The Complex Relationship Between Fire and Yosemite: A Look at the History, Impact, and Management of Wildfires
Related Articles: The Complex Relationship Between Fire and Yosemite: A Look at the History, Impact, and Management of Wildfires
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Complex Relationship Between Fire and Yosemite: A Look at the History, Impact, and Management of Wildfires. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Complex Relationship Between Fire and Yosemite: A Look at the History, Impact, and Management of Wildfires
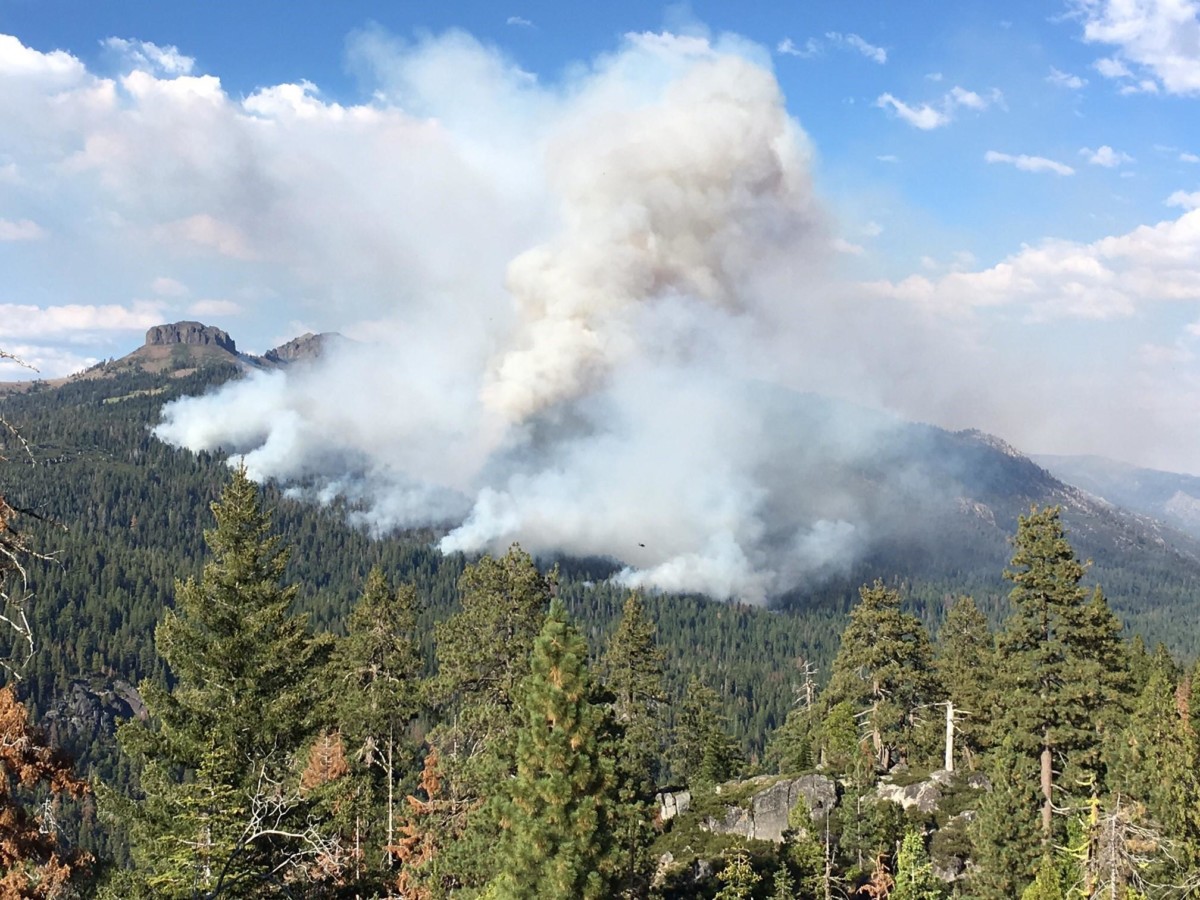

Yosemite National Park, renowned for its towering granite cliffs, cascading waterfalls, and ancient sequoia groves, is a landscape shaped by fire. The park’s diverse ecosystems, from the lush meadows to the rugged high country, have evolved alongside periodic wildfires, a natural process that plays a crucial role in maintaining their health and resilience. However, the delicate balance between fire and the park’s unique environment has been disrupted by human activities and climate change, leading to a complex interplay of challenges and opportunities.
