The Equator: A Line Dividing the World
Related Articles: The Equator: A Line Dividing the World
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Equator: A Line Dividing the World. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Equator: A Line Dividing the World

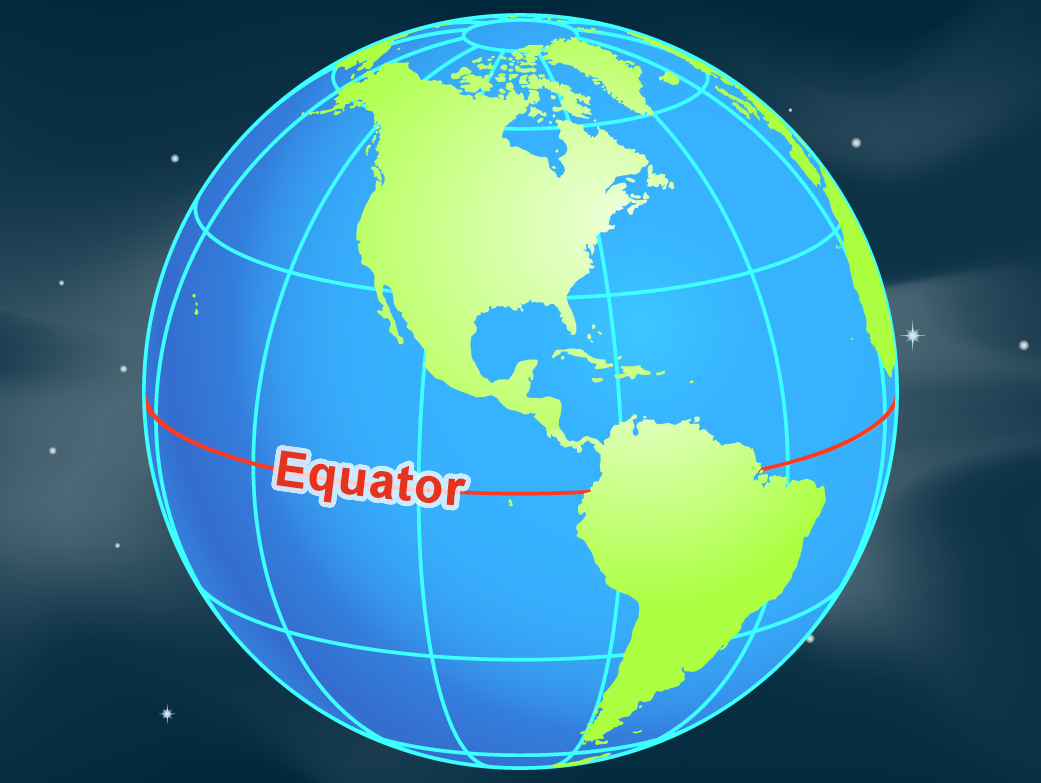
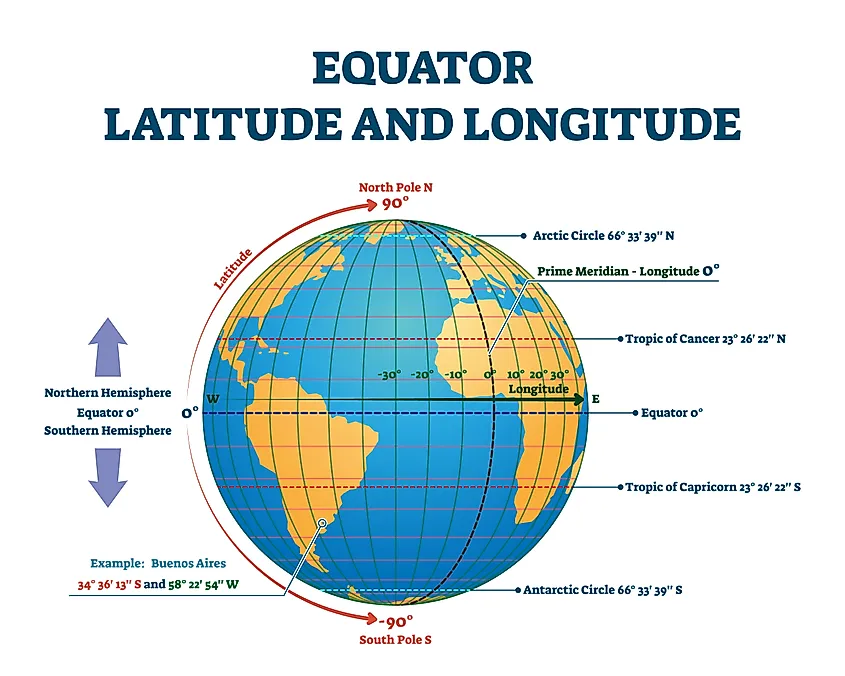
The equator is an imaginary line that circles the Earth at 0 degrees latitude, dividing the planet into the Northern and Southern Hemispheres. It is a fundamental geographical feature, playing a crucial role in understanding Earth’s climate, ecosystems, and cultural diversity.
