The Equator: A Line of Distinction and Significance
Related Articles: The Equator: A Line of Distinction and Significance
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Equator: A Line of Distinction and Significance. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Equator: A Line of Distinction and Significance

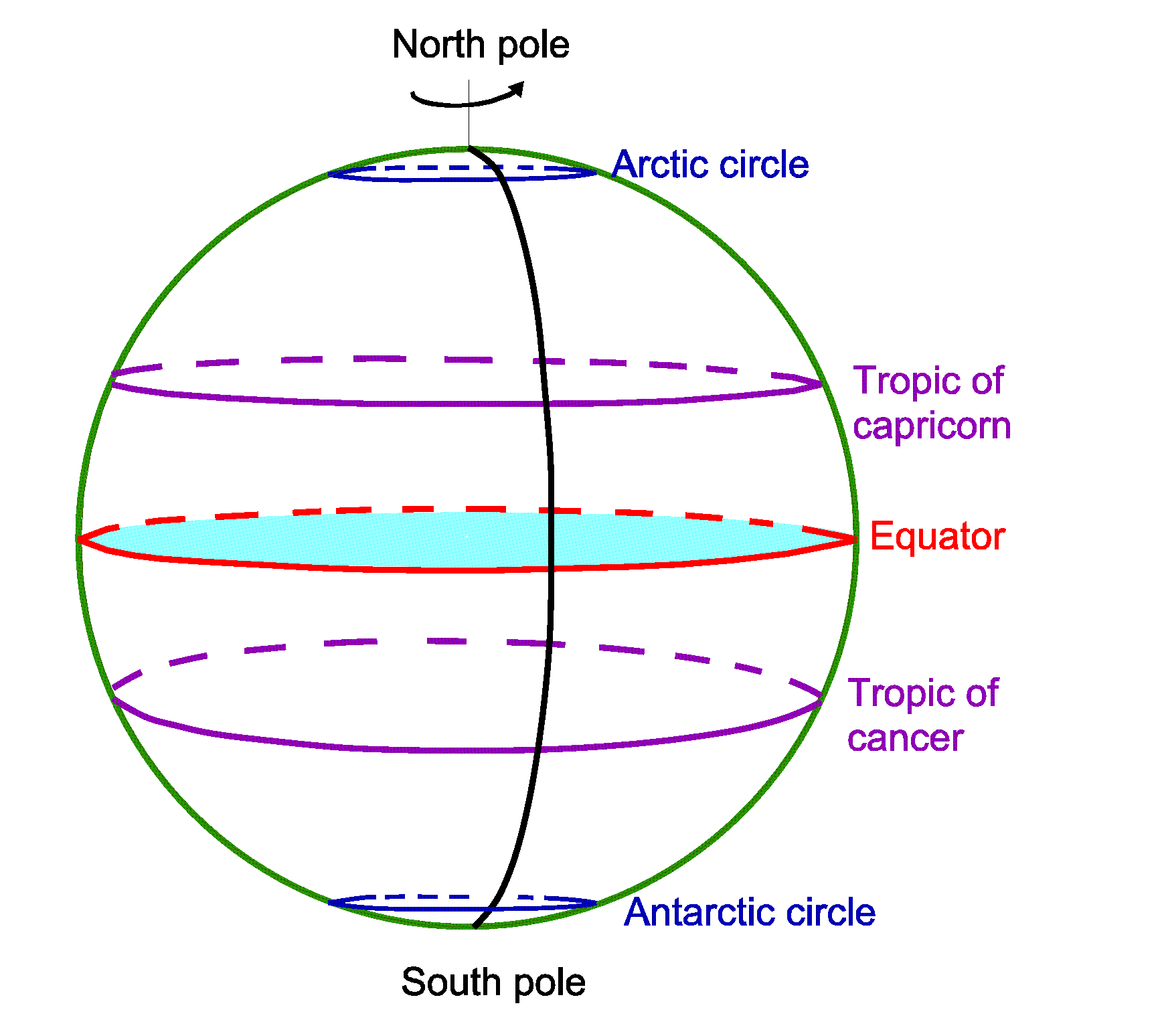
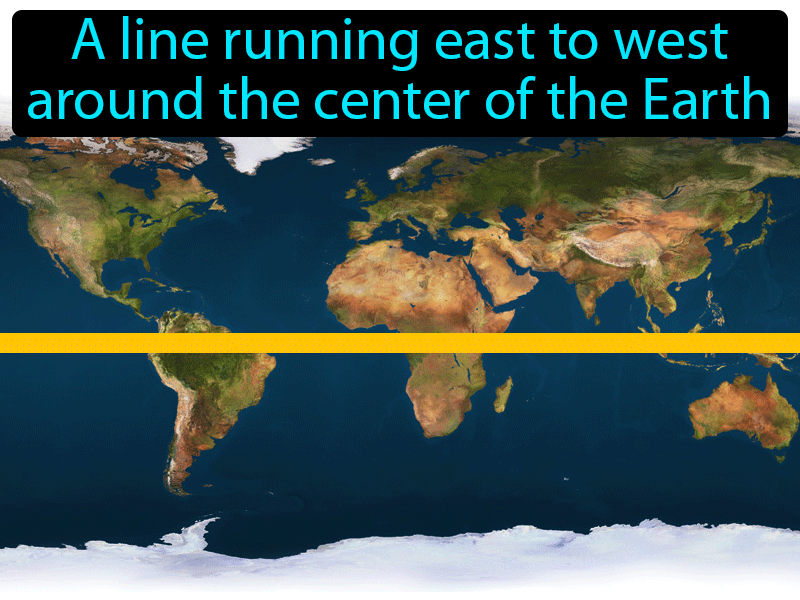
The equator, an imaginary line circling the Earth at 0 degrees latitude, serves as a fundamental reference point in geography and a defining feature of our planet’s physical and cultural landscape. This line, equidistant from the North and South Poles, divides the Earth into the Northern and Southern Hemispheres, influencing climate, ecosystems, and human societies in profound ways.