A Historical Perspective: The Role of Fire in Shaping Yosemite
For millennia, wildfires have been an integral part of the Yosemite ecosystem. Indigenous peoples, deeply connected to the land, intentionally used fire to manage vegetation, promote the growth of desirable plants, and improve hunting grounds. This practice, known as "cultural burning," helped maintain a mosaic of habitats, preventing the accumulation of fuel and reducing the risk of large, destructive fires.
However, with the arrival of European settlers in the 19th century, fire suppression policies became the norm. The belief that all fires were detrimental led to the aggressive suppression of wildfires, resulting in the accumulation of dense undergrowth and an increased risk of catastrophic fires. This shift in fire management practices had profound consequences for Yosemite’s ecosystem.
The Impacts of Fire Suppression: Unintended Consequences
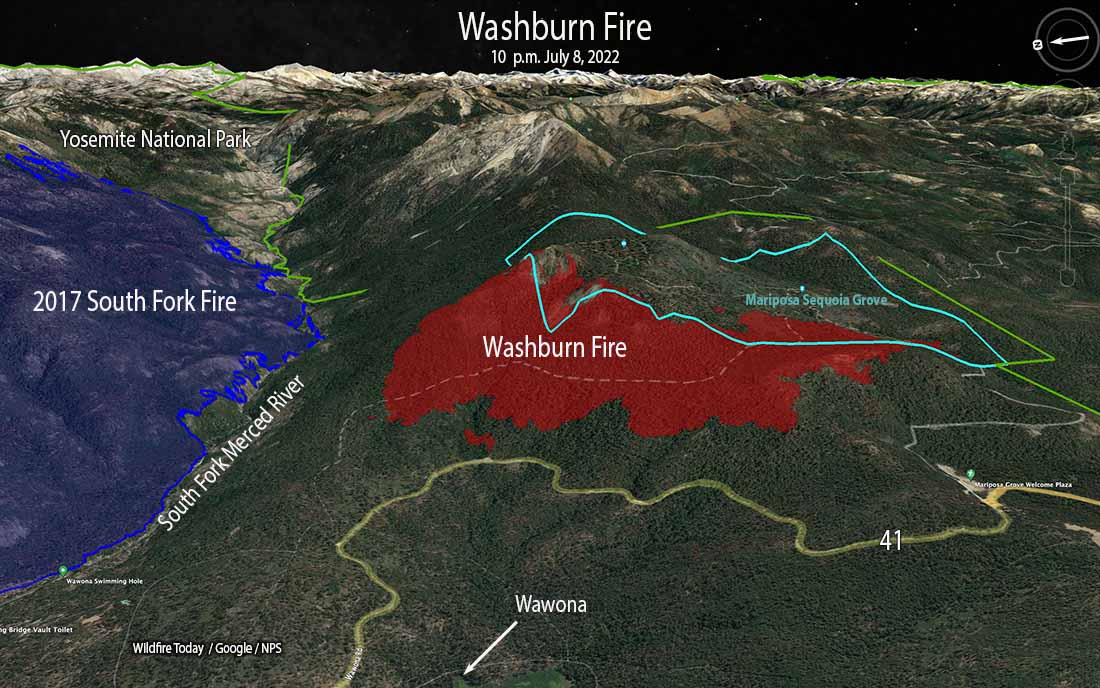
The absence of regular, low-intensity fires created an imbalance in the natural fire cycle. Dense forests, choked with deadwood and undergrowth, became highly flammable, making them susceptible to large and intense wildfires that could devastate entire ecosystems. These fires, fueled by decades of accumulated fuel, often burned with extreme intensity, leaving behind barren landscapes and impacting the park’s biodiversity.
Furthermore, the suppression of fire altered the ecological balance, favoring certain species while suppressing others. For instance, the absence of fire allowed shade-tolerant species to dominate the understory, hindering the growth of fire-adapted plants and trees. This shift in vegetation composition further increased the risk of large, destructive fires.
The Return of Fire: Rethinking Management Strategies
In recent decades, a paradigm shift has occurred in the understanding of fire’s role in Yosemite. Scientists and park managers have recognized the crucial role of fire in maintaining healthy ecosystems and have adopted a more nuanced approach to fire management. This shift involves a combination of strategies, including:
- Prescribed Burning: This involves intentionally setting controlled fires under carefully monitored conditions to reduce fuel loads, promote the growth of fire-adapted species, and restore the natural fire cycle.
- Wildfire Management: When wildfires occur, park managers employ a range of strategies, including suppression, containment, and controlled burns, to minimize damage and protect human life and infrastructure.
