The Equator: A Line of Distinction and Significance
Related Articles: The Equator: A Line of Distinction and Significance
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Equator: A Line of Distinction and Significance. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Equator: A Line of Distinction and Significance

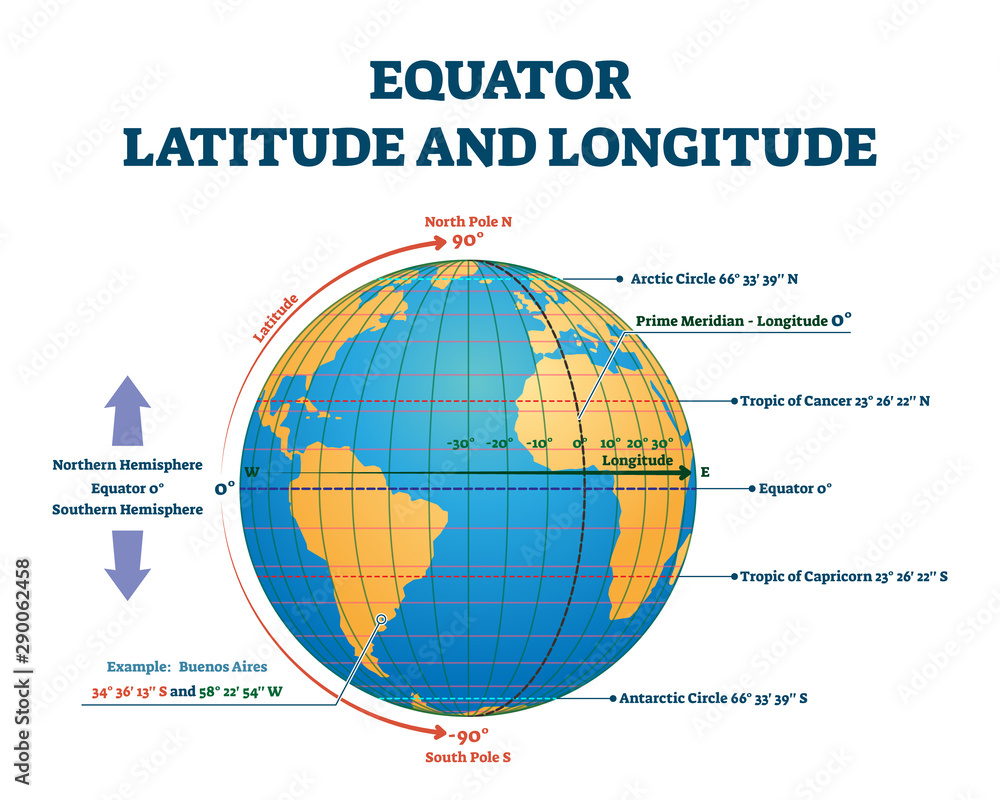
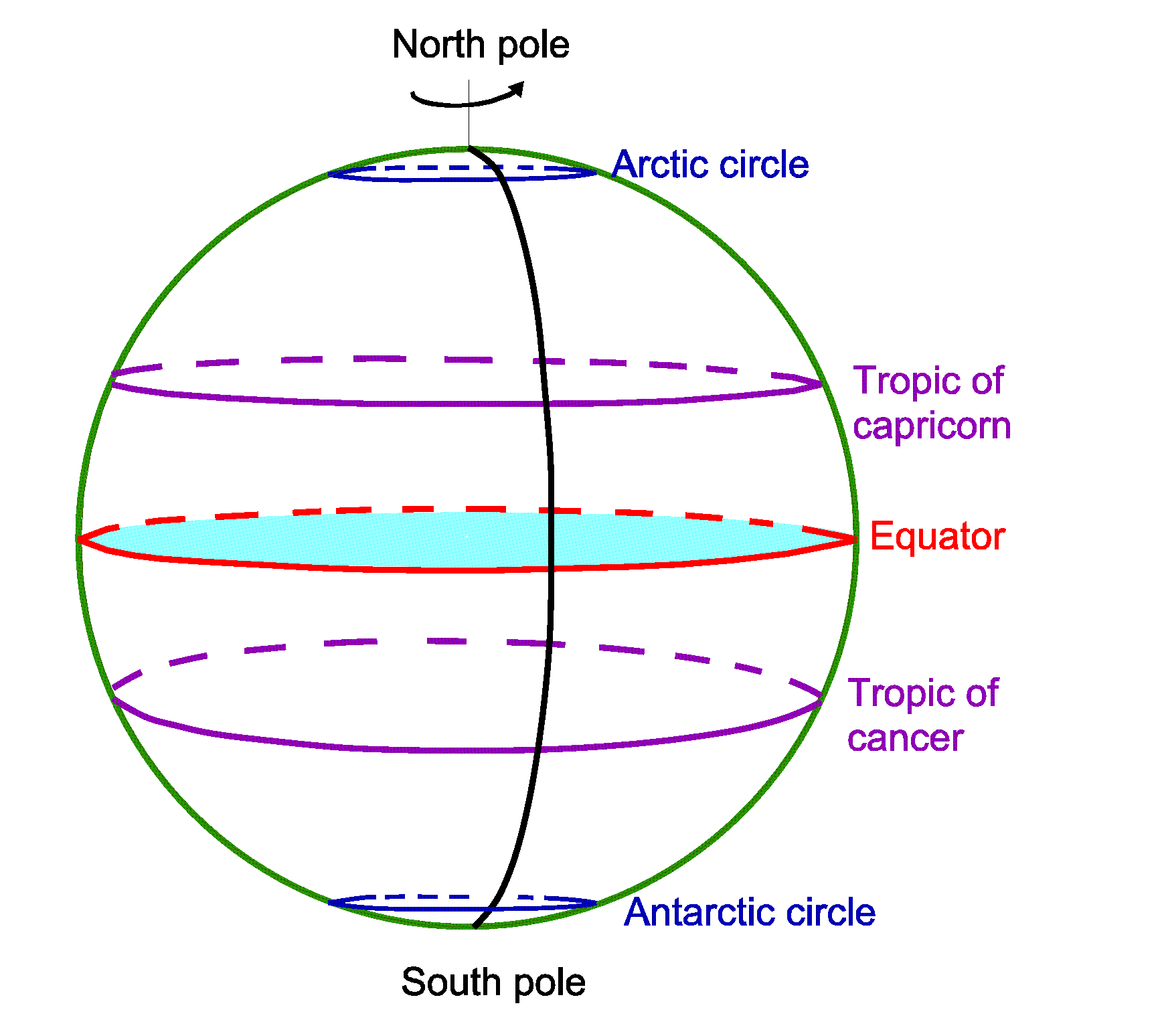
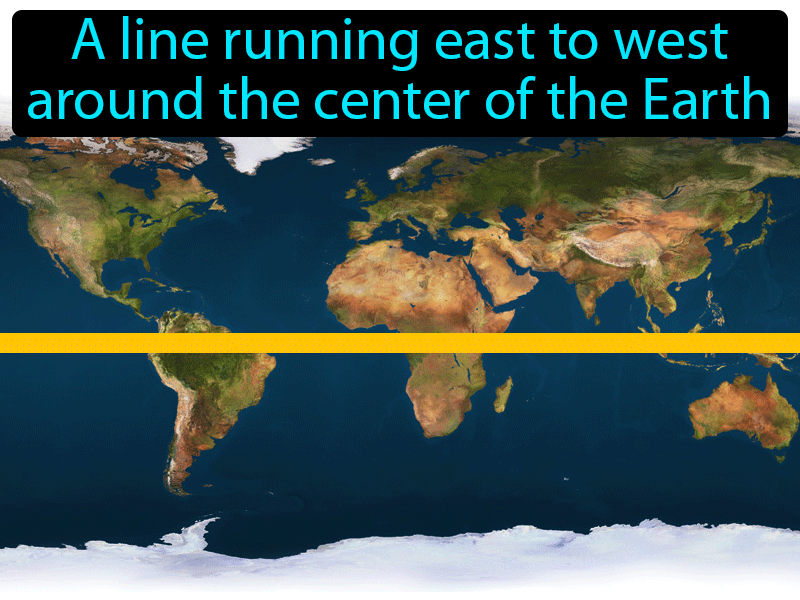
The equator, an imaginary line that circles the Earth at zero degrees latitude, is a fundamental reference point in geography, dividing the planet into the Northern and Southern Hemispheres. While it may appear as a simple line on a map, the equator holds immense significance, influencing climate, ecosystems, and human activity across the globe.
