The Earth’s Equator: A Line of Significance
Related Articles: The Earth’s Equator: A Line of Significance
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Earth’s Equator: A Line of Significance. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Earth’s Equator: A Line of Significance
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/1280px-World_map_with_equator-5c4e470b46e0fb00014c3710.jpg)
The Earth’s equator, an imaginary line circling the globe at 0 degrees latitude, holds a pivotal position in our understanding of the planet’s geography, climate, and even its history. It is not just a line on a map; it is a fundamental element shaping the Earth’s physical and biological systems. This article delves into the significance of the equator, exploring its geographical characteristics, climatic influences, cultural relevance, and its role in various scientific disciplines.
A Geographical Divide
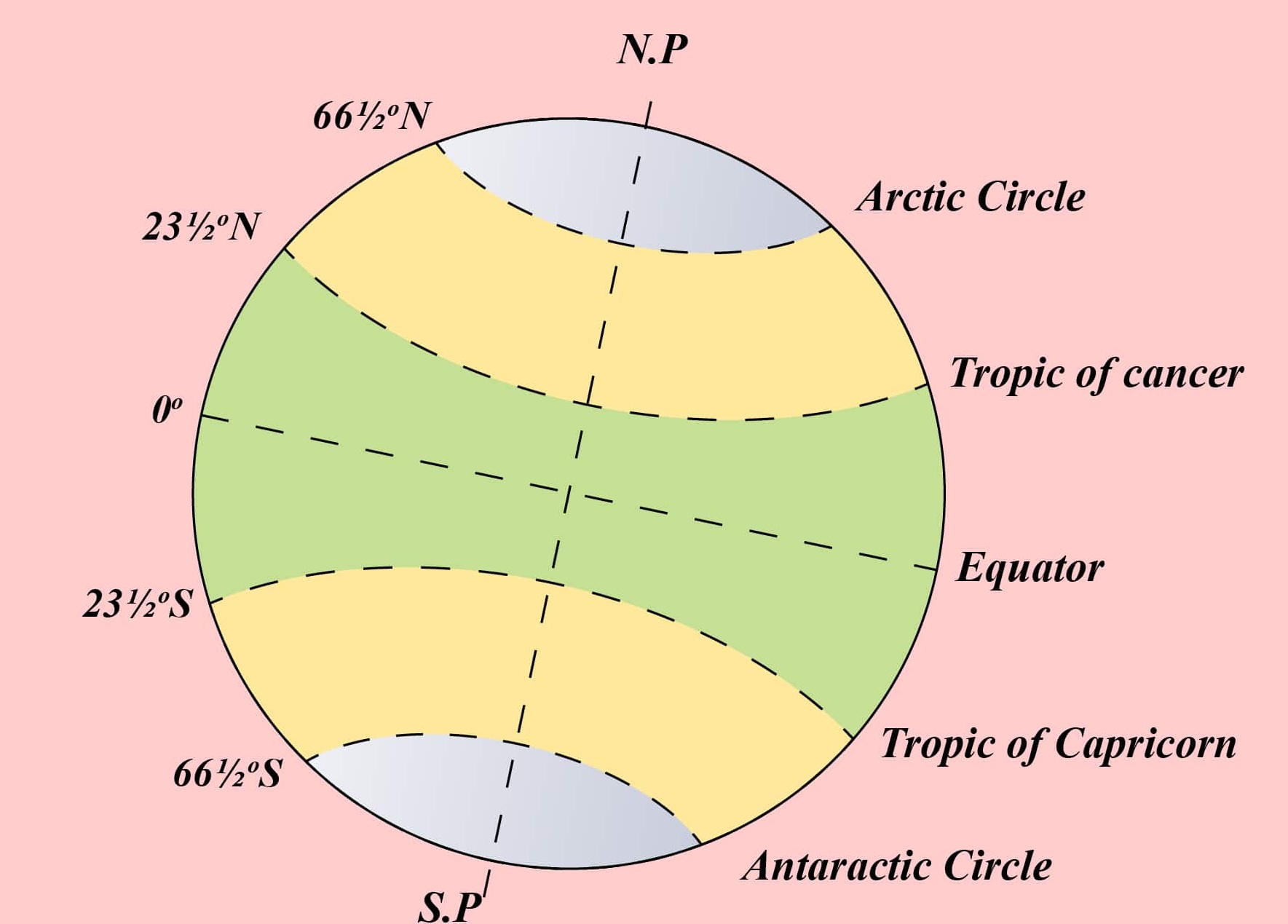
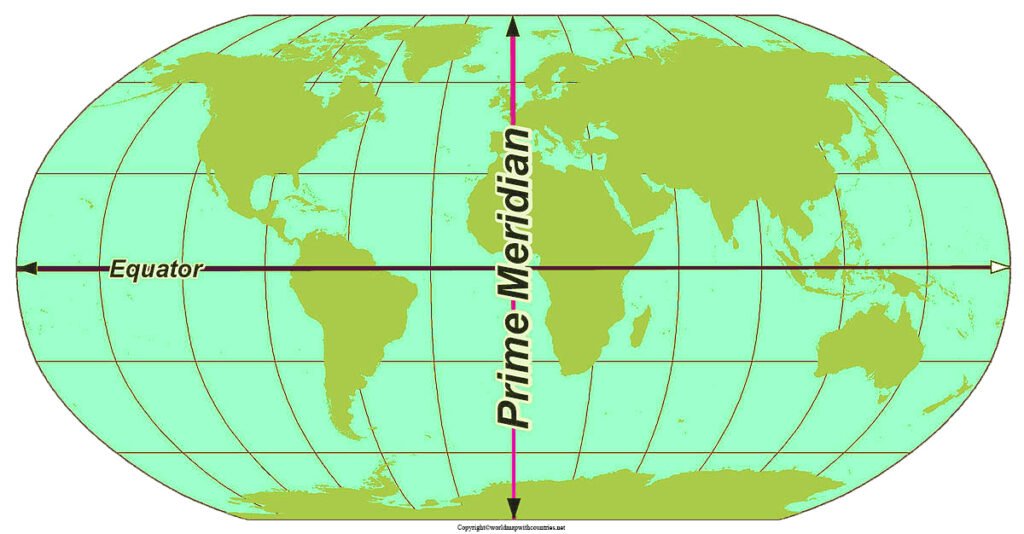
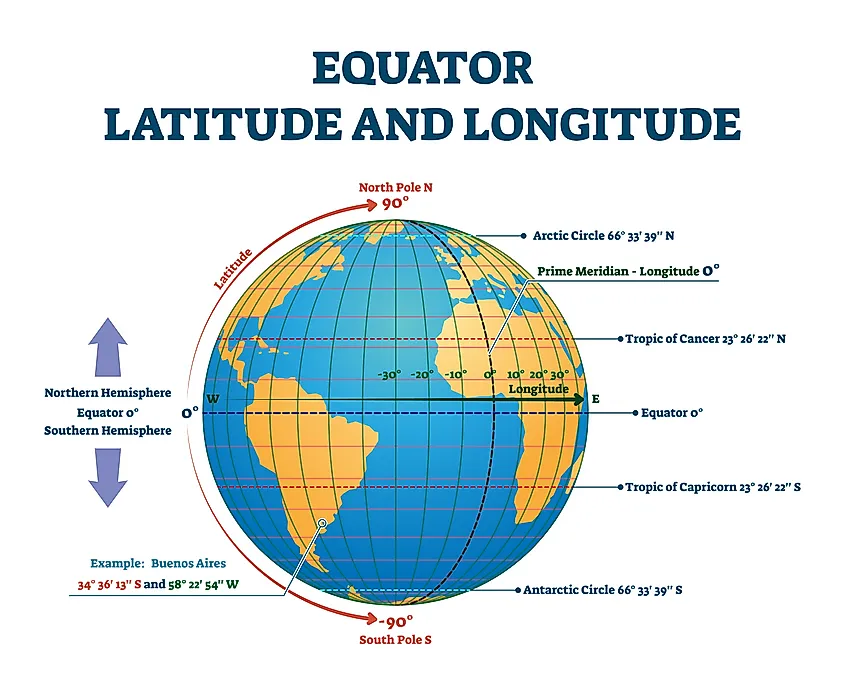
The equator is a defining line that divides the Earth into two hemispheres: the Northern Hemisphere and the Southern Hemisphere. It is the longest line of latitude on the Earth, spanning approximately 40,075 kilometers (24,901 miles). The equator is also the only line of latitude that is a great circle, meaning it divides the Earth into two equal halves.
