The Equator: A Line Dividing the World
Related Articles: The Equator: A Line Dividing the World
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Equator: A Line Dividing the World. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Equator: A Line Dividing the World

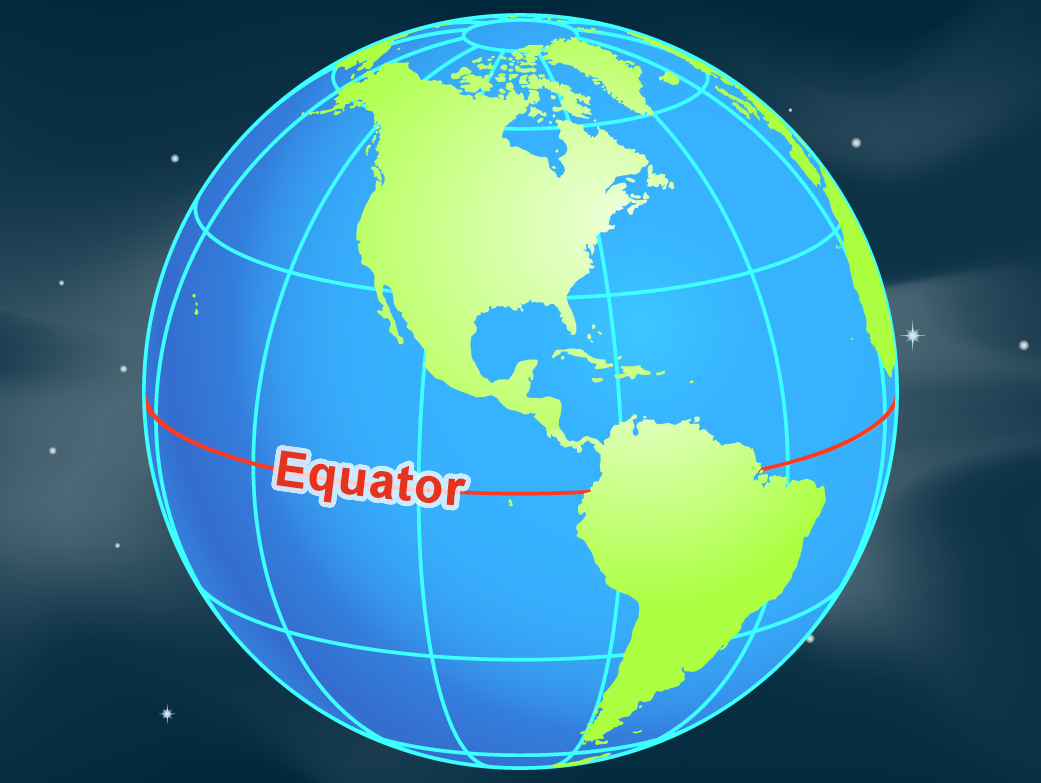
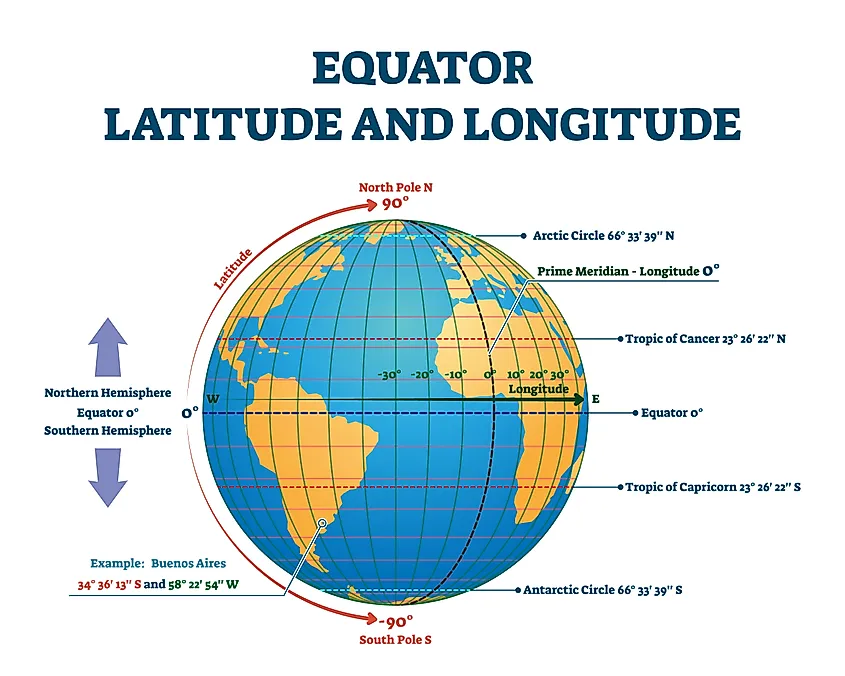
The Earth, a sphere suspended in space, is divided by an imaginary line known as the equator. This line circles the globe at 0 degrees latitude, equidistant from the North and South Poles. While invisible, the equator plays a pivotal role in understanding our planet’s geography, climate, and cultural diversity.
A Line of Division and Unity:
The equator is a fundamental geographical reference point. It divides the Earth into the Northern and Southern Hemispheres, each possessing unique characteristics. The Northern Hemisphere, containing continents like North America, Europe, and Asia, experiences distinct seasons due to the Earth’s tilt. Conversely, the Southern Hemisphere, encompassing continents like South America, Africa, and Australia, experiences seasons in reverse.
