The Equator: A Line of Distinction and Significance
Related Articles: The Equator: A Line of Distinction and Significance
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Equator: A Line of Distinction and Significance. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Equator: A Line of Distinction and Significance

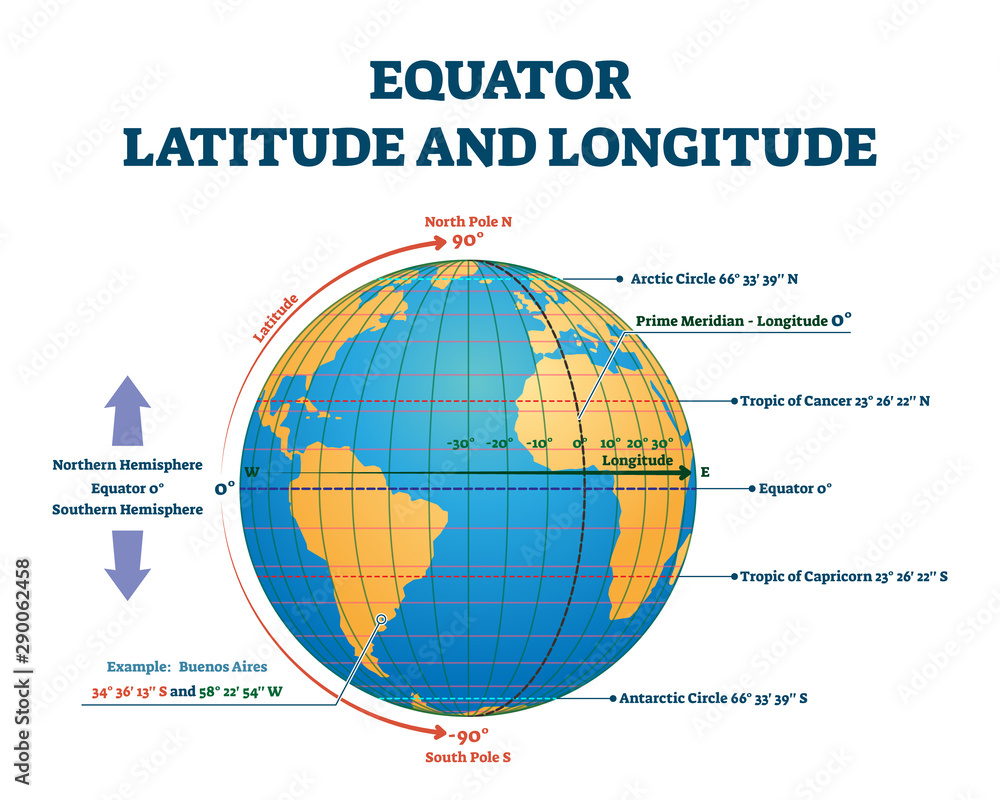
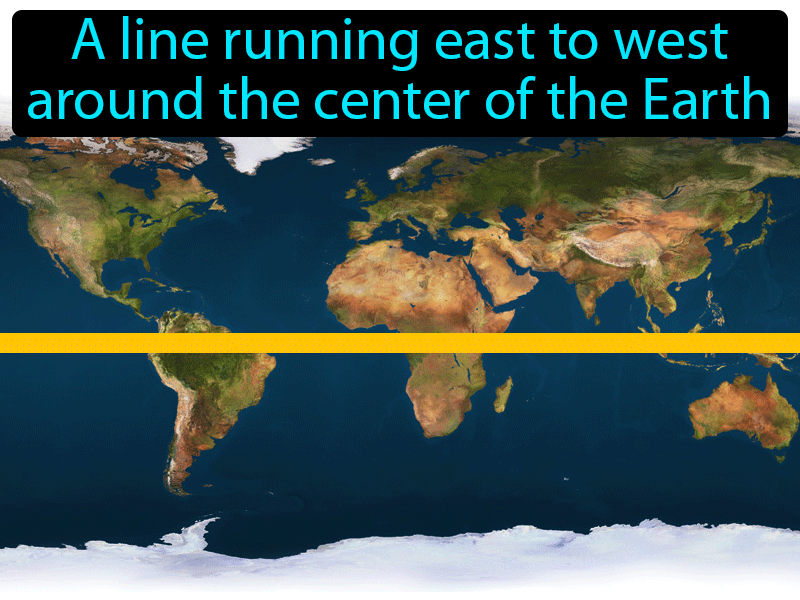
The Earth, a sphere suspended in the vastness of space, is often depicted on maps as a flat surface. These maps, however, can be deceiving, obscuring the planet’s true form and the crucial role played by the Equator. The Equator, an imaginary line encircling the Earth at 0 degrees latitude, serves as a pivotal reference point, dividing the globe into the Northern and Southern Hemispheres. It is a line that transcends mere geography, influencing climate, culture, and even the perception of time.
