The Equator: A Line Dividing the World and Shaping Our Understanding
Related Articles: The Equator: A Line Dividing the World and Shaping Our Understanding
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Equator: A Line Dividing the World and Shaping Our Understanding. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Equator: A Line Dividing the World and Shaping Our Understanding
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/1280px-World_map_with_equator-5c4e470b46e0fb00014c3710.jpg)
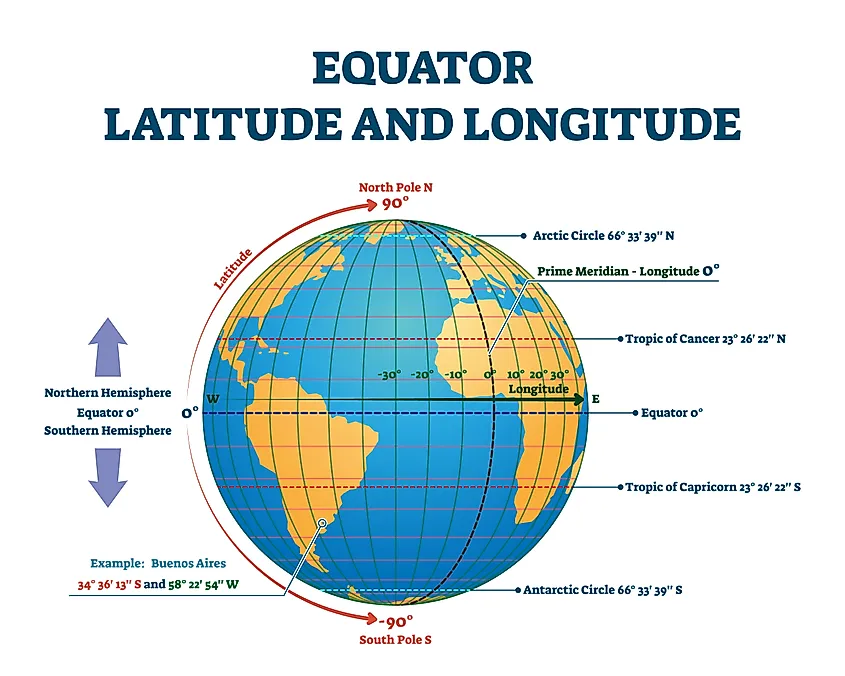
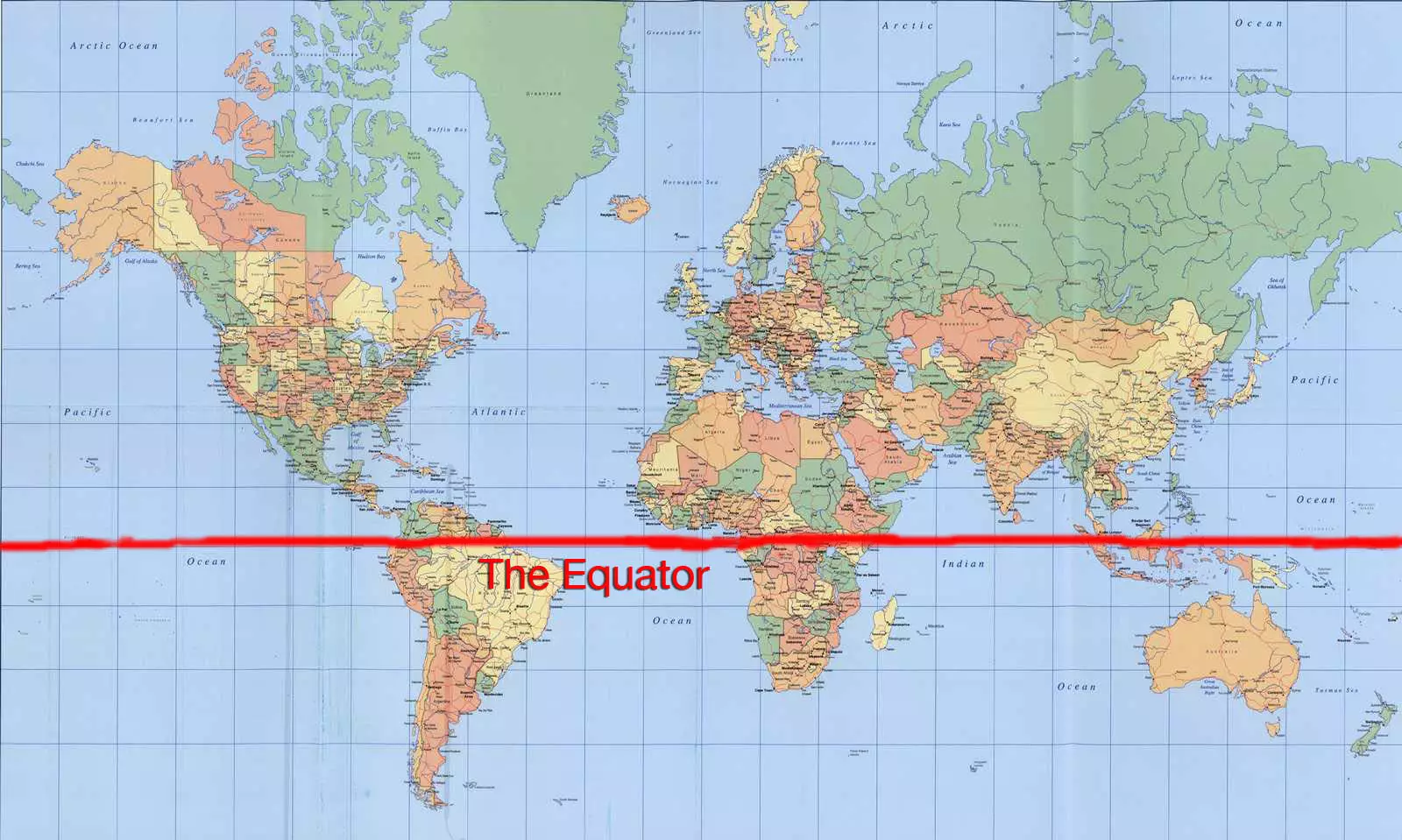
The Earth, our home planet, is a dynamic sphere constantly rotating on its axis. This rotation creates an imaginary line that circles the globe at 0 degrees latitude, dividing it into two hemispheres: the Northern Hemisphere and the Southern Hemisphere. This line, known as the equator, is a fundamental geographical feature that plays a crucial role in shaping our understanding of the world and its diverse environments.
