The Equator: A Line Dividing the World
Related Articles: The Equator: A Line Dividing the World
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Equator: A Line Dividing the World. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Equator: A Line Dividing the World

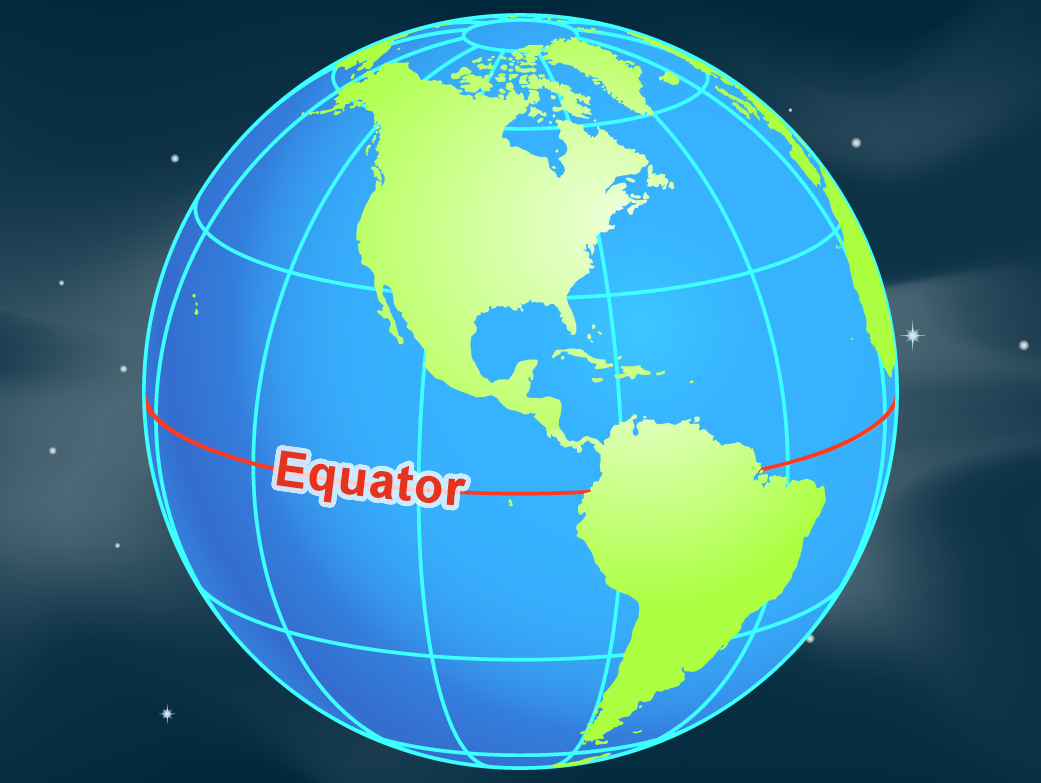
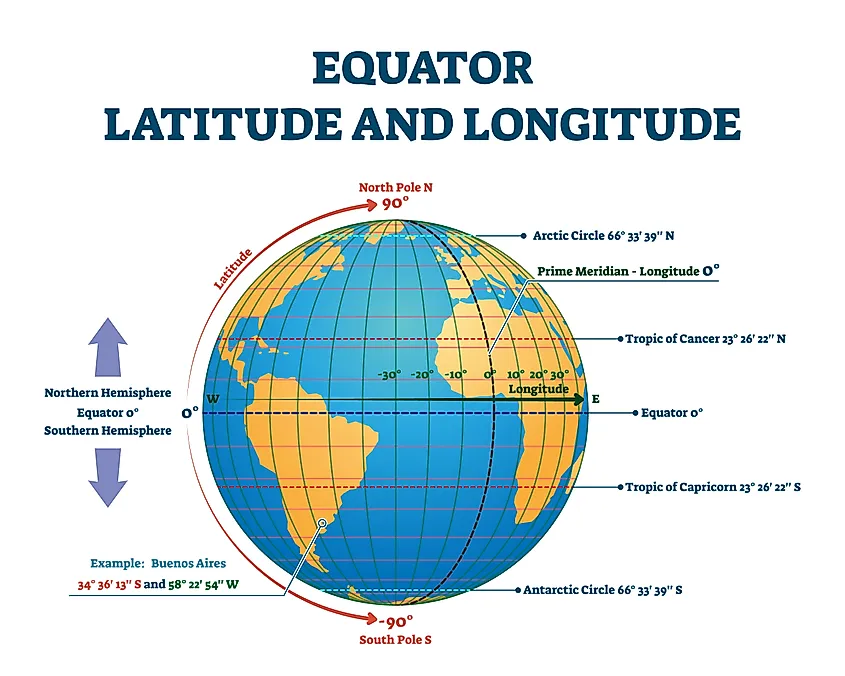
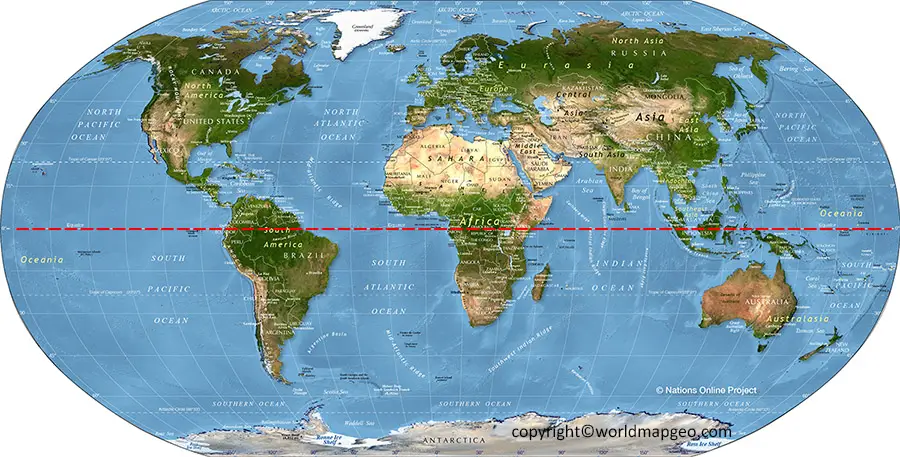
The equator, an imaginary line encircling the Earth at 0 degrees latitude, holds a significant place in our understanding of the planet. It serves as a fundamental reference point for geographical coordinates, influencing climate, day-night cycles, and even the Earth’s shape.
