The Equator: A Line Dividing the World
Related Articles: The Equator: A Line Dividing the World
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Equator: A Line Dividing the World. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Equator: A Line Dividing the World

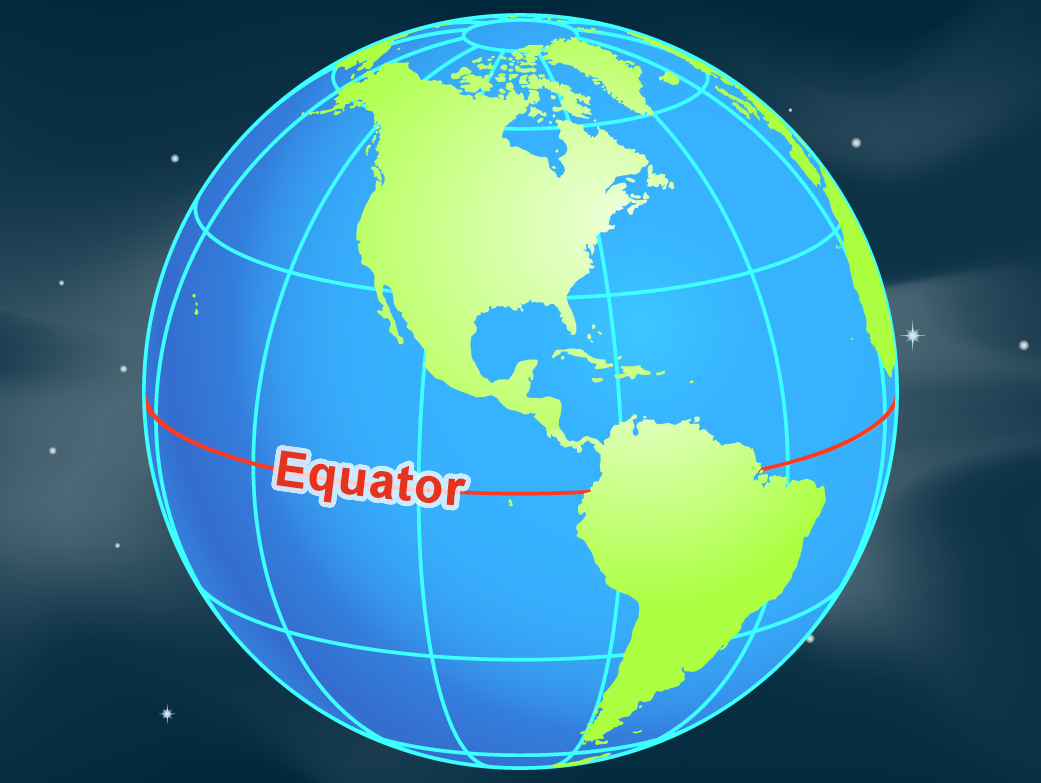
The equator, an imaginary line encircling the Earth at zero degrees latitude, plays a pivotal role in our understanding of the planet’s geography and climate. It serves as a fundamental reference point, dividing the globe into the Northern and Southern Hemispheres. This seemingly simple line holds immense significance, influencing everything from weather patterns to cultural diversity.
Understanding Latitude and the Equator’s Position
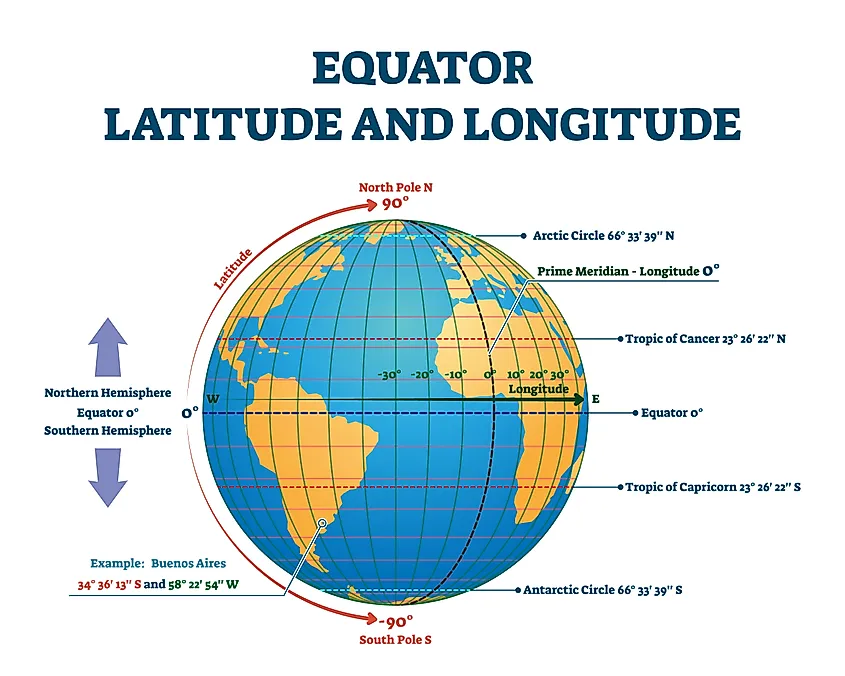
Latitude, measured in degrees north or south of the equator, provides a crucial framework for locating points on Earth. The equator, positioned at 0° latitude, represents the line that bisects the Earth into two equal halves. It is the widest circumference of the planet, spanning approximately 40,075 kilometers (24,901 miles).
