The Equator: A Line of Division and Connection
Related Articles: The Equator: A Line of Division and Connection
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Equator: A Line of Division and Connection. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: The Equator: A Line of Division and Connection
- 2 Introduction
- 3 The Equator: A Line of Division and Connection
- 3.1 A Line of Division: Understanding Latitude and Climate
- 3.2 A Line of Connection: Understanding Global Interactions
- 3.3 World Maps: Visualizing the Equator and Its Significance
- 3.4 The Importance of the Equator: A Summary
- 4 Frequently Asked Questions
- 5 Tips for Understanding the Equator
- 6 Conclusion
- 7 Closure
The Equator: A Line of Division and Connection

The equator, an imaginary line that circles the Earth at 0 degrees latitude, is more than just a geographical marker. It serves as a fundamental reference point for understanding the planet’s geography, climate, and cultural diversity. This article delves into the significance of the equator, exploring its impact on various aspects of the Earth and how its representation on world maps enhances our understanding of the world.
A Line of Division: Understanding Latitude and Climate
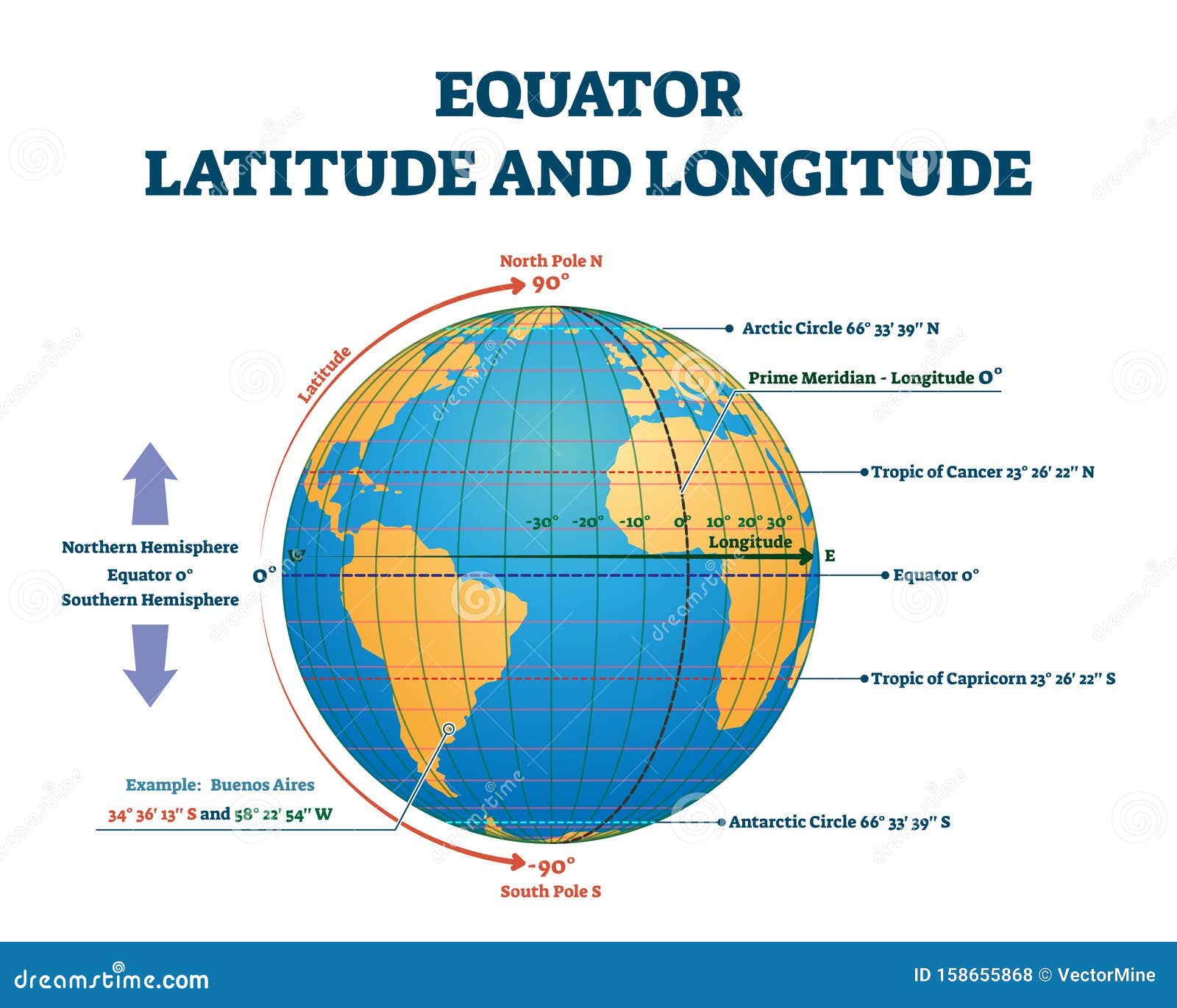
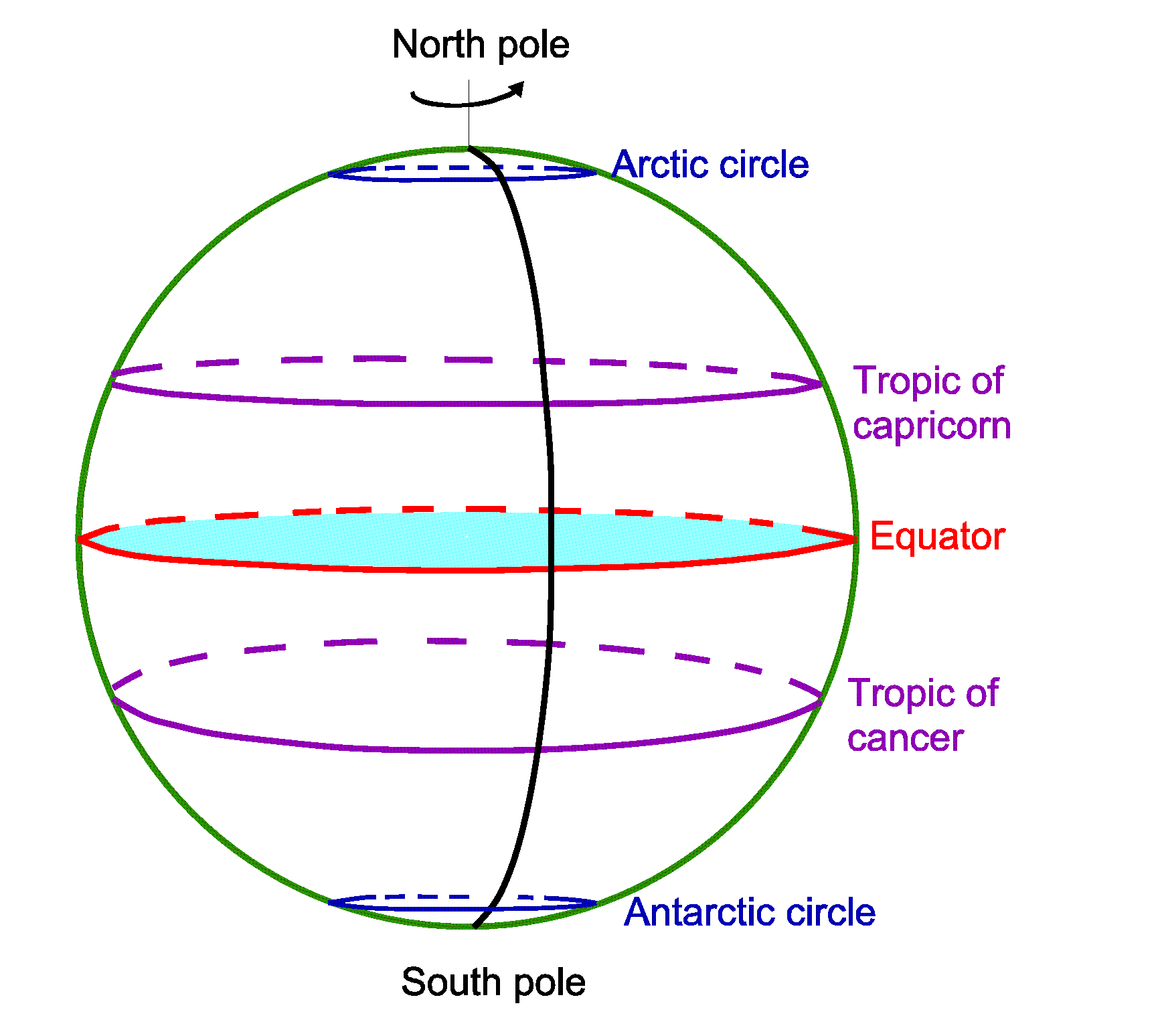
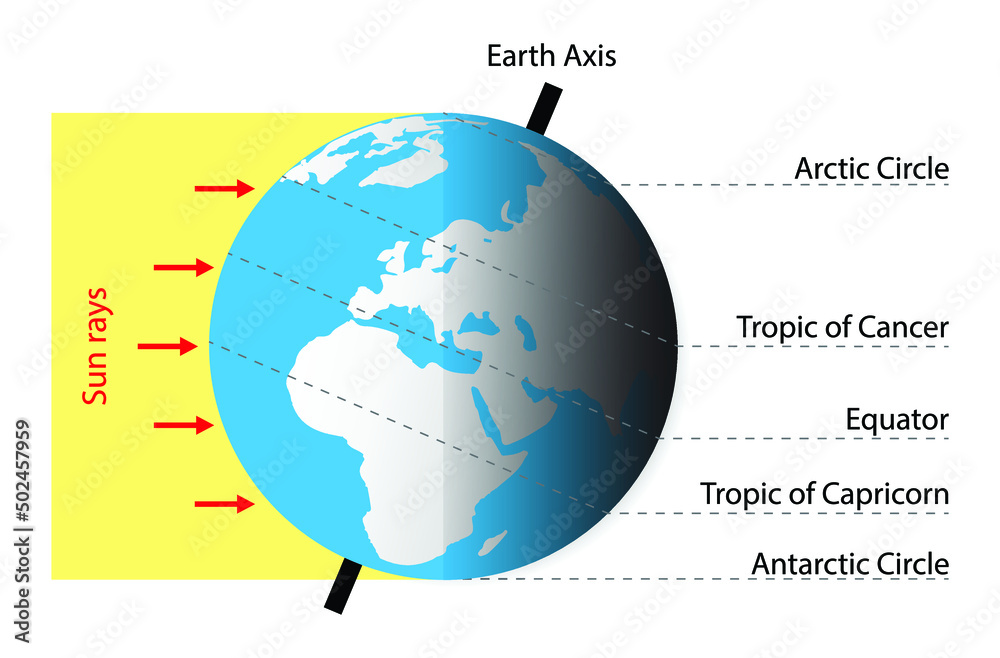
The equator acts as the primary line of division for measuring latitude, dividing the Earth into the Northern and Southern Hemispheres. This division is crucial for understanding global climate patterns. The equator, receiving direct sunlight throughout the year, experiences a tropical climate characterized by high temperatures and consistent rainfall. As one moves away from the equator, the angle of the sun’s rays decreases, leading to a gradual shift in climate zones.
