The Equator: A Line Dividing and Connecting the World
Related Articles: The Equator: A Line Dividing and Connecting the World
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Equator: A Line Dividing and Connecting the World. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Equator: A Line Dividing and Connecting the World

The Earth, a dynamic sphere spinning in the vastness of space, is marked by an invisible line that plays a crucial role in shaping our planet’s climate, geography, and human history. This line, the equator, is an imaginary circle that encircles the Earth at 0 degrees latitude, dividing it into the Northern and Southern Hemispheres.
The Significance of the Equator
The equator’s significance lies in its unique position on the globe. It is the only line of latitude that receives the sun’s rays directly overhead at its zenith twice a year, during the equinoxes. This direct sunlight translates into consistent, year-round warmth, influencing the climate and vegetation of regions situated along the equator.
Climate and Vegetation
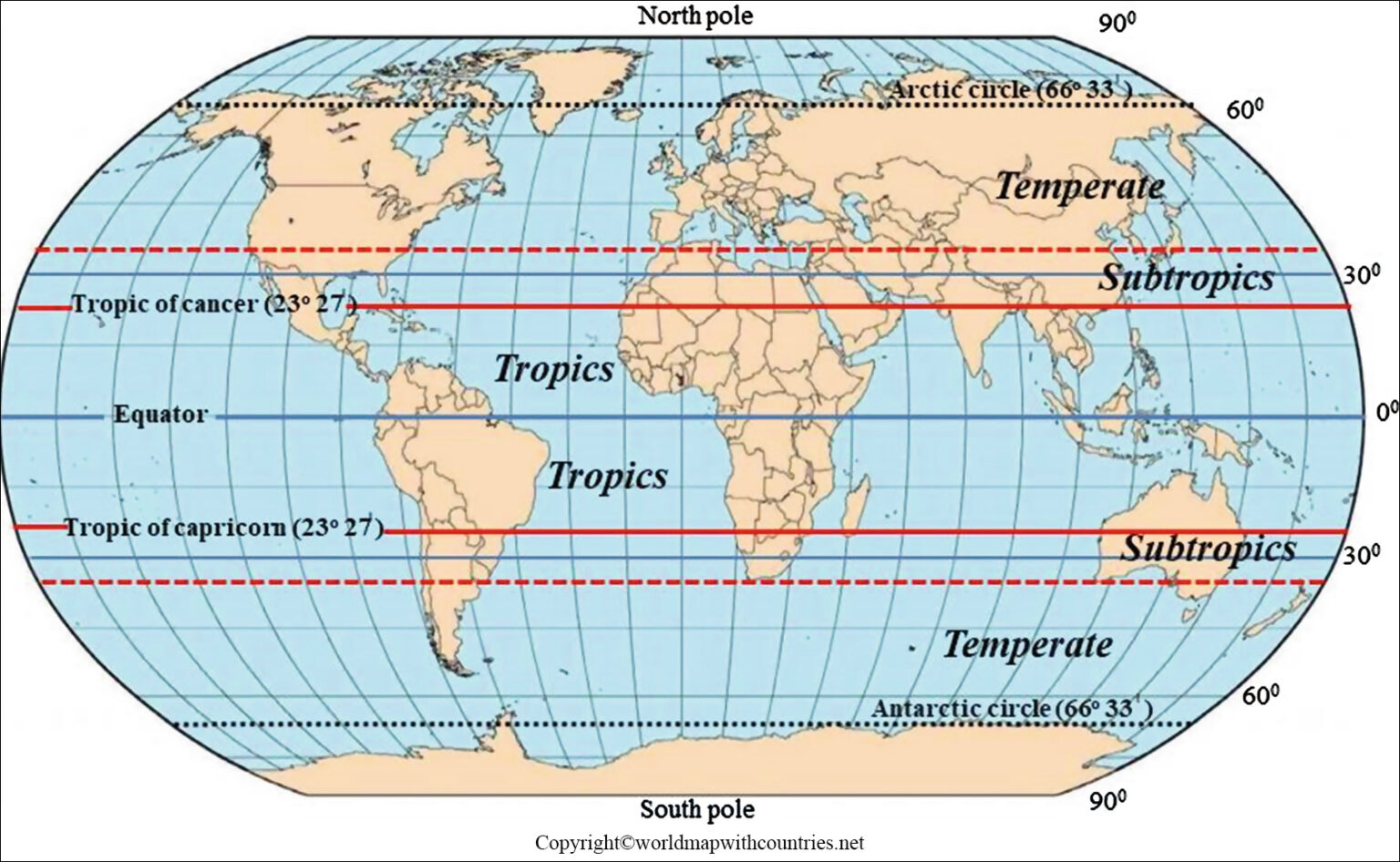
The equatorial zone, encompassing the regions within a few degrees north and south of the equator, is characterized by a tropical climate. This climate is defined by high temperatures, abundant rainfall, and high humidity. The consistent warmth and moisture create ideal conditions for the growth of lush rainforests, teeming with biodiversity. These forests, often referred to as the "lungs of the Earth," play a vital role in absorbing carbon dioxide and releasing oxygen, contributing to global climate regulation.
