The Equator: A Line Dividing and Unifying the World
Related Articles: The Equator: A Line Dividing and Unifying the World
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Equator: A Line Dividing and Unifying the World. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Equator: A Line Dividing and Unifying the World

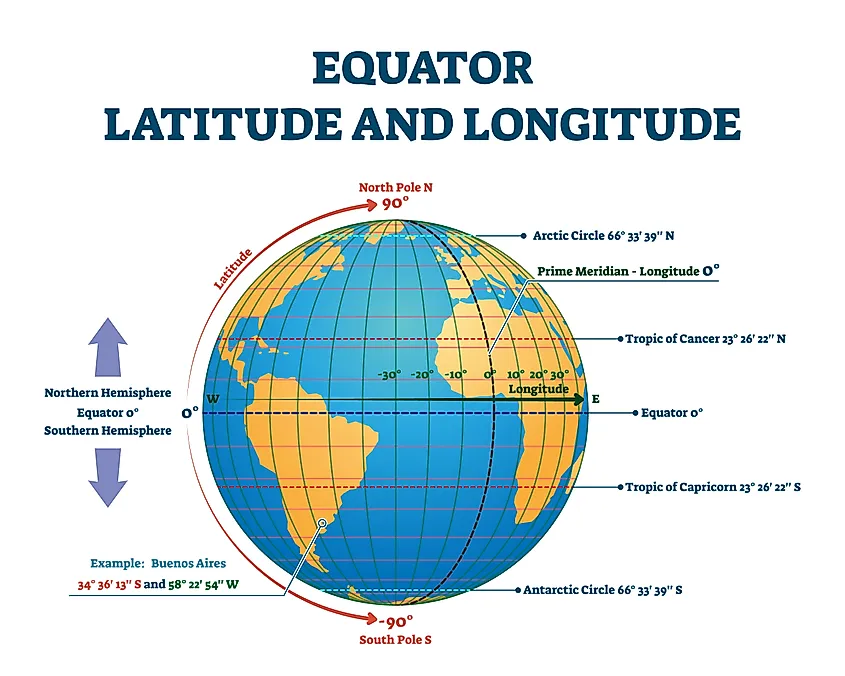
The Earth, a sphere suspended in the vastness of space, is divided by an imaginary line known as the equator. This line, running around the globe at 0 degrees latitude, plays a crucial role in understanding the Earth’s geography, climate, and even the distribution of life.
The equator’s significance stems from its position as the Earth’s largest circle of latitude, effectively dividing the planet into the Northern and Southern Hemispheres. This division has profound implications for various aspects of the Earth’s system.
Geographical Significance:
The equator serves as a fundamental reference point for understanding geographical locations. It is the starting point for measuring latitude, a crucial coordinate system used to pinpoint any location on Earth. By denoting the distance north or south of the equator, latitude provides a precise way to describe a location’s position on the globe.
Beyond its role in defining latitude, the equator also plays a key role in understanding the Earth’s shape and size. The Earth is not a perfect sphere but rather an oblate spheroid, slightly flattened at the poles and bulging at the equator. This shape is a consequence of the Earth’s rotation, which causes the equatorial region to experience a greater centrifugal force, resulting in a slight outward bulge.
Climatic Influence:
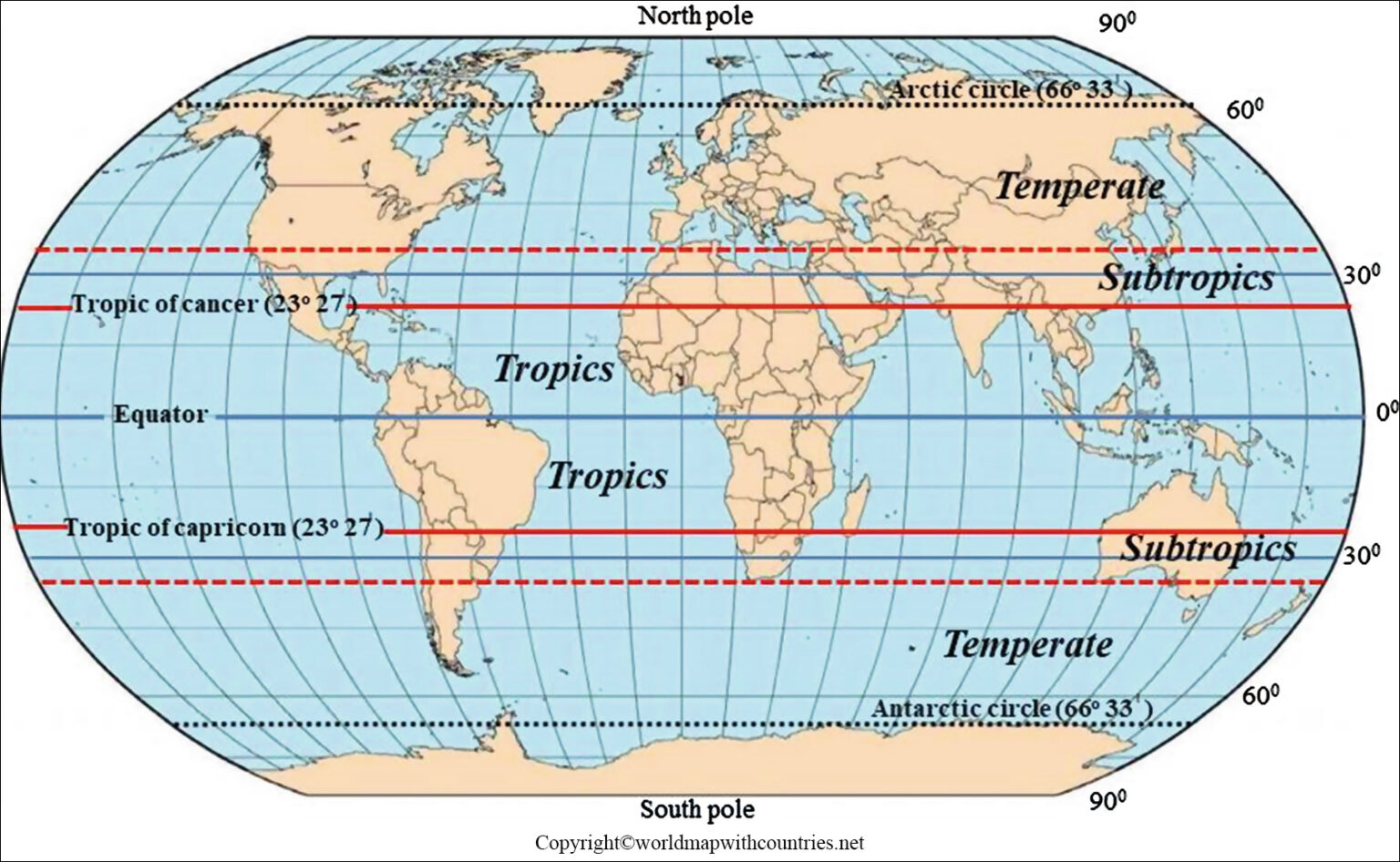
The equator’s position directly influences the Earth’s climate patterns. The region around the equator receives the highest amount of solar radiation, leading to consistently warm temperatures throughout the year. This intense solar exposure drives the formation of large-scale atmospheric circulation patterns, such as the Hadley cells, which transport heat and moisture from the equator towards the poles.