A Line of Demarcation:
The equator divides the Earth into two hemispheres: the Northern Hemisphere and the Southern Hemisphere. This division is not merely geographical; it has profound implications for the distribution of sunlight, temperature, and weather patterns.
The Sun’s Embrace:
The equator experiences the most direct sunlight throughout the year. This is because the Earth’s axis of rotation is tilted at an angle of 23.5 degrees, causing the sun’s rays to fall most directly on the equator during the equinoxes. This constant exposure to solar radiation results in a consistently warm climate along the equator, characterized by high temperatures and humidity.
The Rhythm of Day and Night:
The equator experiences nearly equal day and night lengths throughout the year. This is because the equator is situated at a point where the Earth’s axis of rotation is perpendicular to the sun’s rays during the equinoxes. This results in a relatively stable day-night cycle, unlike regions closer to the poles where the duration of daylight varies significantly throughout the year.
A Defining Influence on Climate:
The equator’s location and the resulting solar energy it receives play a crucial role in shaping global climate patterns. The intense sunlight and warm temperatures lead to high rates of evaporation, creating a band of low atmospheric pressure known as the Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ). This zone is characterized by frequent rainfall and thunderstorms, contributing to the lush vegetation and high biodiversity found in tropical regions.
The Earth’s Shape:
The equator is not just a line on a map; it also serves as a reference point for understanding the Earth’s shape. The Earth is not a perfect sphere but rather an oblate spheroid, meaning it is slightly flattened at the poles and bulging at the equator. This bulge is a result of the Earth’s rotation, which causes centrifugal force to push outwards at the equator.
The Equatorial Belt:
The region encompassing the equator, known as the equatorial belt, is home to some of the most diverse ecosystems on Earth. From the Amazon rainforest in South America to the Congo Basin in Africa, the equatorial belt is characterized by dense vegetation, high biodiversity, and abundant rainfall. This region is crucial for regulating global climate and providing vital ecosystem services.
Navigational Significance:
The equator plays a vital role in navigation and cartography. It serves as the zero-degree line of latitude, providing a reference point for calculating distances and directions. This makes it an essential tool for sailors, pilots, and explorers navigating the globe.
Beyond the Line:
The equator’s influence extends beyond the geographical line itself. It serves as a symbol of unity, connecting diverse cultures and ecosystems across the globe. It is a reminder of the interconnectedness of our planet and the need for global cooperation to address shared challenges.
FAQs:
Q: Is the equator a physical feature on Earth?
A: No, the equator is an imaginary line, not a physical feature. It is defined as the circle that lies at 0 degrees latitude, equidistant from the North and South Poles.
Q: What is the difference between the equator and the prime meridian?
A: The equator is a line of latitude that circles the Earth horizontally, while the prime meridian is a line of longitude that runs vertically from the North Pole to the South Pole. The equator divides the Earth into the Northern and Southern Hemispheres, while the prime meridian divides the Earth into the Eastern and Western Hemispheres.
Q: How does the equator affect the weather?
A: The equator receives the most direct sunlight throughout the year, leading to high temperatures and humidity. This results in a band of low atmospheric pressure known as the Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ), which is characterized by frequent rainfall and thunderstorms.
Q: What are some of the unique features of the equatorial belt?
A: The equatorial belt is home to some of the most diverse ecosystems on Earth, including rainforests, savannas, and wetlands. It is characterized by high biodiversity, abundant rainfall, and warm temperatures.
Q: Why is the equator important for navigation?
A: The equator serves as the zero-degree line of latitude, providing a reference point for calculating distances and directions. This makes it an essential tool for sailors, pilots, and explorers navigating the globe.
Tips:
- Use maps and globes to visualize the equator’s position on Earth.
- Explore the diverse ecosystems found in the equatorial belt.
- Learn about the history of exploration and navigation related to the equator.
- Consider the impact of climate change on the equatorial region.
Conclusion:
The equator, a seemingly simple line on a map, holds immense significance in shaping our understanding of the Earth. Its influence extends to climate, day-night cycles, global navigation, and even the planet’s shape. As we continue to explore and study our planet, the equator remains a vital reference point, reminding us of the interconnectedness and dynamic nature of our world.


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Equator: A Line Dividing the World. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!