A Global Dividing Line:
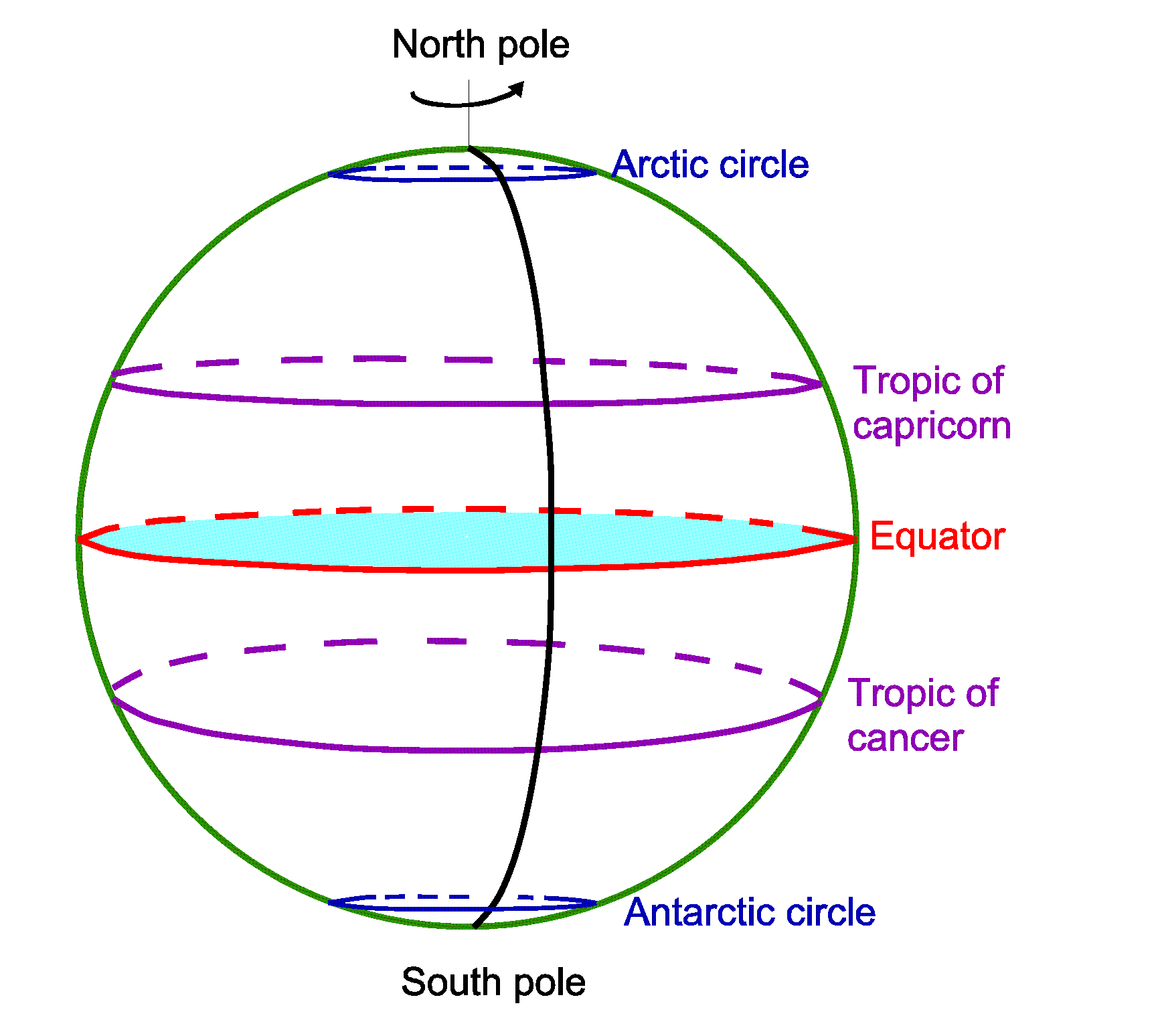
The Equator’s most immediate impact lies in its division of the Earth. This line, running through continents, oceans, and islands, defines the Northern and Southern Hemispheres. It is not merely a geographical boundary but a point of reference for understanding global patterns. For example, the Equator is a crucial marker for understanding the distribution of sunlight and its influence on climate.
