The Equator: A Line of Division and Connection
Related Articles: The Equator: A Line of Division and Connection
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Equator: A Line of Division and Connection. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Equator: A Line of Division and Connection

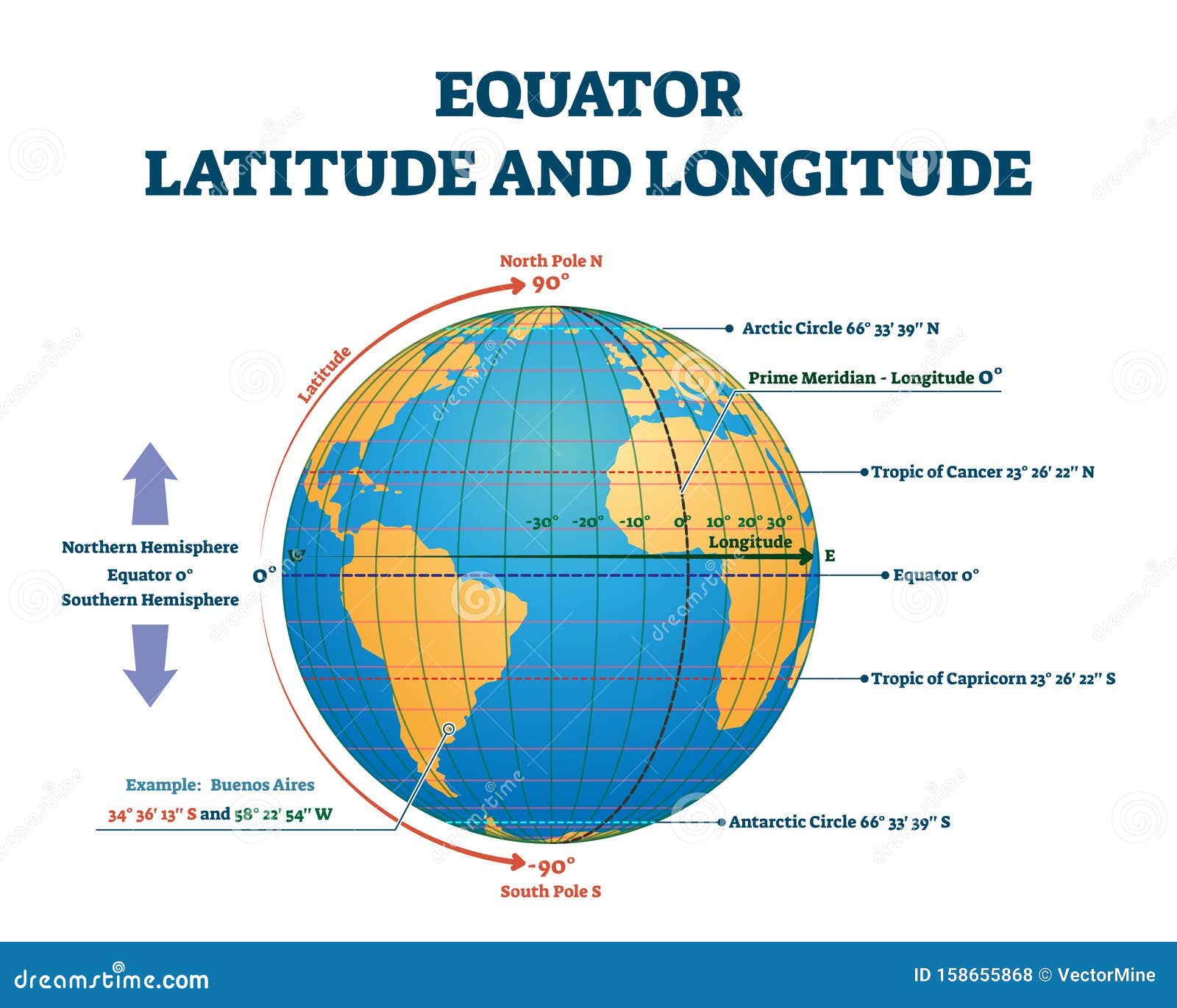
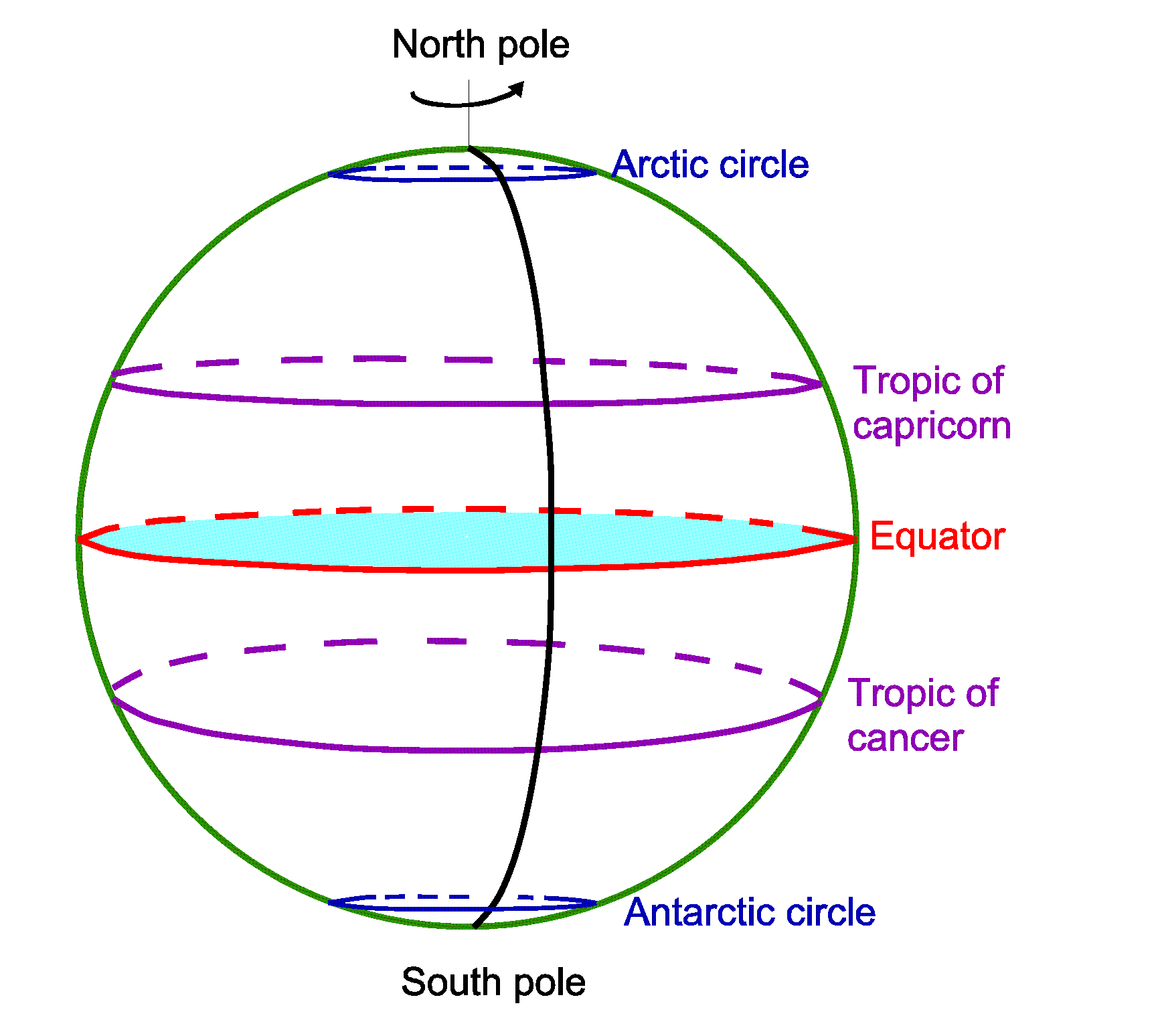
The equator, an imaginary line circling the Earth at 0 degrees latitude, is a pivotal geographical feature with profound implications for the planet’s climate, biodiversity, and human civilization. It serves as a fundamental reference point for understanding global geography, guiding scientific research, and illuminating the interconnectedness of our world.
A Line of Division:
The equator acts as a dividing line, separating the Earth into the Northern and Southern Hemispheres. This division is not merely geographical; it manifests in diverse climatic conditions, distinct ecosystems, and varied cultural landscapes.
Climate and Weather Patterns:
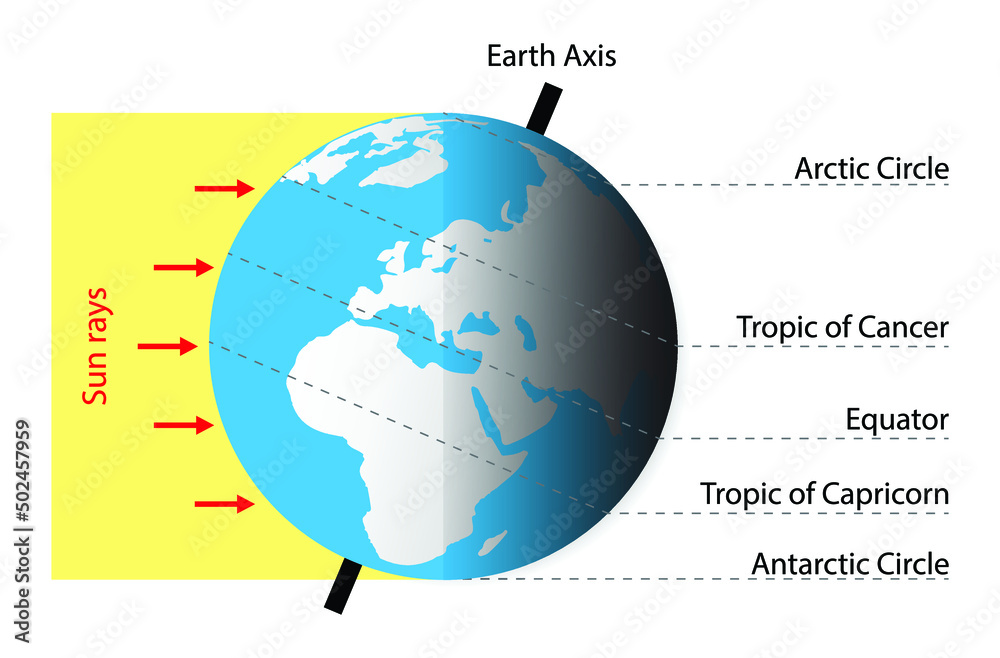
The equator is renowned for its consistently high temperatures and abundant rainfall. This is due to the intense solar radiation it receives, resulting in a predominantly tropical climate characterized by dense vegetation, high humidity, and consistent sunshine. The Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ), a band of low pressure and convergence of trade winds, often hovers near the equator, further contributing to its characteristic weather patterns.