Climatic Significance
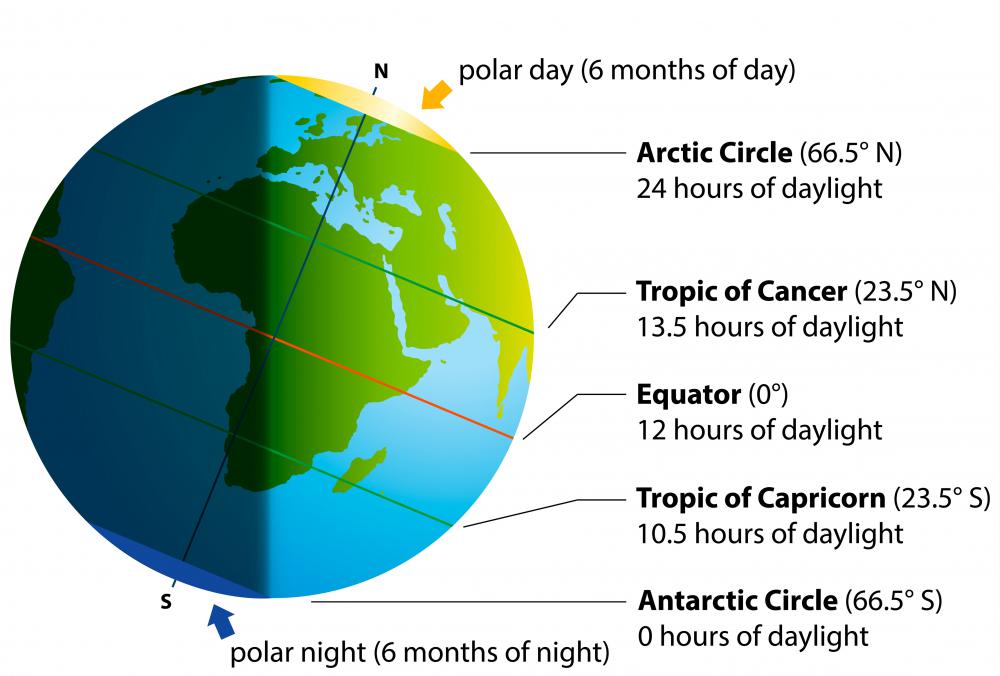
The equator plays a crucial role in shaping the Earth’s climate. Due to its position, the equator receives the most direct sunlight throughout the year. This leads to high temperatures and consistent rainfall, creating the tropical climate zone that characterizes equatorial regions.
The equator is also the location of the Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ), a low-pressure belt where the trade winds from the Northern and Southern Hemispheres converge. This convergence leads to the formation of thunderstorms and abundant rainfall, further contributing to the tropical climate of equatorial regions.
Cultural and Historical Significance
The equator holds cultural and historical significance for numerous civilizations throughout history. Ancient civilizations, like the Inca in South America, recognized the equator’s importance and used it as a reference point for their astronomical observations and calendrical systems.
Many cultures also consider the equator to be a sacred line, symbolizing the intersection of the heavens and the Earth. This symbolism is evident in various rituals and celebrations held across equatorial regions.
Scientific Importance
The equator serves as a crucial reference point for various scientific disciplines:
- Astronomy: The equator is used as a reference point for celestial coordinates, helping astronomers pinpoint the position of stars and other celestial objects.
- Geodesy: The equator is used as a reference point for measuring the Earth’s shape and size.
- Meteorology: The equator is a key factor in understanding global wind patterns and climate dynamics.
- Oceanography: The equator plays a crucial role in shaping ocean currents and marine ecosystems.
FAQs
Q: Why is the equator important?
A: The equator is important because it is a defining line that divides the Earth into two hemispheres and influences climate, culture, and scientific research.
Q: What are the characteristics of the equator?
A: The equator is the longest line of latitude, a great circle, and receives the most direct sunlight, contributing to its tropical climate.
Q: What is the Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ)?
A: The ITCZ is a low-pressure belt located near the equator, where trade winds converge, leading to thunderstorms and abundant rainfall.
Q: How does the equator influence climate?
A: The equator receives the most direct sunlight, leading to high temperatures and consistent rainfall, creating the tropical climate zone.
Q: What are some cultural and historical examples of the equator’s significance?
A: Ancient civilizations like the Inca used the equator for astronomical observations, and many cultures consider it a sacred line symbolizing the intersection of the heavens and the Earth.
Tips
- Use a globe or map to visualize the equator’s position.
- Learn about the different climate zones and their relationship to the equator.
- Explore the cultural and historical significance of the equator in different regions.
- Research the scientific applications of the equator in astronomy, geodesy, meteorology, and oceanography.
Conclusion
The Earth’s equator is more than just an imaginary line; it is a powerful geographical feature that shapes our planet’s climate, influences cultural practices, and serves as a vital reference point for scientific research. Understanding the equator’s significance provides us with a deeper appreciation for the interconnectedness of Earth’s systems and the intricate balance that governs our planet. By recognizing the equator’s importance, we can gain a more comprehensive understanding of the Earth and its diverse inhabitants.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Earth’s Equator: A Line of Significance. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!