Climate and the Equator:
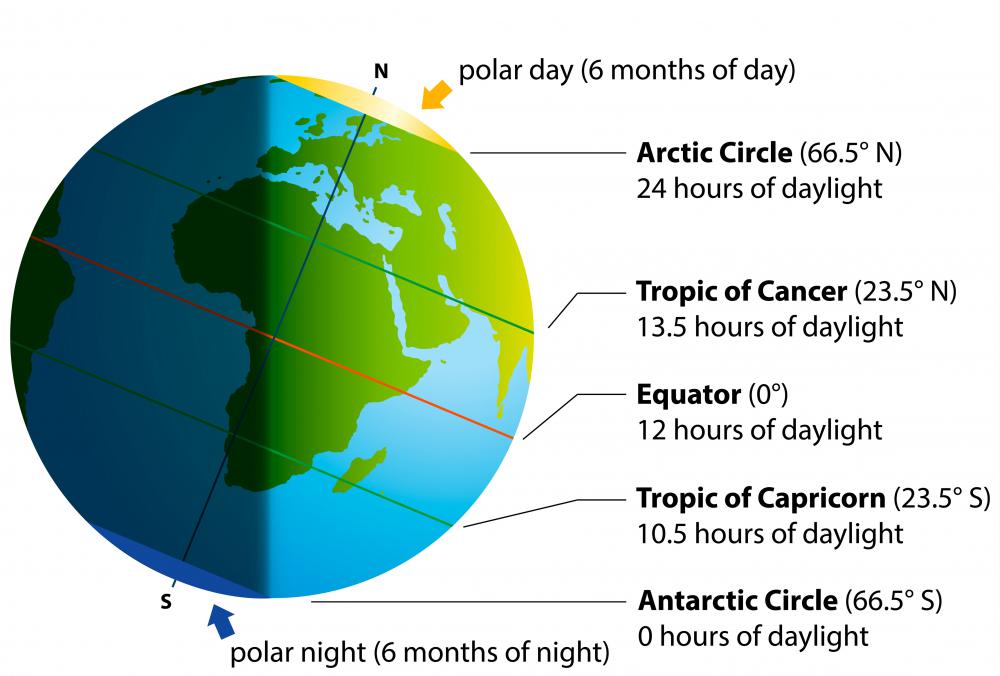
The Earth’s tilt on its axis and the Equator’s position directly influence climate patterns. The Equator receives the most direct sunlight throughout the year, leading to consistently high temperatures and a tropical climate. This region experiences minimal seasonal variation, characterized by consistent rainfall and lush vegetation. As one moves away from the Equator, the angle of sunlight decreases, resulting in cooler temperatures and distinct seasons.
Time Zones and the Equator:
The Equator plays a vital role in the establishment of time zones. The Earth rotates on its axis, completing one full rotation every 24 hours. To account for this rotation, the world is divided into 24 time zones, each encompassing 15 degrees of longitude. The Prime Meridian, another imaginary line running through Greenwich, England, marks the starting point for time zones. The Equator serves as a reference point for calculating time zones, with the time at the Prime Meridian being considered the standard time for the corresponding time zone.
Cultural Significance of the Equator:
The Equator is not just a geographical line; it has also become a cultural marker. Many cultures around the world have developed unique traditions and beliefs associated with the Equator. Some communities celebrate the Equator as a point of balance and harmony, while others view it as a source of power and spiritual energy. The Equator’s influence on cultural practices is evident in festivals, rituals, and even architectural designs.
Understanding the Importance of the Equator:
Maps that depict the Equator are essential tools for comprehending the Earth’s geography and its interconnectedness. By visualizing the Equator, we gain insights into:
- Global climate patterns: The Equator serves as a starting point for understanding how sunlight influences temperature and rainfall, shaping global climates.
- Time zone calculations: The Equator is crucial for understanding how time zones are determined, enabling communication and coordination across the globe.
- Cultural diversity: The Equator highlights the cultural diversity of the Earth, showcasing how different societies have interacted with and adapted to the unique characteristics of this important line.
FAQs about the Equator:
Q: What is the Equator?
A: The Equator is an imaginary line that circles the Earth at 0 degrees latitude, dividing it into the Northern and Southern Hemispheres.
Q: What is the significance of the Equator?
A: The Equator plays a significant role in determining climate patterns, time zones, and cultural practices.
Q: Does the Equator affect climate?
A: Yes, the Equator receives the most direct sunlight throughout the year, resulting in consistently high temperatures and a tropical climate.
Q: How does the Equator relate to time zones?
A: The Equator serves as a reference point for calculating time zones, with the time at the Prime Meridian being the standard time for the corresponding time zone.
Q: Are there any cultural traditions associated with the Equator?
A: Yes, many cultures have developed unique traditions and beliefs associated with the Equator, recognizing its significance in their lives.
Tips for understanding the Equator:
- Use a globe or map: Visualizing the Equator on a globe or map helps to understand its position and significance.
- Learn about latitude and longitude: Understanding these geographical coordinates is essential for grasping the concept of the Equator and its role in mapping the Earth.
- Explore different cultures: Researching cultures located near the Equator can provide valuable insights into how this line has influenced their traditions and beliefs.
Conclusion:
The Equator is more than just an imaginary line; it is a fundamental reference point for understanding the Earth’s geography, climate, and cultural diversity. Maps that depict the Equator serve as invaluable tools for comprehending global patterns and appreciating the interconnectedness of our planet. By acknowledging the significance of the Equator, we gain a deeper understanding of the Earth and its multifaceted nature.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Equator: A Line of Distinction and Significance. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!