A Defining Line:
The equator’s primary function is to serve as a geographical dividing line. It bisects the Earth, separating the Northern Hemisphere from the Southern Hemisphere. This division is not merely symbolic; it carries profound implications for the planet’s climate, ecosystems, and the distribution of life.
Climate and the Equator:
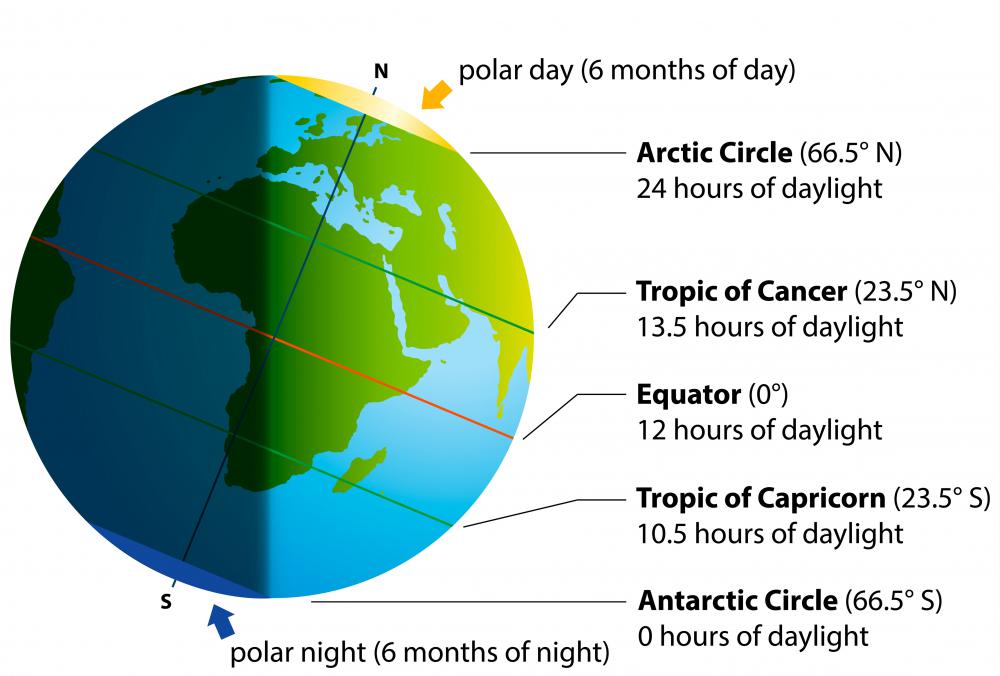
The equator’s position, directly under the sun’s rays, plays a crucial role in shaping global climate patterns. The region experiences consistent, high solar radiation throughout the year, leading to consistently warm temperatures and high humidity. This constant influx of solar energy fuels the formation of tropical rainforests, characterized by dense vegetation, abundant rainfall, and high biodiversity.