Understanding the Equator: A Geographic Perspective
The equator is not merely a line drawn on a map; it represents a specific location on Earth with distinct characteristics. Its significance lies in its position relative to the sun’s rays, influencing climate, time zones, and even cultural and economic development.
-
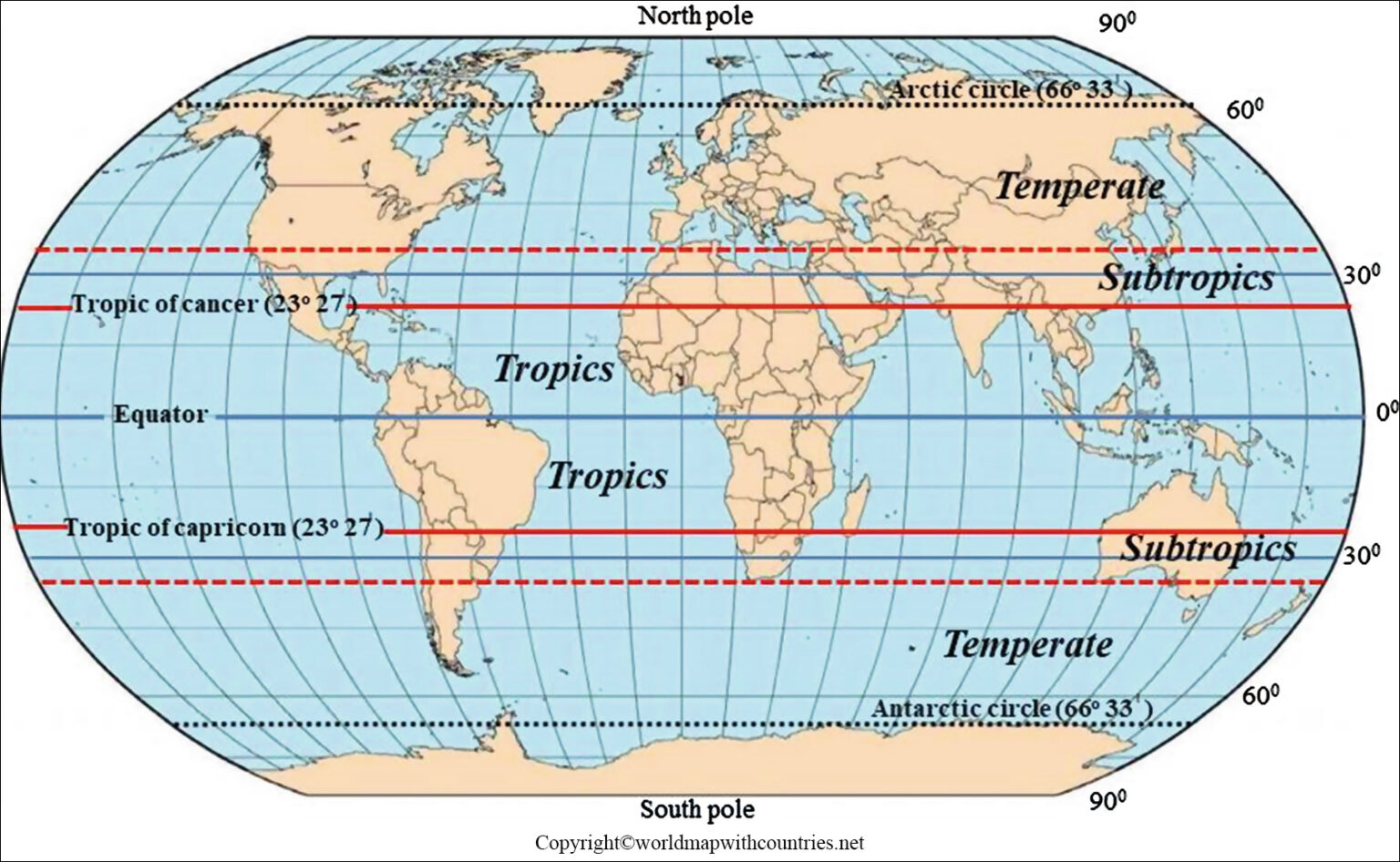
Climate and Weather Patterns: The equator receives the most direct sunlight throughout the year, leading to consistent high temperatures and a tropical climate. This consistent warmth fosters the growth of dense rainforests, abundant biodiversity, and unique ecosystems. Regions closer to the equator experience less variation in day length and temperature throughout the year, resulting in more predictable weather patterns.
