The Equator: A Line Dividing the World
Related Articles: The Equator: A Line Dividing the World
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Equator: A Line Dividing the World. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Equator: A Line Dividing the World

The equator, an imaginary line circling the Earth at 0 degrees latitude, is a fundamental geographical feature that plays a crucial role in our understanding of the planet. It serves as a reference point for various geographical and scientific concepts, influencing climate, time zones, and cultural landscapes. This article delves into the significance of the equator, exploring its definition, characteristics, and the impact it has on our world.
Defining the Equator
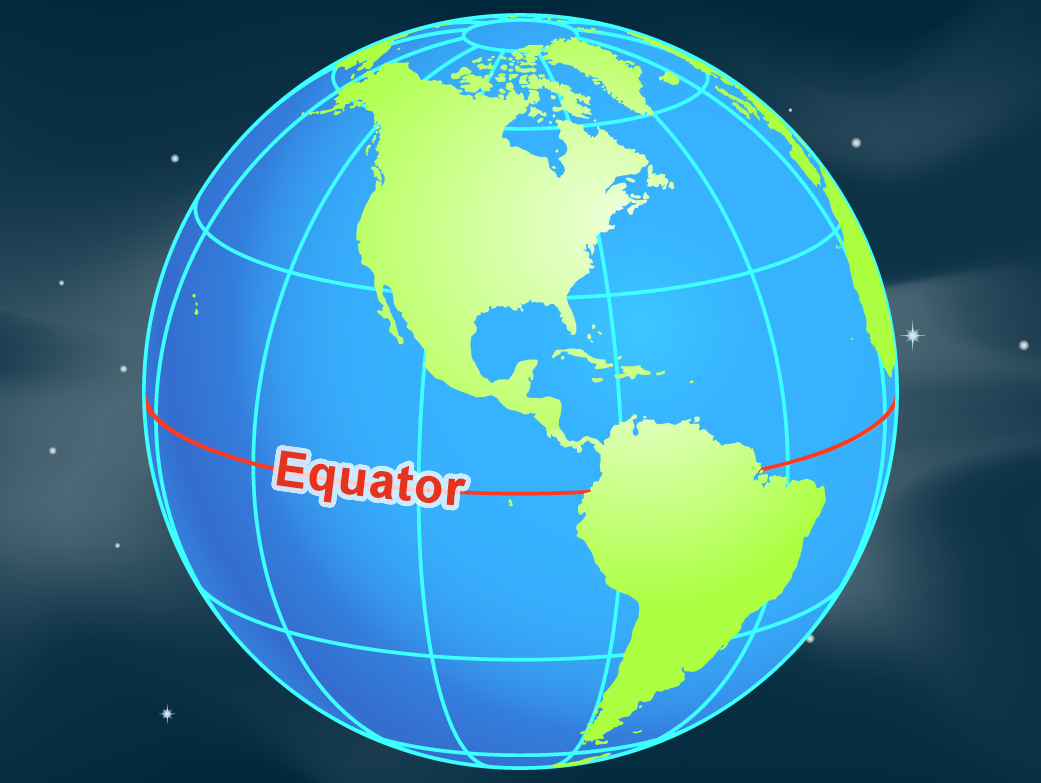
The equator is the line of latitude that divides the Earth into the Northern and Southern Hemispheres. It is equidistant from both the North Pole and the South Pole, forming a great circle that encircles the globe at its widest point. This imaginary line is a vital reference point for various aspects of geography and navigation.
Characteristics of the Equator
The equator is characterized by several unique features:
- Climate: Regions located near the equator experience a tropical climate characterized by high temperatures, high humidity, and abundant rainfall. This is due to the intense solar radiation received at the equator, leading to increased evaporation and precipitation.
- Day and Night: The equator experiences almost equal day and night lengths throughout the year. This is because the Earth’s axis is tilted at an angle of 23.5 degrees, and the equator is the only line of latitude that intercepts the sun’s rays directly at the equinoxes (March and September).
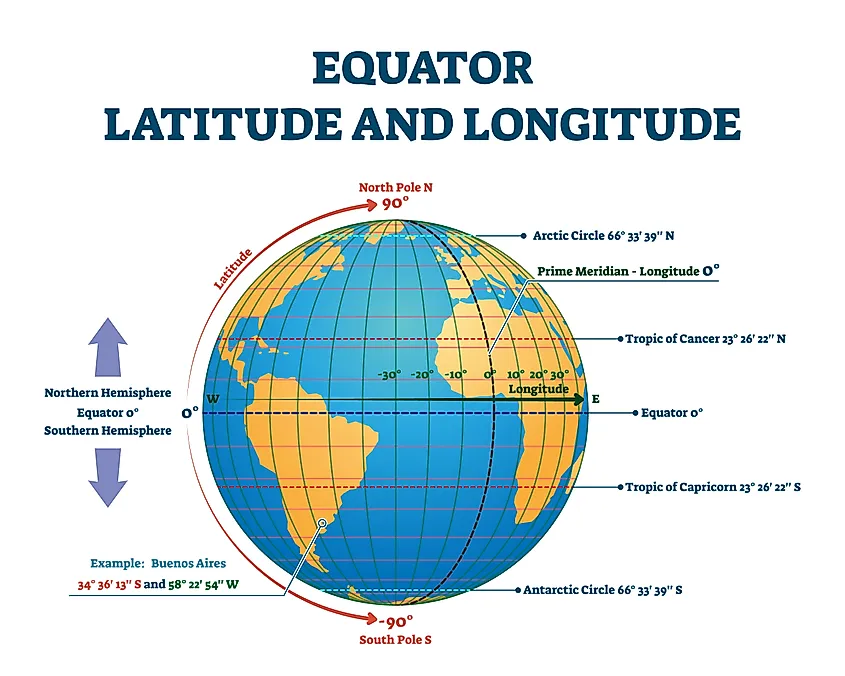
- Time Zones: The equator serves as the basis for the Greenwich Mean Time (GMT) system, which divides the world into 24 time zones. The prime meridian, which runs through Greenwich, England, is the starting point for measuring longitude, and the equator is used to define the boundaries of time zones.
