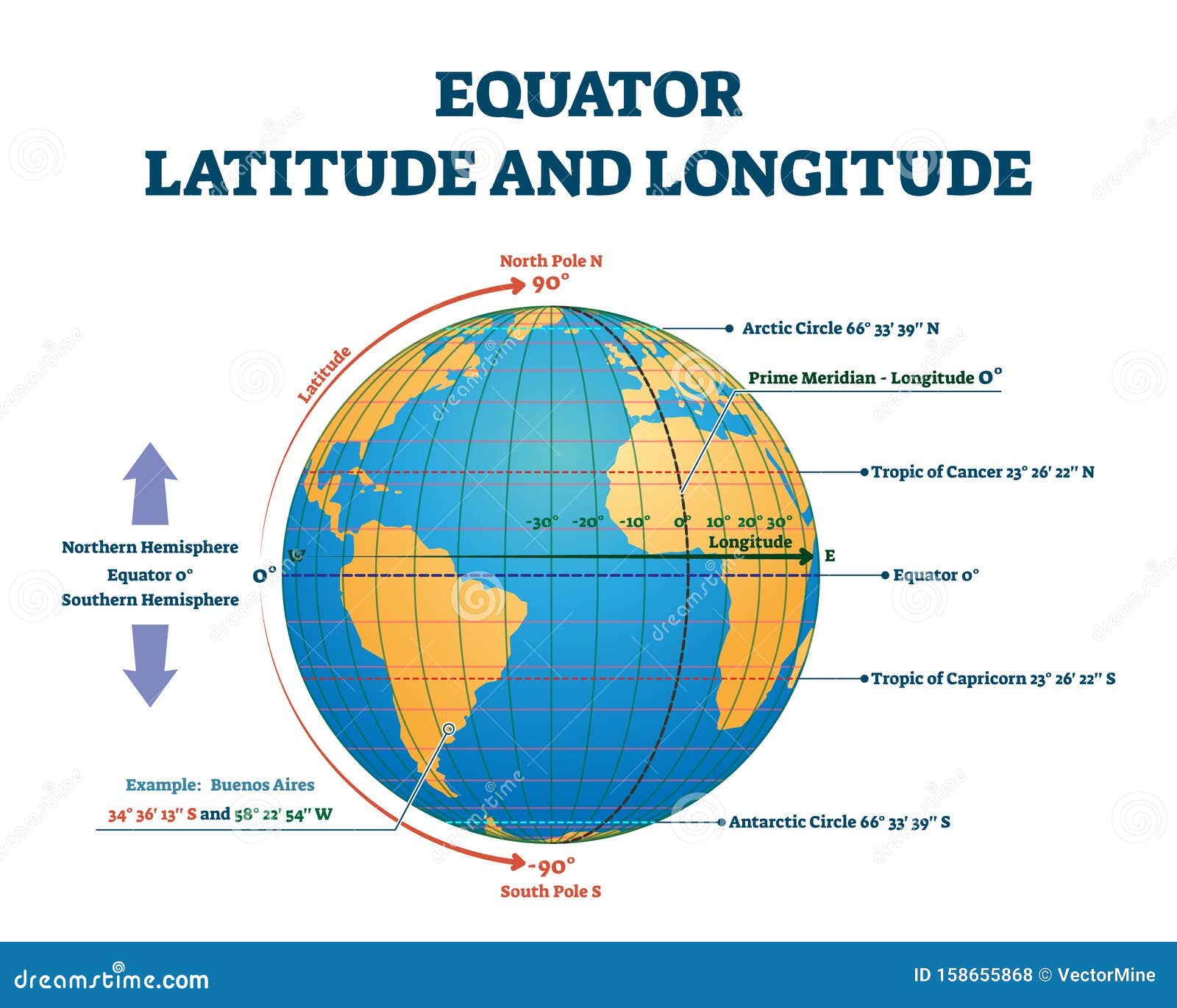
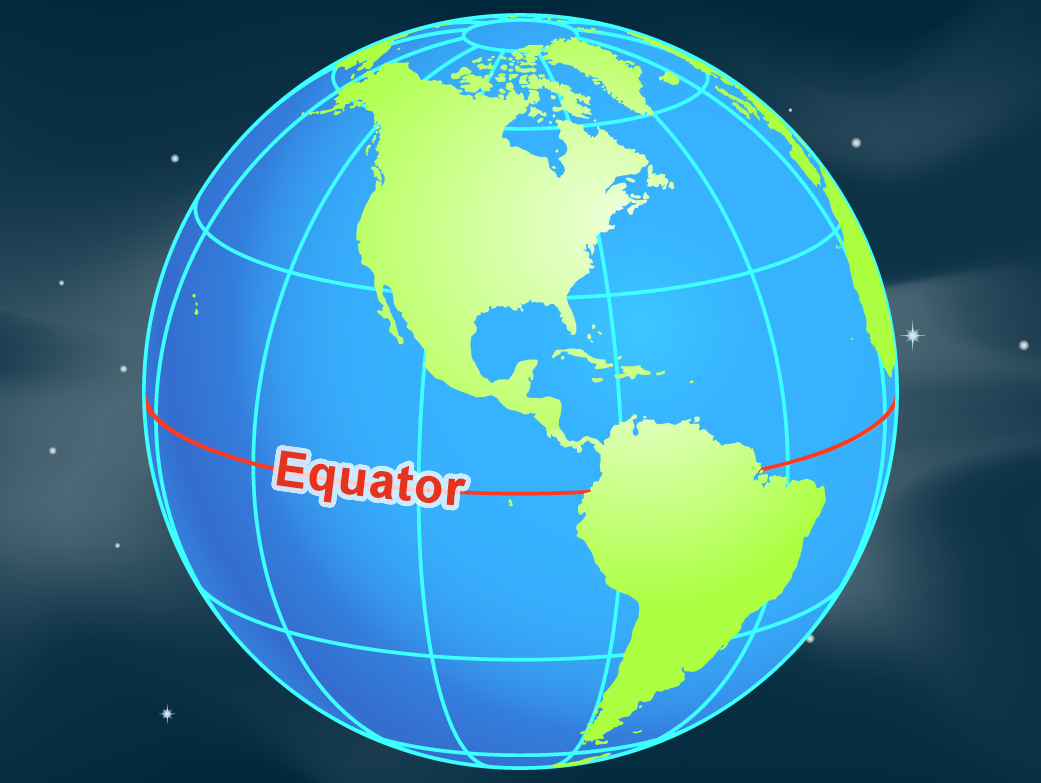
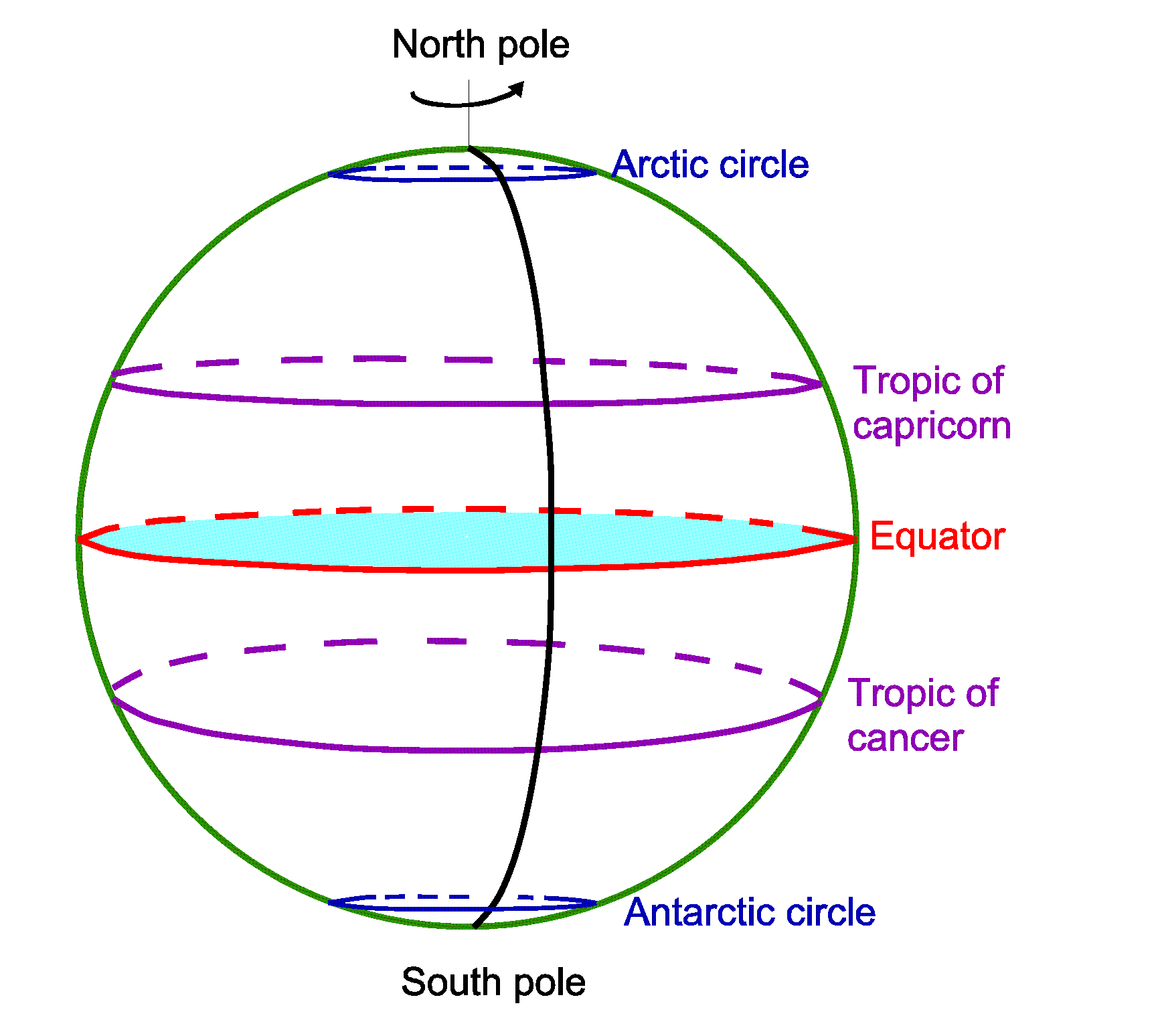
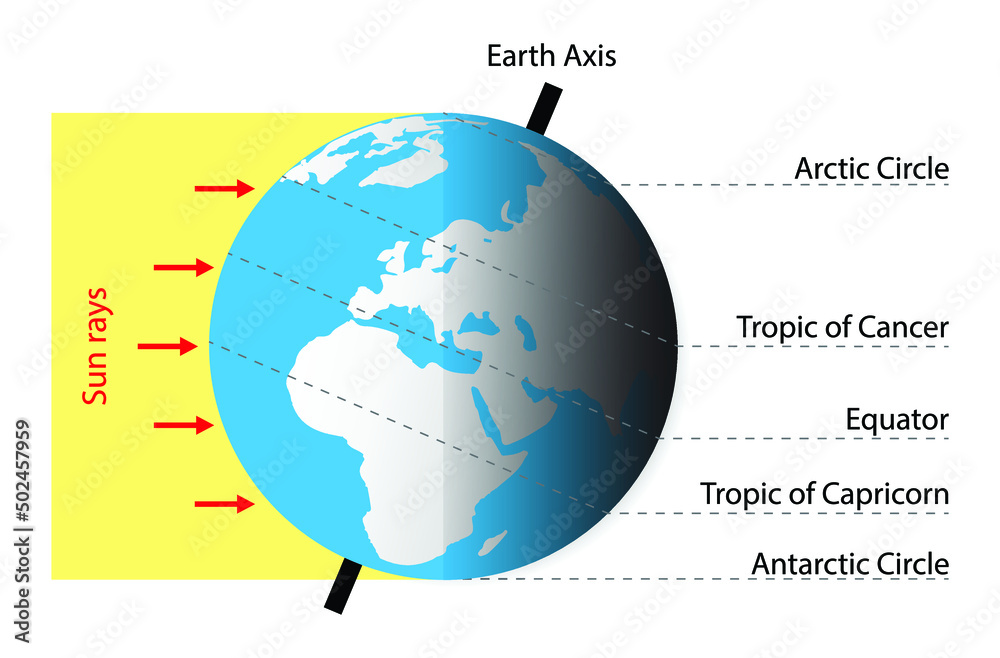
The equator, an imaginary line circling the Earth at 0 degrees latitude, serves as a fundamental reference point in geography and a vital element in understanding the planet’s diverse climates and ecosystems. It divides the Earth into the Northern and Southern Hemispheres, signifying a crucial transition in solar radiation, temperature, and the distribution of plant and animal life.