Defining the Equator: A Circle of Zero Degrees
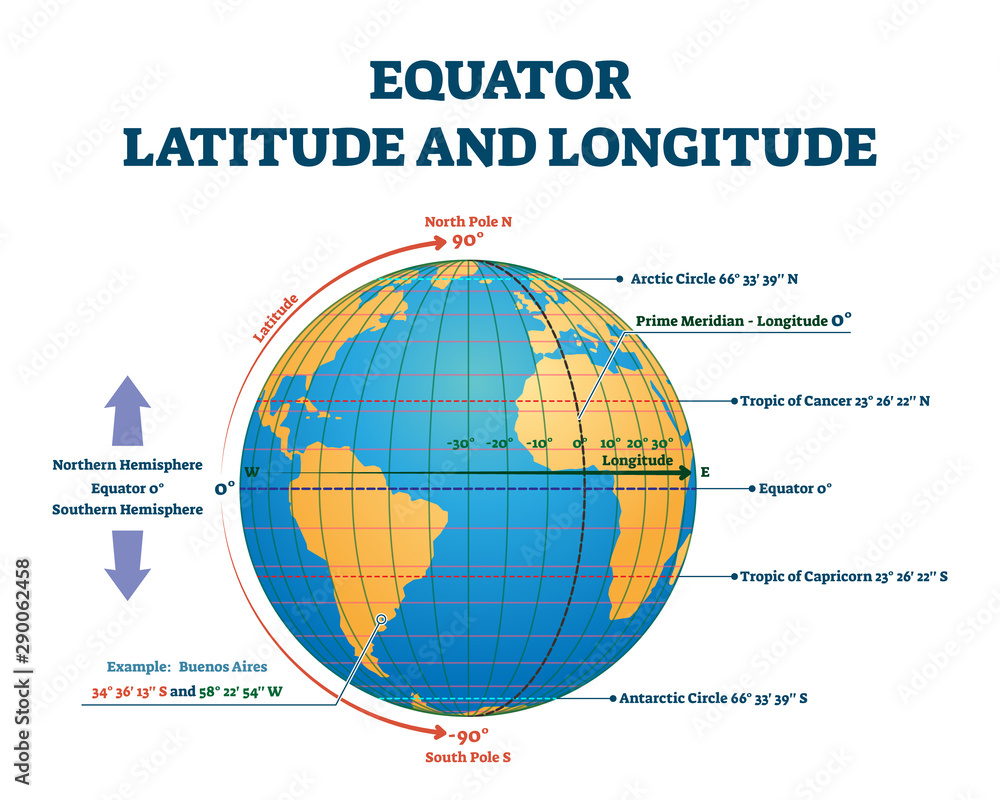
The equator is not a physical feature but a conceptual construct, defined by its position at 0 degrees latitude. This latitude, measured in degrees north or south of the equator, serves as a reference point for all other locations on Earth. It is the longest line of latitude, spanning approximately 40,075 kilometers (24,901 miles) around the Earth’s circumference.