The equator’s proximity to the sun also influences precipitation patterns. The warm, moist air rising from the equatorial region condenses as it cools, resulting in abundant rainfall in the tropics. This high rainfall creates lush vegetation and diverse ecosystems, often characterized by rainforests, savannas, and wetlands.
Biological Diversity:
The equator’s unique climatic conditions support a rich tapestry of life. The abundance of sunlight, warmth, and precipitation fosters an environment ideal for the growth of a wide range of plants and animals. This biodiversity is particularly evident in the equatorial rainforests, which are home to an estimated 50% of the world’s plant and animal species.
The equatorial region is a hotbed of endemic species, meaning species found nowhere else on Earth. This high level of endemism is a testament to the unique evolutionary pressures that have shaped life in this region. The isolation of equatorial ecosystems, coupled with the abundance of resources, has allowed for the development of a wide range of specialized adaptations, contributing to the extraordinary biodiversity found in these areas.
Cultural Significance:
The equator has also played a significant role in human history and culture. For centuries, civilizations have recognized the equator’s importance, using it as a reference point for navigation, trade, and cultural exchange.
Ancient civilizations, such as the Inca in South America, developed complex knowledge systems based on the celestial movements and the position of the sun relative to the equator. This understanding helped them to track seasons, plan agricultural cycles, and navigate vast distances.
The equator has also served as a cultural boundary, separating distinct regions and influencing the development of unique cultural practices and traditions. The diverse cultures found along the equator reflect the rich tapestry of human experience, shaped by the unique environmental and historical factors that define this region.
Challenges and Opportunities:
While the equator offers a wealth of opportunities, it also faces significant challenges. The region is particularly vulnerable to climate change, experiencing increased temperatures, extreme weather events, and rising sea levels. These changes pose threats to the region’s biodiversity, ecosystems, and human populations.
However, the equator also presents opportunities for sustainable development. Its abundant natural resources, including fertile land, renewable energy sources, and diverse biodiversity, offer potential for economic growth and social progress.
FAQs:
Q: What is the significance of the equator?
A: The equator is the imaginary line that divides the Earth into the Northern and Southern Hemispheres. It serves as a crucial reference point for understanding geographical locations, climate patterns, and the distribution of life.
Q: How does the equator influence climate?
A: The equator receives the highest amount of solar radiation, resulting in consistently warm temperatures and abundant rainfall. This creates a unique climate characterized by high humidity and diverse ecosystems.
Q: What are the environmental challenges facing the equator?
A: The equator is particularly vulnerable to climate change, experiencing increased temperatures, extreme weather events, and rising sea levels. These changes pose threats to the region’s biodiversity, ecosystems, and human populations.
Q: What are the opportunities for sustainable development in the equatorial region?
A: The equator offers abundant natural resources, including fertile land, renewable energy sources, and diverse biodiversity, which can contribute to economic growth and social progress.
Tips:
- Use a world map with the equator line prominently displayed. This will help you visualize the equator’s position and its relationship to other geographical features.
- Explore the diverse ecosystems found along the equator. Research the unique flora and fauna that inhabit these regions, including rainforests, savannas, and coral reefs.
- Learn about the cultural traditions and history of the equatorial region. Investigate the unique customs, languages, and art forms that have developed in this diverse area.
- Consider the impact of climate change on the equator. Research the threats posed by rising temperatures, extreme weather events, and rising sea levels to the region’s ecosystems and human populations.
- Explore the potential for sustainable development in the equatorial region. Investigate how the region’s natural resources can be used to create economic opportunities while preserving the environment.
Conclusion:
The equator, a seemingly simple line on a map, plays a pivotal role in shaping the Earth’s geography, climate, and life. Its influence extends from the distribution of sunlight and rainfall to the evolution of unique species and the development of diverse cultures. Understanding the equator’s importance is crucial for appreciating the interconnectedness of the Earth’s systems and for addressing the challenges and opportunities facing this vital region. By recognizing the equator’s significance, we can gain a deeper understanding of our planet and its inhabitants, fostering a sense of global responsibility and promoting sustainable practices for a healthier future.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Equator: A Line Dividing and Unifying the World. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!