Biodiversity Hotspot:
The equatorial region is a haven for biodiversity, teeming with a vast array of plant and animal species. The equatorial rainforests, with their dense canopies and rich soils, support an extraordinary array of life, including unique and endangered species found nowhere else on Earth. The abundance of sunlight and consistent rainfall provide ideal conditions for a thriving ecosystem, highlighting the equator’s role in global biodiversity.
Human Settlements and Culture:
The equator has been a cradle of human civilization, hosting diverse cultures and societies throughout history. The equatorial belt encompasses a wide range of human settlements, from bustling cities to remote villages, each with its own unique traditions, languages, and ways of life. The equator’s strategic location and abundant resources have attracted human populations for millennia, shaping the cultural tapestry of the planet.
Navigational Significance:
The equator serves as a crucial navigational reference point, guiding explorers, sailors, and modern-day pilots. Its zero-degree latitude provides a fundamental baseline for measuring locations and calculating distances across the globe. This navigational significance has been essential for trade, exploration, and global communication throughout history.
Scientific Research and Exploration:
The equator is a focal point for scientific research and exploration. Scientists study the unique ecosystems, climate patterns, and geological formations found in this region, contributing to our understanding of Earth’s complex systems. From studying the impact of climate change on equatorial rainforests to analyzing the evolution of species in this biodiversity hotspot, the equator remains a vital research frontier.
Economic Importance:
The equatorial region is rich in natural resources, including fertile land, mineral deposits, and abundant marine life. These resources contribute significantly to the global economy, supporting agriculture, mining, fishing, and tourism industries. The equator’s strategic location also makes it a vital hub for trade and transportation, connecting diverse regions of the world.
Global Interconnectedness:
The equator is a powerful symbol of global interconnectedness. Its influence extends far beyond its physical location, impacting weather patterns, ecosystems, and human societies across the globe. The movement of air currents, ocean currents, and migratory species connects the equator to distant regions, highlighting the intricate web of life on Earth.
FAQs:
1. What is the significance of the equator for climate?
The equator experiences consistently high temperatures and abundant rainfall due to intense solar radiation and the presence of the Intertropical Convergence Zone. This creates a predominantly tropical climate with significant implications for global weather patterns.
2. Why is the equator a biodiversity hotspot?
The equatorial region’s warm temperatures, abundant rainfall, and fertile soils create ideal conditions for a thriving ecosystem. This results in a high concentration of diverse plant and animal species, including many unique and endangered species.
3. How has the equator influenced human civilization?
The equator has been a cradle of human civilization, hosting diverse cultures and societies throughout history. Its strategic location and abundant resources have attracted human populations for millennia, shaping the cultural tapestry of the planet.
4. What is the navigational significance of the equator?
The equator serves as a crucial navigational reference point, providing a fundamental baseline for measuring locations and calculating distances across the globe. This has been essential for trade, exploration, and global communication throughout history.
5. How does the equator contribute to global interconnectedness?
The equator’s influence extends far beyond its physical location, impacting weather patterns, ecosystems, and human societies across the globe. The movement of air currents, ocean currents, and migratory species connects the equator to distant regions, highlighting the intricate web of life on Earth.
Tips for Understanding the Equator:
- Use a globe or map: Visualizing the equator on a globe or map helps to grasp its position and significance.
- Explore equatorial regions: Learn about the diverse ecosystems, cultures, and societies found in the equatorial belt.
- Research climate patterns: Investigate the factors contributing to the unique climate of the equator and its impact on global weather patterns.
- Understand biodiversity: Explore the rich biodiversity of equatorial rainforests and the importance of conservation efforts.
- Consider the human impact: Analyze how human activities, such as deforestation and climate change, affect the equator and its surrounding regions.
Conclusion:
The equator is more than just an imaginary line on a map. It is a powerful geographical feature that shapes our planet’s climate, biodiversity, and human civilization. Understanding the equator’s significance is crucial for comprehending the interconnectedness of our world and the importance of sustainable practices for preserving this vital region. As we continue to explore and learn from this unique part of our planet, we gain a deeper appreciation for the intricate web of life that sustains us all.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Equator: A Line of Division and Connection. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!