The Equator: A Line of Distinction and Discovery
Related Articles: The Equator: A Line of Distinction and Discovery
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Equator: A Line of Distinction and Discovery. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Equator: A Line of Distinction and Discovery

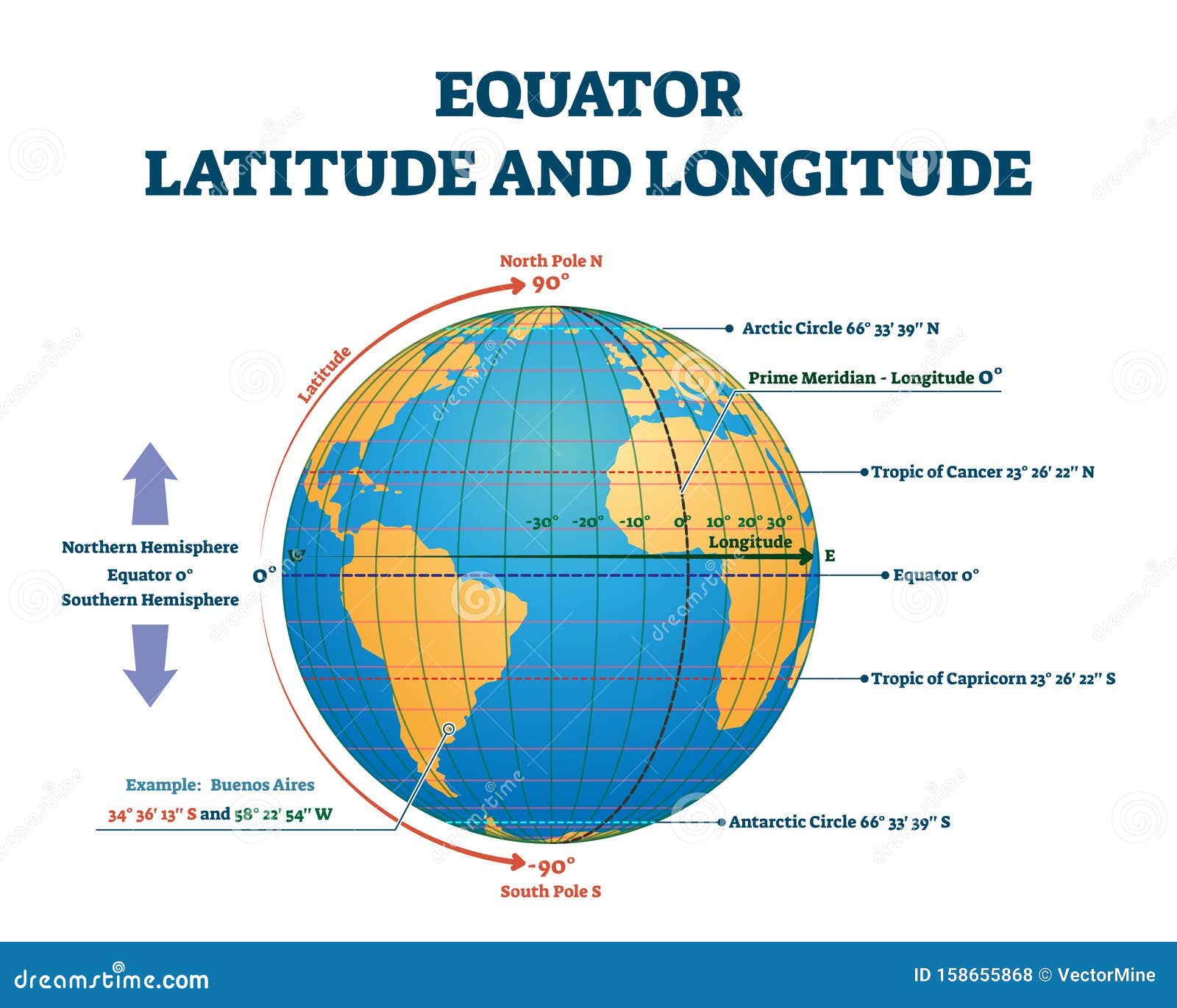
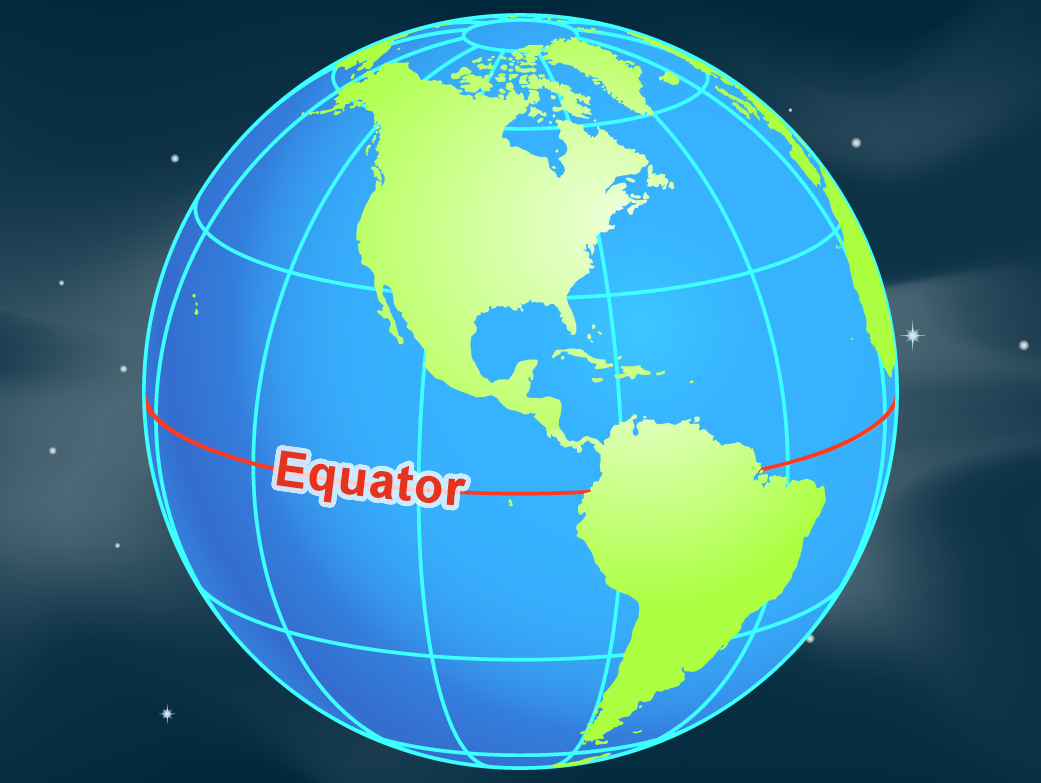
The equator, an imaginary line circling the Earth at 0 degrees latitude, is a fundamental geographical concept with profound implications for our understanding of the planet. It divides the Earth into the Northern and Southern Hemispheres, influencing climate, ecosystems, and human civilization. This article explores the significance of the equator, highlighting its role in cartography, climate patterns, and global interconnectedness.
A Line of Demarcation on the Global Canvas:
Maps depicting the equator serve as a visual representation of this crucial geographical feature. Its presence on maps is essential for understanding the Earth’s spatial organization and the distribution of various phenomena. The equator is often depicted as a bold, continuous line, clearly distinguishing the Northern and Southern Hemispheres. This visual distinction allows for easy identification of locations based on their latitude and provides a framework for understanding the global distribution of diverse geographical features, such as continents, oceans, and climate zones.
The Equator’s Influence on Climate and Ecosystems:
The equator’s position directly influences the Earth’s climate patterns. The sun’s rays strike the equator at a near-perpendicular angle, resulting in the highest concentration of solar radiation. This constant influx of solar energy creates a band of high temperatures along the equator, leading to the development of tropical rainforests and other unique ecosystems. The equatorial region experiences consistent high temperatures and rainfall, fostering biodiversity and supporting a wide range of flora and fauna.
Furthermore, the equator’s influence extends beyond the immediate region. The unequal distribution of solar energy between the equator and the poles drives atmospheric circulation patterns. The Hadley cells, a major atmospheric circulation pattern, are driven by the temperature differential between the equator and higher latitudes. This circulation results in the movement of air masses, precipitation patterns, and the formation of distinct climate zones across the globe.
The Equator’s Significance in Global Interconnectivity:
The equator is not merely a geographical line; it symbolizes the interconnectedness of the world. It serves as a focal point for global trade routes, facilitating the exchange of goods, ideas, and cultures. The equator’s position in the middle of the Earth makes it a natural hub for maritime transportation, connecting continents and fostering economic and cultural exchanges.
Moreover, the equator’s influence extends to the realm of human history and civilization. Many ancient civilizations flourished along the equatorial regions, benefiting from the abundant resources and fertile lands. These civilizations developed unique cultural practices, languages, and traditions that have shaped the course of human history.
FAQs: Unraveling the Mysteries of the Equator
Q: What are the exact coordinates of the equator?
A: The equator is defined as 0 degrees latitude. It is an imaginary line that circles the Earth at an equal distance from the North and South Poles.
Q: Why is the equator important for navigation?
A: The equator serves as a reference point for latitude measurements, which are essential for navigation and mapping. Latitude lines run parallel to the equator, allowing for precise location identification.
Q: What are some of the unique characteristics of equatorial ecosystems?
A: Equatorial ecosystems are characterized by high biodiversity, dense vegetation, and a constant warm and humid climate. They support a wide range of flora and fauna, including tropical rainforests, mangrove swamps, and coral reefs.
Q: Does the equator pass through any continents?
A: Yes, the equator passes through South America, Africa, Asia, and Oceania. It also intersects with the Pacific Ocean, the Atlantic Ocean, and the Indian Ocean.
Tips for Understanding and Visualizing the Equator:
- Utilize globes and maps: Globes provide a three-dimensional representation of the Earth, allowing for a better understanding of the equator’s position and its relationship to other geographical features.
- Explore online resources: Numerous websites and interactive maps offer detailed information about the equator and its significance.
- Engage in real-world applications: Consider exploring local landmarks or geographical features that lie on or near the equator.
Conclusion: The Equator’s Enduring Relevance
The equator, a seemingly simple line on a map, holds profound significance for our understanding of the Earth’s geography, climate, and global interconnectedness. Its influence extends to diverse fields, from cartography and navigation to climate science and cultural studies. By recognizing the importance of the equator, we gain a deeper appreciation for the complexities and interconnectedness of our planet.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Equator: A Line of Distinction and Discovery. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!