- Fuel Reduction: This involves thinning dense forests by removing deadwood and undergrowth, reducing the amount of fuel available for wildfires.
These strategies aim to create a more resilient landscape, one that can withstand the inevitable occurrence of wildfires while minimizing the risk of catastrophic events.
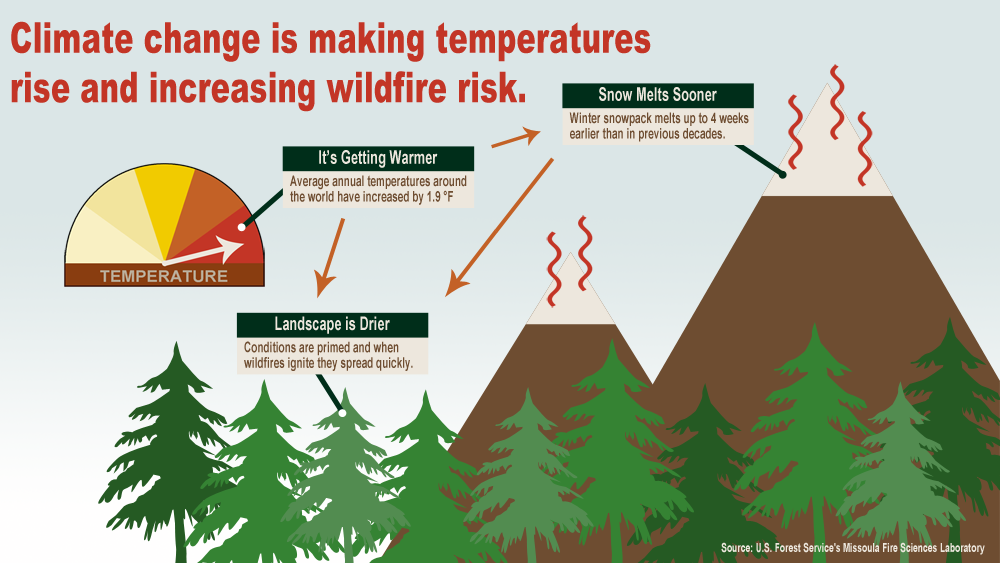
The Impact of Climate Change: A New Challenge for Fire Management
Climate change has added another layer of complexity to fire management in Yosemite. Rising temperatures, prolonged droughts, and changes in precipitation patterns have increased the frequency, intensity, and severity of wildfires. This creates a challenging environment for fire managers, who must adapt their strategies to cope with these changing conditions.
The Importance of Fire: Benefits for the Ecosystem
While wildfires can be destructive, they also play a vital role in maintaining the health and resilience of Yosemite’s ecosystems. Here are some of the key benefits:
- Nutrient Cycling: Fire releases nutrients from dead organic matter, making them available for plant growth. This nutrient cycling is essential for the health and productivity of the ecosystem.
- Seed Germination: Some plant species require fire for their seeds to germinate. This process, known as "serotiny," ensures the regeneration of these species after a fire.
- Habitat Creation: Fire creates openings in the forest canopy, allowing sunlight to reach the forest floor and promoting the growth of a diverse range of plants. This in turn creates habitat for a variety of animals.
- Disease Control: Fire can help control the spread of pests and diseases by killing infected trees and clearing out deadwood.
- Landscape Diversity: Fire helps maintain a mosaic of habitats by creating a mix of different vegetation types, supporting a greater diversity of species.
FAQs about Fire in Yosemite
1. How often do wildfires occur in Yosemite National Park?
Wildfires occur naturally in Yosemite National Park, with an average of 30-40 wildfires reported annually. However, the frequency and severity of wildfires can vary significantly depending on weather conditions, fuel availability, and human activity.
2. How do park managers decide when and where to use prescribed burns?
Prescribed burns are carefully planned and executed, considering factors such as weather conditions, fuel availability, and the presence of sensitive ecosystems. Park managers utilize a comprehensive risk assessment process to ensure the safety of personnel and the environment.
3. What are the dangers of wildfires in Yosemite?
Wildfires pose significant risks to human life, property, and the environment. They can cause injuries, destroy infrastructure, and release harmful pollutants into the air. Additionally, wildfires can negatively impact water quality and wildlife populations.
4. How can visitors help prevent wildfires in Yosemite?
Visitors can play a crucial role in preventing wildfires by following basic fire safety guidelines, such as:
- Never leave a campfire unattended.
- Ensure campfires are completely extinguished before leaving.
- Use designated fire rings and follow park regulations.
- Be aware of the fire danger level and avoid activities that could spark a fire.
