The Equator: A Lifeline Around the World
Related Articles: The Equator: A Lifeline Around the World
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Equator: A Lifeline Around the World. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Equator: A Lifeline Around the World
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/1280px-World_map_with_equator-5c4e470b46e0fb00014c3710.jpg)
The Equator, an invisible line that circles the Earth at 0 degrees latitude, holds a unique and pivotal position in our planet’s geography. It serves as a fundamental reference point, dividing the Earth into the Northern and Southern Hemispheres, and plays a crucial role in shaping climate patterns, biodiversity, and human civilization.
The Equator’s Geographic Significance
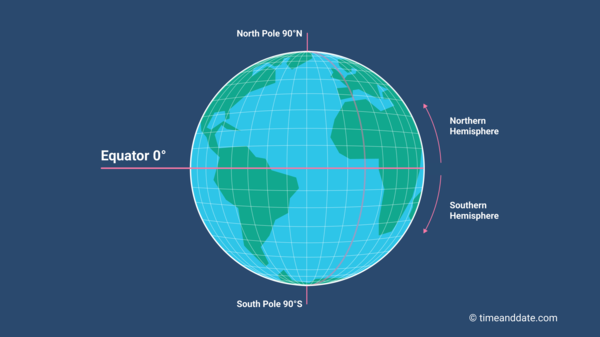
At the heart of the Earth’s coordinate system, the Equator is the primary line of latitude, acting as the starting point for measuring distances north and south. It divides the globe into two equal halves: the Northern Hemisphere, encompassing all locations north of the Equator, and the Southern Hemisphere, encompassing all locations south of the Equator.
The Equator’s significance extends beyond mere division. Its position directly influences the Earth’s climate, as it receives the most direct sunlight throughout the year. This constant exposure to solar radiation results in consistently warm temperatures and high humidity, creating a unique tropical climate found along the Equator and in nearby regions.
The Equator’s Impact on Climate and Ecosystems
The Equator’s location and the resulting tropical climate give rise to diverse and vibrant ecosystems. Lush rainforests, teeming with life, flourish along the Equator, harboring a vast array of plant and animal species. These forests play a crucial role in regulating the Earth’s climate by absorbing carbon dioxide and releasing oxygen.
The high temperatures and rainfall along the Equator also contribute to the formation of unique ecosystems like mangrove swamps and coral reefs. These ecosystems, while fragile, are vital for marine life and coastal protection.
The Equator’s Influence on Human Civilization
The Equator’s influence on human civilization is profound. It has historically been a focal point for trade and cultural exchange, connecting diverse populations and fostering the development of unique cultures. The Equator’s proximity to the tropics has made it a source of valuable resources, including tropical fruits, spices, and valuable timber.
However, the Equator’s location also poses challenges. The high humidity and rainfall can lead to flooding and soil erosion, requiring careful land management practices. The region is also susceptible to extreme weather events, such as hurricanes and typhoons, which can have devastating impacts on communities.
Navigating the Equator: Finding Your Way
Identifying the Equator on a map is relatively straightforward. It is represented as a horizontal line running across the globe at 0 degrees latitude. The Equator is often marked with a bold line or a specific color to distinguish it from other lines of latitude.
Many countries lie directly on the Equator, including Ecuador, which takes its name from the line. Other countries that intersect with the Equator include Brazil, Colombia, Kenya, and Indonesia.
Understanding the Equator: Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the significance of the Equator?
The Equator is the primary line of latitude, dividing the Earth into the Northern and Southern Hemispheres. It plays a crucial role in shaping climate patterns, influencing biodiversity, and impacting human civilization.
2. How does the Equator affect climate?
The Equator receives the most direct sunlight throughout the year, resulting in consistently warm temperatures and high humidity, leading to a tropical climate.
3. What are some of the unique ecosystems found along the Equator?
The Equator is home to lush rainforests, mangrove swamps, and coral reefs, all of which are characterized by high biodiversity and unique ecological features.
4. What are some of the challenges faced by communities living along the Equator?
Communities living along the Equator face challenges such as flooding, soil erosion, and the potential for extreme weather events like hurricanes.
5. How can I find the Equator on a map?
The Equator is represented as a horizontal line running across the globe at 0 degrees latitude. It is often marked with a bold line or a specific color to distinguish it from other lines of latitude.
Navigating the Equator: Tips for Understanding its Importance
- Visualize the Earth: Imagine the Equator as a belt wrapped around the Earth, dividing it into two equal halves.
- Focus on the climate: The Equator’s tropical climate is a key factor in understanding its unique ecosystems and the challenges faced by communities living there.
- Explore the Equator’s influence on human civilization: Research the historical significance of the Equator in trade, cultural exchange, and resource development.
- Study the Equator’s impact on biodiversity: Learn about the diverse flora and fauna found in equatorial regions, and the importance of these ecosystems for global climate regulation.
- Engage with the Equator’s challenges: Consider the challenges faced by communities living along the Equator, and how these challenges can be addressed through sustainable development and environmental protection.
Conclusion
The Equator is a vital geographical feature that holds immense significance for our planet’s climate, ecosystems, and human civilization. Understanding its location, influence, and challenges is crucial for appreciating the interconnectedness of our world and for making informed decisions regarding sustainable development and environmental conservation. As we continue to explore and understand our planet, the Equator will remain a critical reference point, reminding us of the intricate web of life that binds us all.





/wov007-58b9cea93df78c353c388df1.jpg)

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Equator: A Lifeline Around the World. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!