- Biodiversity: The equatorial regions are renowned for their exceptional biodiversity. The warm, humid climate and abundant sunlight support a wide array of plant and animal life, making these regions some of the most biodiverse on Earth.
Significance of the Equator
The equator holds immense significance in various fields:
- Navigation: The equator is a crucial reference point for navigation, especially for ships and aircraft. It helps determine location and direction, facilitating efficient and safe travel.
- Climate Studies: The equator is a focal point for climate studies, as it experiences the most direct solar radiation, influencing global weather patterns and ocean currents. Understanding the equator’s climate dynamics is vital for predicting and mitigating climate change.
- Cultural Significance: The equator has significant cultural significance in many societies. It has been a source of inspiration for myths, legends, and artistic expressions, reflecting its unique geographical and environmental characteristics.
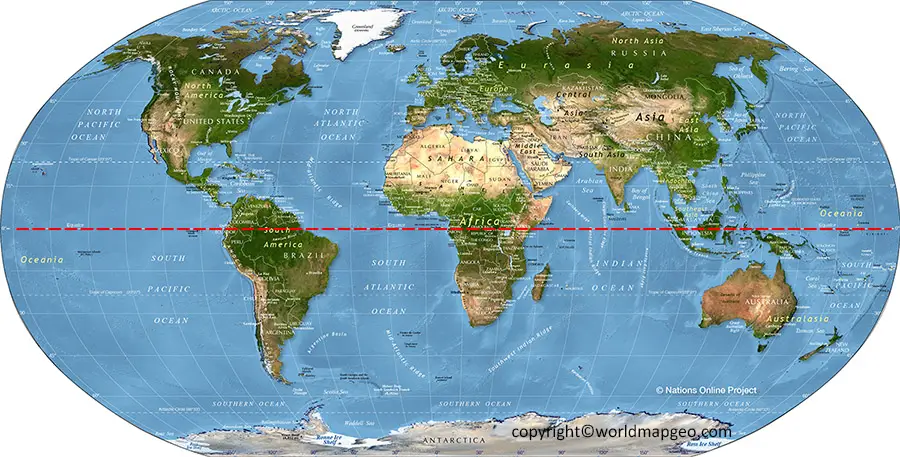
The Equator on a Map
Representing the equator on a map is essential for understanding global geography. It is typically depicted as a horizontal line that divides the map into two hemispheres. Maps often use different colors, symbols, or labels to highlight the equator, making it easily recognizable.
Illustrating the Equator on a Map
To illustrate the equator on a map, consider these points:
- World Map: The equator is most prominently displayed on world maps, where it forms a continuous line around the globe.
- Regional Maps: The equator is also marked on regional maps, highlighting its position in relation to specific countries or continents.
- Latitude and Longitude: The equator is defined as 0 degrees latitude, and its position on a map can be easily identified by locating this line.
- Geographic Features: The equator often passes through significant geographical features, such as oceans, mountains, and forests. Highlighting these features on a map helps illustrate the equator’s impact on the landscape.
FAQs
Q1: Why is the equator important for climate?
The equator is crucial for climate because it receives the most direct solar radiation, leading to high temperatures and high humidity. This intense solar energy drives global weather patterns, influencing rainfall, wind patterns, and ocean currents.
Q2: What is the difference between the equator and the prime meridian?
The equator is a line of latitude that divides the Earth into the Northern and Southern Hemispheres, while the prime meridian is a line of longitude that divides the Earth into the Eastern and Western Hemispheres. The equator is horizontal, while the prime meridian is vertical.
Q3: Does the equator pass through any major cities?
Yes, several major cities are located near or on the equator, including Quito, Ecuador; Kampala, Uganda; and Jakarta, Indonesia. These cities experience a tropical climate and are often important economic and cultural hubs.
Q4: How can I find the equator on a map?
The equator is typically depicted as a horizontal line on a map, often marked with a specific color or label. It is also defined as 0 degrees latitude, making it easy to locate using latitude and longitude coordinates.
Tips
- Use a globe: A globe provides a three-dimensional representation of the Earth, making it easier to visualize the equator’s position and its relationship to other geographical features.
- Interactive maps: Many online maps allow users to zoom in and out, explore different regions, and identify the equator using interactive tools.
- Educational resources: Websites, books, and documentaries offer valuable insights into the equator’s significance and its impact on the world.
Conclusion
The equator, an imaginary line circling the Earth at 0 degrees latitude, is a fundamental geographical feature that plays a crucial role in our understanding of the planet. It influences climate, time zones, biodiversity, and cultural landscapes, making it a vital reference point for various scientific and societal aspects. By understanding the equator’s characteristics and significance, we gain a deeper appreciation for the interconnectedness of our world and the importance of geographical knowledge in shaping our understanding of the Earth.


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Equator: A Line Dividing the World. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!