-
Time Zones: The equator is a crucial reference point for establishing time zones. The Earth is divided into 24 time zones, each representing a one-hour difference. The International Date Line, which marks the transition between days, roughly follows the 180th meridian, running close to the equator.
-
Cultural and Economic Significance: The equator has long influenced human settlement patterns and cultural development. Many ancient civilizations thrived near the equator, taking advantage of its fertile land and abundant resources. Today, equatorial regions are home to diverse cultures and economies, with major agricultural production, tourism, and resource extraction industries.
Visualizing the Equator: The Importance of Maps
Maps are essential tools for understanding the world and its geographic features. Maps that depict the equator clearly provide a visual representation of its significance and allow us to explore its impact on different regions.
-
Global Perspective: World maps with the equator prominently displayed offer a global perspective, highlighting the equator’s role as a dividing line between the Northern and Southern Hemispheres. This visualization helps us understand the distribution of landmasses, oceans, and major geographical features across the globe.
-
Regional Focus: Maps that zoom in on specific regions along the equator provide detailed insights into local environments, climate, and cultural landscapes. These maps can be used to study the effects of the equator on specific ecosystems, agricultural practices, and human settlement patterns.
-
Navigational Aid: Maps with the equator clearly marked serve as navigational aids, guiding explorers, sailors, and travelers across the globe. The equator acts as a reference point for determining latitude and longitude, facilitating accurate navigation and understanding of geographic locations.
Exploring the Equator: Beyond the Line
The equator is not merely a geographical boundary; it is a vibrant and dynamic region brimming with life and cultural diversity. Exploring the equator through maps and other resources offers a glimpse into the fascinating world that exists along this unique line.
-
Rainforests and Biodiversity: The Amazon rainforest, the Congo rainforest, and the Indonesian rainforest are just a few examples of the vast and diverse ecosystems found along the equator. These rainforests are home to an incredible array of plant and animal species, representing a significant portion of global biodiversity.
-
Cultural Heritage and Traditions: The equator is a meeting point for diverse cultures and traditions. From the indigenous communities of the Amazon to the vibrant cities of Southeast Asia, the equatorial region showcases a rich tapestry of languages, religions, and artistic expressions.
-
Economic Opportunities and Challenges: Equatorial regions face a range of economic opportunities and challenges. The abundance of natural resources, fertile land, and diverse ecosystems present potential for economic growth. However, these regions also face challenges related to environmental conservation, sustainable development, and social equity.
FAQs About the Equator
Q: Is the equator a straight line?
A: No, the equator is a circle that encircles the Earth at 0 degrees latitude. While it appears as a straight line on many maps, it is actually a curved line that follows the Earth’s spherical shape.
Q: What are the effects of the equator on climate?
A: The equator receives the most direct sunlight throughout the year, resulting in consistently high temperatures and a tropical climate. This consistent warmth fosters the growth of dense rainforests, abundant biodiversity, and unique ecosystems.
Q: What are some of the major cities located near the equator?
A: Some major cities located near the equator include Quito (Ecuador), Nairobi (Kenya), Singapore, and Jakarta (Indonesia).
Q: How does the equator affect time zones?
A: The equator is a crucial reference point for establishing time zones. The Earth is divided into 24 time zones, each representing a one-hour difference. The International Date Line, which marks the transition between days, roughly follows the 180th meridian, running close to the equator.
Tips for Studying the Equator
- Use interactive maps: Explore online maps that allow you to zoom in and out of the equator, providing detailed views of different regions and their geographical features.
- Read about equatorial ecosystems: Dive into the world of rainforests, coral reefs, and other unique ecosystems found along the equator, learning about their biodiversity and ecological importance.
- Discover equatorial cultures: Explore the rich cultural heritage of equatorial regions, learning about indigenous traditions, languages, and artistic expressions.
- Consider the challenges and opportunities: Explore the economic, environmental, and social challenges and opportunities facing equatorial regions, understanding the complexities of sustainable development and conservation.
Conclusion
The equator, a seemingly simple line on a map, holds profound significance in shaping our understanding of the world. It influences climate, time zones, and cultural development, creating a unique and dynamic region that deserves our attention and exploration. By studying the equator through maps and other resources, we gain valuable insights into the interconnectedness of our planet and the diverse wonders that exist along this vital line.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Equator: A Line Dividing the World and Shaping Our Understanding. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!