Day and Night
The equator also plays a crucial role in the distribution of daylight hours. Unlike regions further from the equator, where day and night lengths vary significantly throughout the year, the equator experiences nearly equal day and night lengths year-round. This is due to the Earth’s tilt, which causes the sun’s rays to fall directly on the equator during the equinoxes.
Time Zones
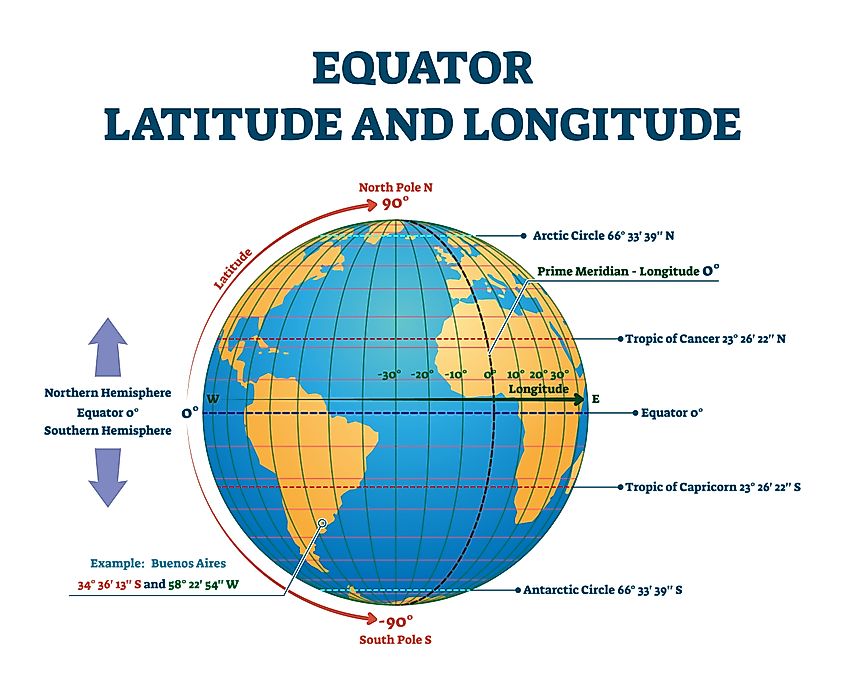
The equator serves as a reference point for establishing time zones. The Prime Meridian, which passes through Greenwich, England, and is designated as 0 degrees longitude, intersects the equator at a specific point. This point is considered the starting point for calculating time zones around the world.
Navigation and Mapping
For centuries, navigators and cartographers have relied on the equator as a fundamental reference point for mapping and navigating the globe. Its position at 0 degrees latitude provides a fixed point from which to measure distances and directions.
Cultural and Historical Significance
The equator holds cultural and historical significance for many civilizations. Ancient cultures, particularly in equatorial regions, often recognized the equator’s importance in their understanding of the cosmos and their relationship with the natural world. Many societies have developed unique traditions and beliefs associated with the equator, reflecting its influence on their lives.
The Equator’s Impact on Human Life
The equator’s influence extends beyond climate and geography, shaping human societies and economies. The abundance of natural resources in equatorial regions, including fertile land, valuable minerals, and diverse flora and fauna, has attracted populations and spurred economic development. However, the equatorial zone also faces challenges related to deforestation, climate change, and poverty.
Understanding the Equator: A Global Perspective
The equator is not merely an imaginary line on a map; it is a powerful force that shapes our planet’s environment, influences human societies, and connects us all. By understanding the equator’s significance, we gain a deeper appreciation for the intricate web of relationships that govern our world.
FAQs
Q: What is the equator?
A: The equator is an imaginary line that circles the Earth at 0 degrees latitude, dividing it into the Northern and Southern Hemispheres.
Q: Why is the equator important?
A: The equator is significant because it receives the sun’s rays directly overhead twice a year, influencing the climate, vegetation, and day/night lengths of regions along its path. It also serves as a reference point for navigation, mapping, and time zones.
Q: What are the characteristics of the equatorial climate?
A: The equatorial climate is characterized by high temperatures, abundant rainfall, and high humidity. This consistent warmth and moisture foster lush rainforests with high biodiversity.
Q: How does the equator affect day and night lengths?
A: Regions along the equator experience nearly equal day and night lengths year-round, unlike regions further from the equator where day and night lengths vary significantly throughout the year.
Q: What are the cultural and historical implications of the equator?
A: The equator holds cultural and historical significance for many civilizations, influencing their understanding of the cosmos and their relationship with the natural world.
Tips for Understanding the Equator
- Use a globe or map: Visualizing the equator on a globe or map can help you understand its position and significance.
- Explore equatorial regions: Research and learn about the diverse cultures, environments, and challenges faced by people living in equatorial regions.
- Connect the equator to other geographical concepts: Relate the equator to other concepts like latitude, longitude, time zones, and climate zones.
- Consider the impact of climate change: Explore how climate change is affecting equatorial regions and the implications for the global environment.
Conclusion
The equator, an invisible line encircling our planet, plays a vital role in shaping Earth’s environment and influencing human societies. It serves as a crucial reference point for understanding climate, navigation, and time, while also highlighting the interconnectedness of our world. By appreciating the significance of the equator, we gain a deeper understanding of the complex forces that govern our planet and the challenges and opportunities facing humanity in the 21st century.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Equator: A Line Dividing and Connecting the World. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!