The Significance of the Equator
The equator’s significance lies in its unique position relative to the sun. Due to the Earth’s tilt on its axis, the equator receives the most direct sunlight throughout the year. This constant exposure to the sun results in:
- Consistent Temperatures: The equator experiences relatively stable temperatures throughout the year, with minimal seasonal variation. The consistent solar radiation leads to warm, humid conditions, fostering diverse ecosystems and unique plant and animal life.
- Day and Night Length: The equator experiences almost equal day and night lengths throughout the year, with slight variations depending on the time of year. This consistent day-night cycle influences the biological rhythms of plants and animals, contributing to the vibrant biodiversity found in equatorial regions.
- Global Wind Patterns: The equator is a key factor in shaping global wind patterns. The intense solar radiation at the equator creates an area of low atmospheric pressure, leading to the convergence of air masses and the formation of the Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ). This zone of low pressure influences the movement of air masses, contributing to the global circulation of air and moisture.
- Ocean Currents: The equator also plays a crucial role in shaping ocean currents. The warm waters at the equator create a region of low density, leading to the formation of equatorial currents. These currents transport heat and nutrients across the globe, influencing the distribution of marine life and shaping coastal climates.
Mapping the Equator
The equator is represented on maps as a horizontal line that divides the Earth into two hemispheres. Its position on a map is crucial for understanding the Earth’s geography and interpreting the distribution of various phenomena, including:
- Latitude: The equator serves as the starting point for measuring latitude, which is the angular distance north or south of the equator. Latitude is measured in degrees, with 0 degrees representing the equator and 90 degrees representing the North and South Poles.
- Time Zones: The equator is also a key factor in determining time zones. The Earth is divided into 24 time zones, each representing a 15-degree longitude interval. The equator is used as a reference point for establishing the standard time for each time zone.
- Climate Zones: The equator is a key factor in defining climate zones. The consistent solar radiation at the equator creates a distinct tropical climate zone, characterized by high temperatures, abundant rainfall, and diverse ecosystems.
The Equator’s Impact on Life
The equator’s unique position and influence have profound impacts on life on Earth:
- Biodiversity: Equatorial regions boast exceptional biodiversity due to the warm, humid climate and consistent solar radiation. They are home to a wide array of plant and animal species, including rainforests, coral reefs, and diverse ecosystems.
- Human Civilization: The equator has played a significant role in the development of human civilization. Many ancient civilizations, such as the Maya and Inca, thrived in equatorial regions, utilizing the abundant resources and favorable climate.
- Global Trade: The equator is a major hub for global trade, connecting different regions through shipping routes and facilitating the exchange of goods and services.
FAQs about the Equator:
1. What is the exact length of the equator?
The equator is approximately 40,075 kilometers (24,901 miles) in length.
2. Does the equator pass through any landmasses?
Yes, the equator passes through 14 countries, including Ecuador, Brazil, Colombia, and Indonesia.
3. What are some of the unique ecosystems found near the equator?
Equatorial regions are home to diverse ecosystems, including rainforests, savannas, coral reefs, and mangrove forests.
4. How does the equator affect the Earth’s climate?
The equator’s consistent solar radiation influences global wind patterns, ocean currents, and the distribution of temperature and rainfall, shaping the Earth’s climate.
5. Is the equator always at 0 degrees latitude?
Yes, the equator is always defined as 0 degrees latitude.
Tips for Understanding the Equator:
- Use a globe or map: Visualizing the Earth as a sphere and the equator as a line circling it can help understand its position and significance.
- Explore equatorial regions: Learning about the diverse ecosystems, cultures, and unique features of equatorial regions can provide a deeper understanding of the equator’s influence.
- Track the sun’s path: Observing the sun’s path across the sky at different times of the year can help visualize the equator’s role in regulating solar radiation.
Conclusion:
The equator is a fundamental geographical feature that plays a crucial role in shaping the Earth’s climate, ecosystems, and human civilization. It serves as a line of division and connection, influencing temperature, wind patterns, ocean currents, and the distribution of life on Earth. Understanding the equator’s significance is essential for comprehending the planet’s complex and interconnected systems.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Equator: A Line of Division and Connection. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!