The Equator’s Influence on Climate
The equator’s position is central to understanding global climate patterns. Due to its location, the region receives the most direct sunlight throughout the year, leading to consistently high temperatures. This constant solar radiation drives the formation of tropical rainforests, characterized by lush vegetation, high humidity, and abundant rainfall.
The equator’s influence extends beyond the tropics. It acts as a boundary between the Earth’s major wind belts, influencing the direction and intensity of prevailing winds. The Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ), a band of low pressure found near the equator, is a key driver of weather patterns in the tropics, often leading to heavy rainfall and thunderstorms.
The Equator’s Impact on Culture and Geography
The equator’s influence extends beyond climate, shaping cultural landscapes and geographic features. The equatorial regions boast a diverse range of ecosystems, from rainforests to savannas and coral reefs, each harboring unique flora and fauna.
The equatorial regions are also home to a vast array of cultures, each with its own traditions, languages, and customs. The diversity of cultures found along the equator reflects the region’s rich history and the influence of various civilizations throughout the ages.
Navigational Significance and Global Importance
The equator serves as a fundamental reference point for navigation and mapping. It is used to determine the position of ships, airplanes, and satellites, facilitating accurate global positioning and communication.
The equator’s importance extends beyond navigation. It plays a vital role in international law and diplomacy, defining territorial boundaries and influencing geopolitical relations. The equator’s location has been a subject of debate and negotiation, shaping international agreements and influencing the distribution of resources.
FAQs about the Equator
1. Does the equator pass through any countries?
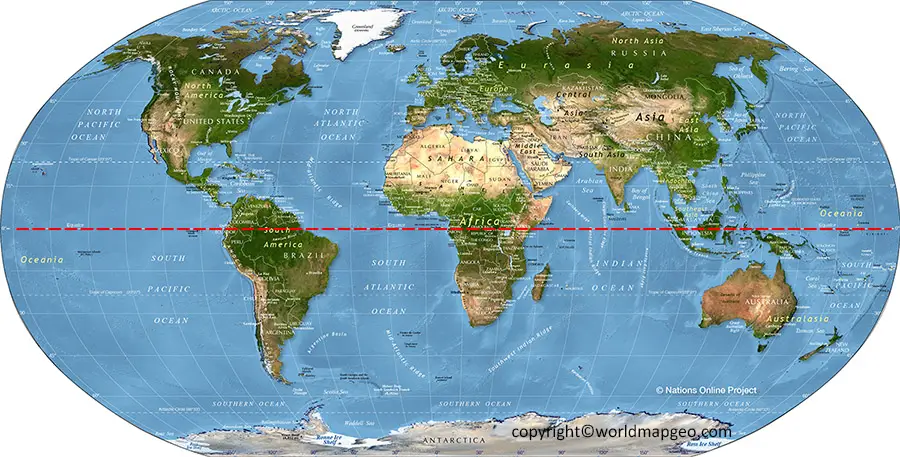
Yes, the equator passes through 14 countries: Ecuador, Colombia, Brazil, São Tomé and Príncipe, Gabon, Republic of the Congo, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Uganda, Kenya, Somalia, Maldives, Indonesia, Kiribati, and Ecuador.
2. What is the significance of the equator’s position?
The equator’s position is significant because it defines the boundary between the Northern and Southern Hemispheres. It also influences climate patterns, cultural diversity, and navigation.
3. What are the benefits of living near the equator?
Living near the equator offers benefits such as consistent sunshine, warm temperatures, and diverse ecosystems. However, it also presents challenges such as high humidity, potential for extreme weather events, and a greater risk of certain diseases.
4. Is the equator a fixed line?
The equator is not a fixed line. Due to the Earth’s rotation and gravitational forces, the equator experiences slight shifts over time. However, these changes are minimal and do not significantly alter its overall position.
5. How does the equator affect the Earth’s rotation?
The equator is the fastest-moving part of the Earth’s surface due to its greater circumference. This rotation influences the Earth’s magnetic field and contributes to the Coriolis effect, which influences weather patterns and ocean currents.
Tips for Understanding the Equator
- Use a globe or map: Visualizing the equator on a globe or map provides a clear understanding of its position and its relationship to other geographical features.
- Explore online resources: Numerous websites and educational platforms offer detailed information about the equator, its influence on climate, and its cultural significance.
- Engage with documentaries and films: Documentaries and films often depict the equatorial regions, showcasing their diverse ecosystems and the people who live there.
Conclusion
The equator, an imaginary line encircling the Earth at zero degrees latitude, plays a crucial role in our understanding of the planet. It influences climate patterns, shapes cultural landscapes, and serves as a fundamental reference point for navigation and mapping. From its impact on the Earth’s rotation to its role in international law, the equator remains a vital element in our understanding of the world we live in. Understanding the equator’s significance provides a deeper appreciation for the complexities of our planet and the interconnectedness of its various systems.


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Equator: A Line Dividing the World. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!