A Line of Significance:
The equator’s significance extends beyond its simple definition. It marks the point on Earth where the sun’s rays hit directly overhead at noon on the vernal and autumnal equinoxes. This unique position influences the Earth’s climate, creating distinct patterns of temperature, precipitation, and wind patterns.
Climate and the Equator:
Regions near the equator experience a tropical climate characterized by high temperatures and humidity throughout the year. The consistent sunlight and abundant rainfall support lush rainforests, teeming with diverse flora and fauna. The equator’s influence extends beyond the tropics, contributing to the global climate system. It acts as a heat sink, transferring energy from the tropics to higher latitudes through atmospheric and oceanic currents.
Ecosystems and the Equator:
The equator’s influence on climate directly impacts the distribution of ecosystems. The tropical rainforests, with their dense canopies and rich biodiversity, are a prime example. Other equatorial ecosystems include savannas, mangroves, and coral reefs, each adapted to the unique conditions of the region. These ecosystems provide essential services like carbon sequestration, water purification, and habitat for countless species.
Cultural Diversity and the Equator:
The equator is home to a vast array of cultures and societies, each with its own unique traditions, languages, and beliefs. The equatorial regions have served as hubs for trade and migration, leading to a rich tapestry of cultural exchange and diversity.
Navigating the Equator:
The equator serves as a key reference point for navigation. Sailors and explorers have used it for centuries to determine their position and course. Its importance in navigation is further underscored by its role in defining time zones. The equator is the starting point for the Greenwich Mean Time (GMT) system, which divides the world into 24 time zones.
Understanding the Equator:
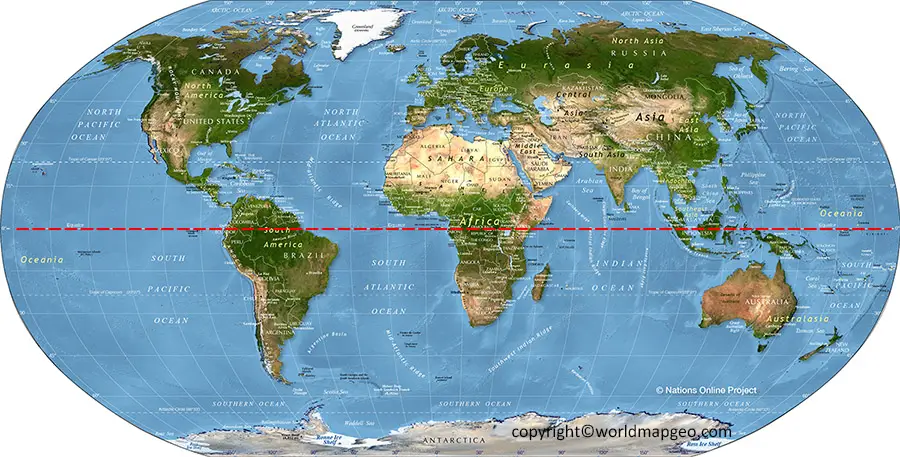
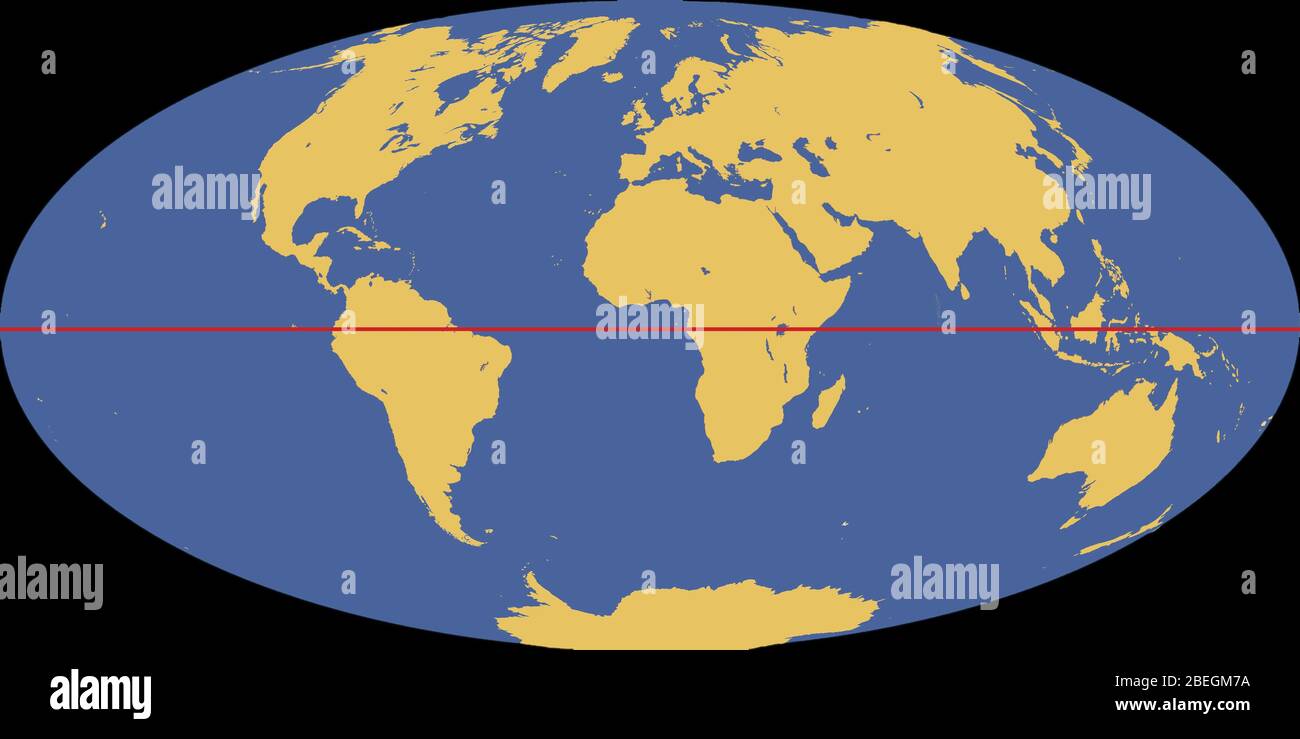
To fully grasp the significance of the equator, it is essential to visualize it on a map. Global maps typically depict the equator as a bold line, often accompanied by latitude and longitude lines. By tracing the equator on a map, one can gain a deeper understanding of its geographical position, its influence on climate and ecosystems, and its role in shaping human history and culture.