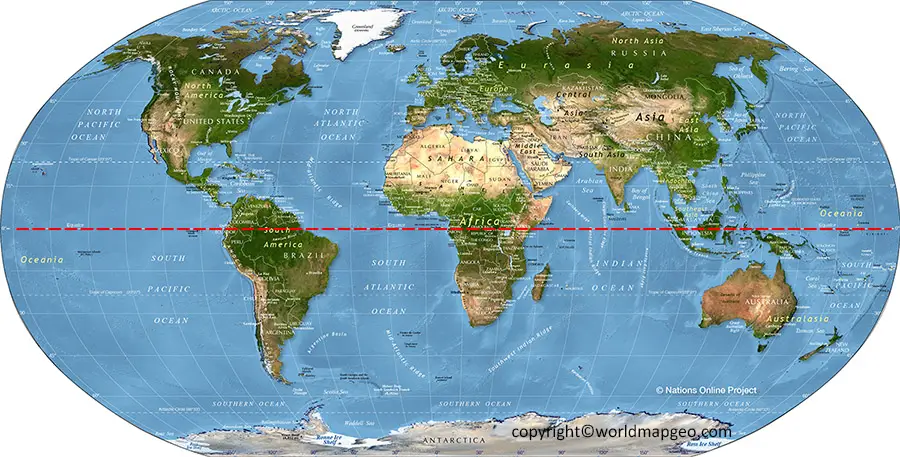
The equator also serves as a unifying element, connecting diverse cultures and ecosystems. It traverses through 14 countries, highlighting the interconnectedness of our planet. From the bustling cities of Quito, Ecuador, to the lush rainforests of the Amazon, the equator showcases the vast array of landscapes and human settlements that exist along its path.
Climate and Weather Patterns:
The equator is a region of intense solar radiation, receiving the most direct sunlight throughout the year. This constant influx of solar energy results in consistently high temperatures and abundant rainfall. The equator is home to the world’s tropical rainforests, characterized by dense vegetation, high biodiversity, and a humid climate.
The equator’s influence extends beyond its immediate vicinity. The Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ), a band of low pressure located near the equator, is responsible for the convergence of trade winds and the formation of heavy precipitation. This zone shifts seasonally, influencing rainfall patterns across the globe and impacting agricultural production and water availability.
Time Zones and Navigational Importance:
The equator is a crucial reference point for time zones. The Greenwich Meridian, located at 0 degrees longitude, intersects the equator, forming the Prime Meridian. This intersection serves as the starting point for calculating time zones across the globe. Each time zone is 15 degrees wide, with the equator serving as a central reference line.
The equator’s importance extends to navigation. Sailors and explorers have relied on its position for centuries, using it as a guide for charting courses and navigating vast oceans. The equator’s consistent latitude and its position on the Earth’s surface provide a reliable reference point for determining locations and calculating distances.
Cultural Significance and Symbolism:
The equator holds significant cultural and symbolic meaning in various societies. In many cultures, the equator represents a line of transition, a boundary between different worlds or realms. In some indigenous communities, the equator is seen as a sacred place, imbued with spiritual significance.
The equator’s presence in literature and art reflects its symbolic power. From the writings of Jules Verne to the paintings of Paul Gauguin, the equator has inspired artists and writers to explore themes of exploration, discovery, and the interconnectedness of human experiences.
Exploring the Equator: A Journey of Discovery:
For those seeking adventure and a deeper understanding of our planet, the equator offers a unique opportunity for exploration. Travelers can experience the diverse landscapes, cultures, and ecosystems that characterize this region. From the bustling markets of Kampala, Uganda, to the pristine beaches of the Maldives, the equator offers a glimpse into the richness and diversity of our world.
FAQs:
Q: What are the coordinates of the equator?
A: The equator is located at 0 degrees latitude, circling the Earth equidistant from the North and South Poles.
Q: What are the countries that the equator crosses?
A: The equator crosses 14 countries: Ecuador, Colombia, Brazil, São Tomé and Príncipe, Gabon, Republic of the Congo, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Uganda, Kenya, Somalia, Maldives, Indonesia, Kiribati, and Ecuador (again).
Q: What is the climate like at the equator?
A: The equator experiences a tropical climate with consistently high temperatures and abundant rainfall throughout the year.
Q: What are the major ecosystems found near the equator?
A: The equator is home to tropical rainforests, characterized by dense vegetation, high biodiversity, and a humid climate.
Q: What is the importance of the equator for navigation?
A: The equator serves as a reference point for charting courses and navigating vast oceans, providing a consistent latitude for determining locations and calculating distances.
Q: What is the cultural significance of the equator?
A: The equator holds symbolic meaning in various societies, representing a line of transition, a boundary between different worlds, and a place of spiritual significance.
Tips for Exploring the Equator:
- Research the specific countries and regions you wish to visit, considering their cultural norms, language, and safety precautions.
- Pack lightweight, breathable clothing suitable for hot and humid climates.
- Bring appropriate footwear for walking on diverse terrains, including jungle trails and city streets.
- Be mindful of the local customs and traditions, respecting the cultures you encounter.
- Consider taking a guided tour or hiring a local guide for a deeper understanding of the region’s history, culture, and ecosystems.
Conclusion:
The equator, an invisible line circling the globe, plays a vital role in shaping our planet’s geography, climate, and cultural diversity. It serves as a line of division and unity, connecting diverse ecosystems and cultures. Understanding the equator’s significance allows us to appreciate the interconnectedness of our world and the intricate forces that govern our planet. Whether exploring its vibrant landscapes or appreciating its cultural and symbolic meaning, the equator offers a unique perspective on the wonders of our Earth.


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Equator: A Line Dividing the World. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!