The equator’s influence on climate is evident in the distribution of biomes. Tropical rainforests, teeming with biodiversity, flourish along the equator, while further north and south, savannas, grasslands, and deserts emerge. The equator’s position also dictates the length of day and night. At the equator, day and night are nearly equal throughout the year, while regions further from the equator experience significant variations in daylight hours.
A Line of Connection: Understanding Global Interactions
While the equator divides the Earth into hemispheres, it also serves as a point of connection for global interactions. The equatorial region, encompassing a diverse array of cultures, languages, and ecosystems, is a hub of global trade and communication. The equator’s location, straddling major oceans, facilitates the movement of goods and people across continents.
The equator’s influence on global trade is evident in the presence of major shipping lanes and ports along its path. These ports serve as gateways for international commerce, connecting distant markets and facilitating the exchange of goods and services. The equatorial region also plays a vital role in global agriculture, producing a significant portion of the world’s food supply.
World Maps: Visualizing the Equator and Its Significance
World maps, by depicting the equator, provide a visual representation of its importance. The equator serves as a reference line, helping us understand the relative positions of continents, oceans, and other geographical features. Furthermore, world maps often incorporate climate zones and other geographical data, illustrating the equator’s impact on global climate and biodiversity.
The choice of map projection can significantly influence the depiction of the equator and its relationship to other geographical features. While some projections accurately represent the equator as a straight line, others may distort its shape and position, impacting our understanding of global relationships.
The Importance of the Equator: A Summary
The equator, a seemingly simple line on a map, holds profound significance. It divides the Earth into hemispheres, influences global climate patterns, and serves as a vital connection point for global interactions. Understanding the equator’s impact on geography, climate, and cultural diversity is crucial for comprehending the complexities of our planet.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Why is the equator important?
The equator is important for several reasons:
- Latitude and Climate: It serves as the primary reference line for measuring latitude and understanding global climate patterns.
- Global Interactions: It connects continents and facilitates global trade, communication, and cultural exchange.
- Biodiversity: It is home to diverse ecosystems and a significant portion of the world’s biodiversity.
2. What is the significance of the equator’s location?
The equator’s location at 0 degrees latitude makes it the point on Earth where the sun’s rays hit directly, resulting in consistent high temperatures and rainfall, influencing climate and biodiversity.
3. How does the equator affect climate?
The equator receives direct sunlight throughout the year, leading to a tropical climate characterized by high temperatures and consistent rainfall. As one moves away from the equator, the angle of the sun’s rays decreases, resulting in a gradual shift in climate zones.
4. What are some examples of the equator’s influence on global interactions?
The equator’s location facilitates global trade through major shipping lanes and ports, connects distant markets, and contributes to global agriculture by producing a significant portion of the world’s food supply.
5. How is the equator depicted on world maps?
World maps often depict the equator as a straight line, serving as a reference point for understanding the relative positions of continents, oceans, and other geographical features. The choice of map projection can influence the depiction of the equator and its relationship to other features.
Tips for Understanding the Equator
- Use a Globe: Globes provide a more accurate representation of the Earth’s shape and the equator’s position compared to flat maps.
- Explore Online Resources: Websites and online maps offer interactive tools to visualize the equator and its impact on different regions.
- Study Climate Zones: Learn about the various climate zones and how they are influenced by the equator’s position.
- Research Equatorial Cultures: Explore the diverse cultures and traditions found along the equator, understanding their unique adaptations to the region’s climate and environment.
Conclusion
The equator, though an imaginary line, is a vital reference point for understanding our planet’s geography, climate, and cultural diversity. It divides the Earth into hemispheres, influences global climate patterns, and serves as a point of connection for global interactions. By recognizing the equator’s significance, we gain a deeper appreciation for the interconnectedness of our world and the vital role it plays in shaping human history and civilization.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Equator: A Line of Division and Connection. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!