FAQs about the Equator:
Q: Why is the equator important?
A: The equator is a fundamental geographical feature that influences Earth’s climate, ecosystems, cultural diversity, and navigation. It acts as a boundary between the Northern and Southern Hemispheres, marking the point where the sun’s rays hit directly overhead at noon on the equinoxes.
Q: What are the characteristics of the equatorial climate?
A: The equatorial climate is characterized by high temperatures and humidity throughout the year. It is influenced by consistent sunlight and abundant rainfall, creating ideal conditions for tropical rainforests.
Q: What are some examples of equatorial ecosystems?
A: Equatorial ecosystems include tropical rainforests, savannas, mangroves, and coral reefs. These ecosystems are adapted to the unique conditions of the region and provide essential services for the planet.
Q: How does the equator affect cultural diversity?
A: The equator has served as a hub for trade and migration, leading to a rich tapestry of cultural exchange and diversity in the equatorial regions.
Q: How is the equator used in navigation?
A: The equator serves as a key reference point for navigation, allowing sailors and explorers to determine their position and course. It also plays a role in defining time zones, with the Greenwich Mean Time (GMT) system starting at the equator.
Tips for Visualizing the Equator:
- Use a globe: A globe provides a more accurate representation of the Earth than a flat map, allowing you to visualize the equator as a true circle.
- Focus on latitude lines: The equator is marked by 0 degrees latitude, which is a horizontal line running across the globe.
- Identify key locations: Look for countries and cities that lie on or near the equator, such as Ecuador, Kenya, and Indonesia.
- Explore online maps: Interactive online maps allow you to zoom in on specific regions and explore the equator in greater detail.
Conclusion:
The equator is a line of immense significance, shaping the Earth’s climate, ecosystems, and cultural diversity. By understanding its geographical position, its influence on the natural world, and its role in human history, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the interconnectedness of our planet.


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Equator: A Line Dividing the World. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!