The Equator’s Impact on Climate and Ecosystems
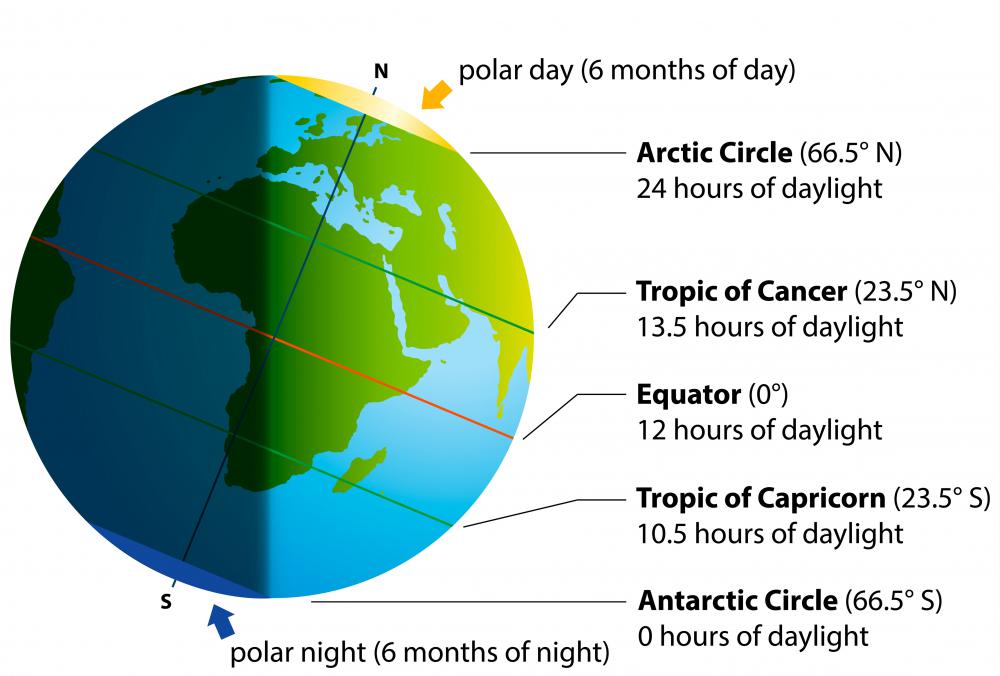
The equator’s location directly under the sun’s rays has a profound influence on global climate patterns. The intense solar radiation received at the equator drives a unique atmospheric circulation system, characterized by rising air masses, abundant rainfall, and the formation of tropical rainforests. This equatorial climate, characterized by consistently high temperatures and humidity, supports a diverse array of plant and animal life.
Tropical Rainforests: The Equator’s Green Jewel
The equator’s climatic influence fosters the development of tropical rainforests, the planet’s most biodiverse ecosystems. These dense, lush forests, found primarily within 10 degrees latitude north and south of the equator, are home to an astounding array of species, including countless plants, animals, insects, and microorganisms. The intricate web of life within these forests plays a vital role in regulating global climate, absorbing carbon dioxide, and providing essential resources for humanity.
The Equator’s Influence on Human Societies
The equator’s unique climate and ecosystems have significantly shaped human societies throughout history. The abundance of natural resources, including fertile land, abundant rainfall, and diverse plant and animal life, has attracted human settlements and fostered the development of distinct cultures and traditions. From the indigenous peoples of the Amazon rainforest to the diverse communities of Southeast Asia, the equator’s influence on human societies is undeniable.
The Equator’s Role in Navigation and Mapping
The equator serves as a fundamental reference point for navigation and mapping. Its position at 0 degrees latitude provides a clear baseline for measuring distances and directions. The global grid system, consisting of lines of latitude and longitude, uses the equator as its starting point, enabling accurate location identification and efficient navigation.
FAQs about the Equator:
Q: What is the significance of the equator?
A: The equator is a fundamental reference point in geography, dividing the Earth into the Northern and Southern Hemispheres and influencing climate, ecosystems, and human societies.
Q: How does the equator affect climate?
A: The equator’s location directly under the sun’s rays leads to intense solar radiation, driving a unique atmospheric circulation system characterized by rising air masses, abundant rainfall, and the formation of tropical rainforests.
Q: Why are tropical rainforests found near the equator?
A: The equator’s climate, characterized by consistently high temperatures and humidity, supports the growth of tropical rainforests, the planet’s most biodiverse ecosystems.
Q: How does the equator influence human societies?
A: The equator’s abundant natural resources, including fertile land, rainfall, and diverse plant and animal life, has attracted human settlements and fostered the development of distinct cultures and traditions.
Q: What is the role of the equator in navigation and mapping?
A: The equator serves as a reference point for navigation and mapping, providing a baseline for measuring distances and directions.
Tips for Understanding the Equator:
- Visualize the globe: Imagine the Earth as a sphere, and picture the equator as a circle around the middle, dividing it into two halves.
- Explore maps: Use maps to identify the equator and its relationship to other lines of latitude and longitude.
- Learn about climate zones: Understand how the equator’s climate influences the distribution of different climate zones around the world.
- Research ecosystems: Explore the unique ecosystems found near the equator, such as tropical rainforests and coral reefs.
- Investigate human societies: Discover how the equator has influenced human settlements, cultures, and traditions throughout history.
Conclusion:
The equator, a line of distinction and significance, plays a vital role in shaping our planet’s geography, climate, ecosystems, and human societies. Its influence extends beyond its physical location, impacting global patterns of weather, biodiversity, and human interaction. Understanding the equator’s importance is essential for appreciating the interconnectedness of our planet and the profound influence of natural forces on human life.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Equator: A Line of Distinction and Significance. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!