The equator’s influence extends beyond its immediate vicinity. The Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ), a band of low pressure and converging winds, shifts north and south of the equator throughout the year, bringing rain to different regions. This seasonal shift in the ITCZ influences the monsoon cycles in South Asia and Southeast Asia, impacting agricultural practices and water availability.
Ecosystems and Biodiversity:
The equator’s unique climate conditions foster a diversity of ecosystems, including tropical rainforests, savannas, and coral reefs. These ecosystems are teeming with life, harboring a disproportionately large percentage of the Earth’s biodiversity. The Amazon rainforest, for instance, is estimated to hold ten percent of the world’s known species, highlighting the immense ecological richness found along the equator.
The equator’s influence on biodiversity extends beyond terrestrial ecosystems. The warm, nutrient-rich waters of the equatorial oceans support vibrant coral reefs, home to a kaleidoscope of marine life. These reefs provide essential habitat for countless species and play a vital role in coastal protection and food security.
Human Activity and the Equator:
The equator’s significance extends to human activity. The region’s fertile soils and favorable climate have historically attracted human settlements, leading to the development of diverse cultures and civilizations. The equator’s proximity to the sun has also led to the development of solar energy technology, offering a sustainable alternative to fossil fuels.
However, the equator’s rich resources and strategic location have also made it vulnerable to exploitation and environmental degradation. Deforestation, pollution, and climate change threaten the unique ecosystems and biodiversity found along the equator. Sustainable development strategies are crucial to ensure the long-term well-being of the region and its inhabitants.
Navigating the Equator:
The equator is a crucial reference point for navigation, serving as the starting point for measuring latitude. Navigators and explorers have long relied on the equator to chart their courses and understand their position on Earth.
The Equator in Popular Culture:
The equator’s unique position and significance have captured the imagination of artists, writers, and explorers throughout history. From the ancient myths surrounding the "equatorial line" to contemporary depictions of the tropics, the equator has been a source of fascination and inspiration.
FAQs About the Equator:
Q: Is the equator a physical line?
A: No, the equator is an imaginary line that circles the Earth at zero degrees latitude. It is not a physical feature but a geographical reference point.
Q: How is the equator important for climate?
A: The equator receives consistent, high solar radiation, leading to warm temperatures and high humidity. This influences the formation of tropical rainforests and the Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ), which brings rain to different regions throughout the year.
Q: What are the main ecosystems found along the equator?
A: The equator is home to a variety of ecosystems, including tropical rainforests, savannas, and coral reefs. These ecosystems are characterized by high biodiversity and play a crucial role in global ecological balance.
Q: How does the equator affect human activity?
A: The equator’s fertile soils and favorable climate have attracted human settlements, leading to diverse cultures and civilizations. Its proximity to the sun has also led to the development of solar energy technology.
Q: What are the threats to the equator’s ecosystems?
A: Deforestation, pollution, and climate change pose significant threats to the unique ecosystems and biodiversity found along the equator. Sustainable development strategies are crucial to mitigate these threats.
Tips for Understanding the Equator:
- Use a globe or map to visualize the equator’s position and its division of the Earth into hemispheres.
- Explore the different ecosystems found along the equator, such as tropical rainforests, savannas, and coral reefs.
- Research the impact of the equator on climate patterns, particularly the Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ).
- Investigate the cultural and historical significance of the equator, exploring its influence on human settlements and civilizations.
- Learn about the challenges facing the equator’s ecosystems and the importance of sustainable development strategies.
Conclusion:
The equator, though an imaginary line on a map, represents a fundamental geographical division and a powerful influence on the planet’s climate, ecosystems, and human activity. Understanding the equator’s significance is essential for appreciating the interconnectedness of the Earth’s systems and for promoting sustainable practices that protect its unique and valuable resources.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Equator: A Line of Distinction and Significance. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!