5. How does climate change impact fire management in Yosemite?
Climate change is intensifying the challenges of fire management in Yosemite. Warmer temperatures, prolonged droughts, and changes in precipitation patterns are increasing the frequency, intensity, and severity of wildfires. This necessitates a more adaptive and proactive approach to fire management.
Tips for Visitors During Wildfire Season
- Stay informed: Check the park website and social media for updates on fire activity and any closures or restrictions.
- Be aware of your surroundings: Pay attention to smoke, ash, and any changes in air quality.
- Follow park regulations: Adhere to all fire restrictions and safety guidelines.
- Have a plan: Know where to go and what to do in case of a wildfire evacuation.
- Be prepared: Pack a go-bag with essential items such as water, food, medications, and important documents.
Conclusion: A Complex and Evolving Relationship
The relationship between fire and Yosemite is a complex and evolving one. While wildfires can be destructive, they also play a vital role in maintaining the health and resilience of the park’s ecosystems. Through a combination of prescribed burning, wildfire management, and fuel reduction, park managers are working to create a more fire-adapted landscape, one that can withstand the inevitable occurrence of wildfires while minimizing the risk of catastrophic events. However, the challenges of fire management are increasing due to climate change, requiring a more adaptive and proactive approach. By understanding the role of fire and following park regulations, visitors can help protect Yosemite’s unique natural heritage for generations to come.
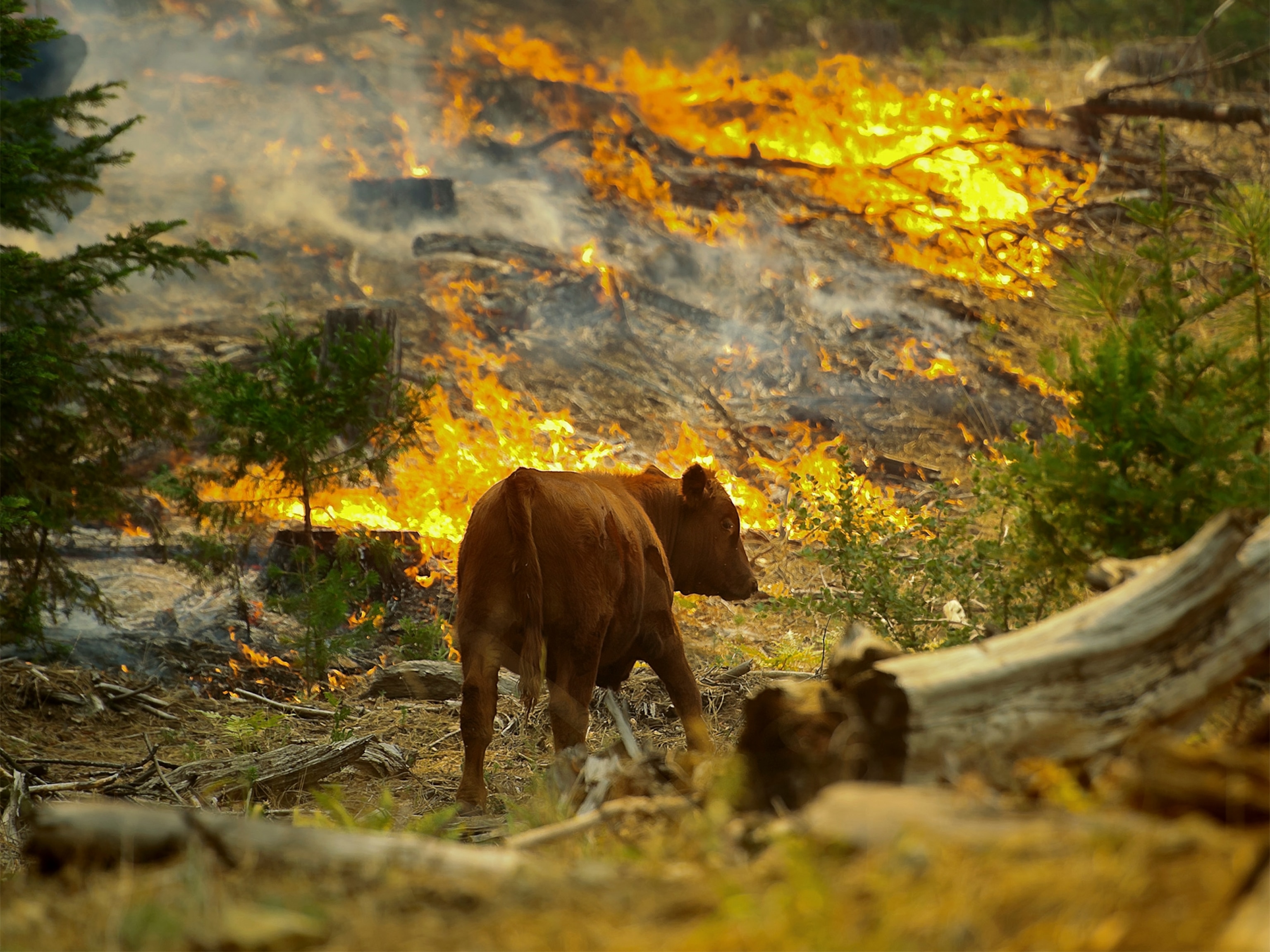
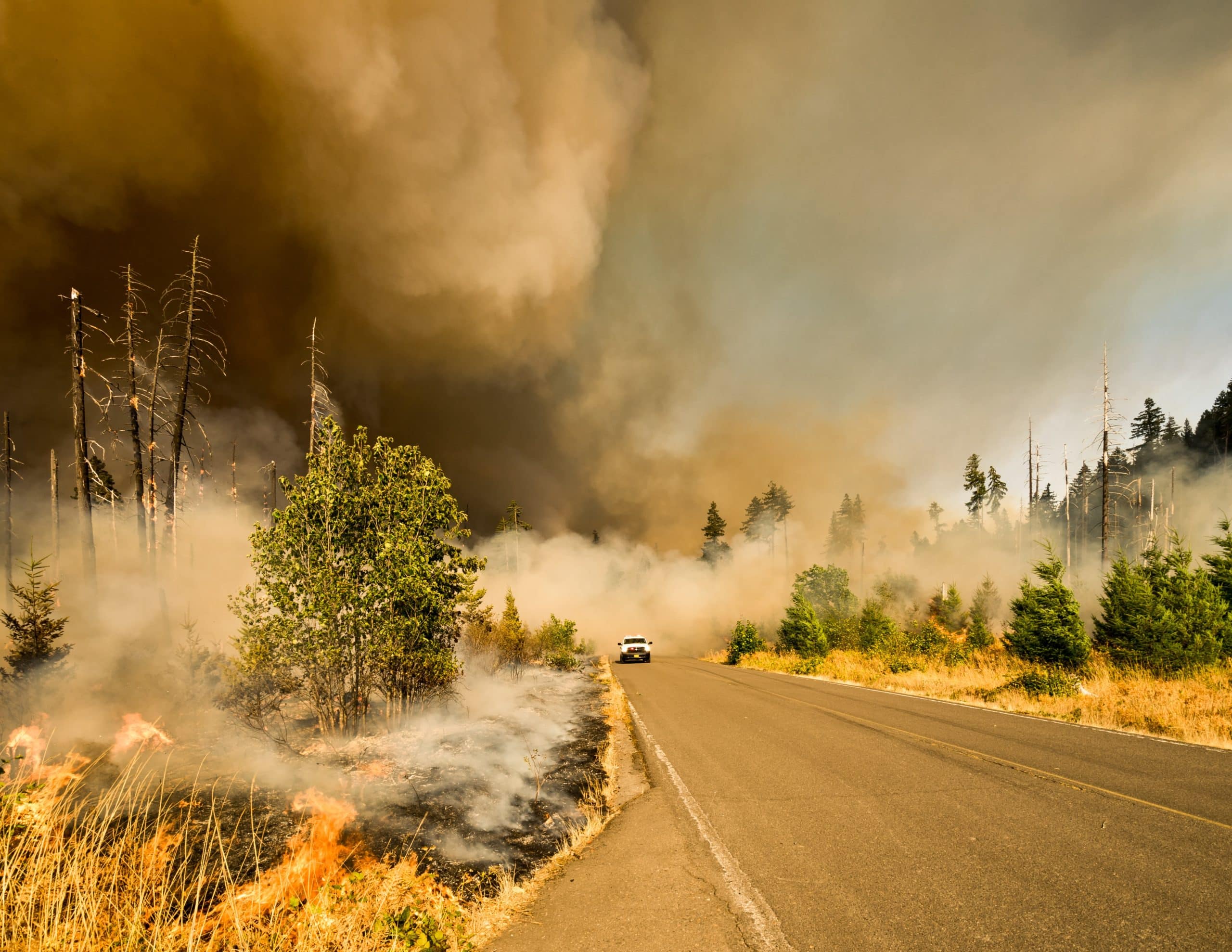
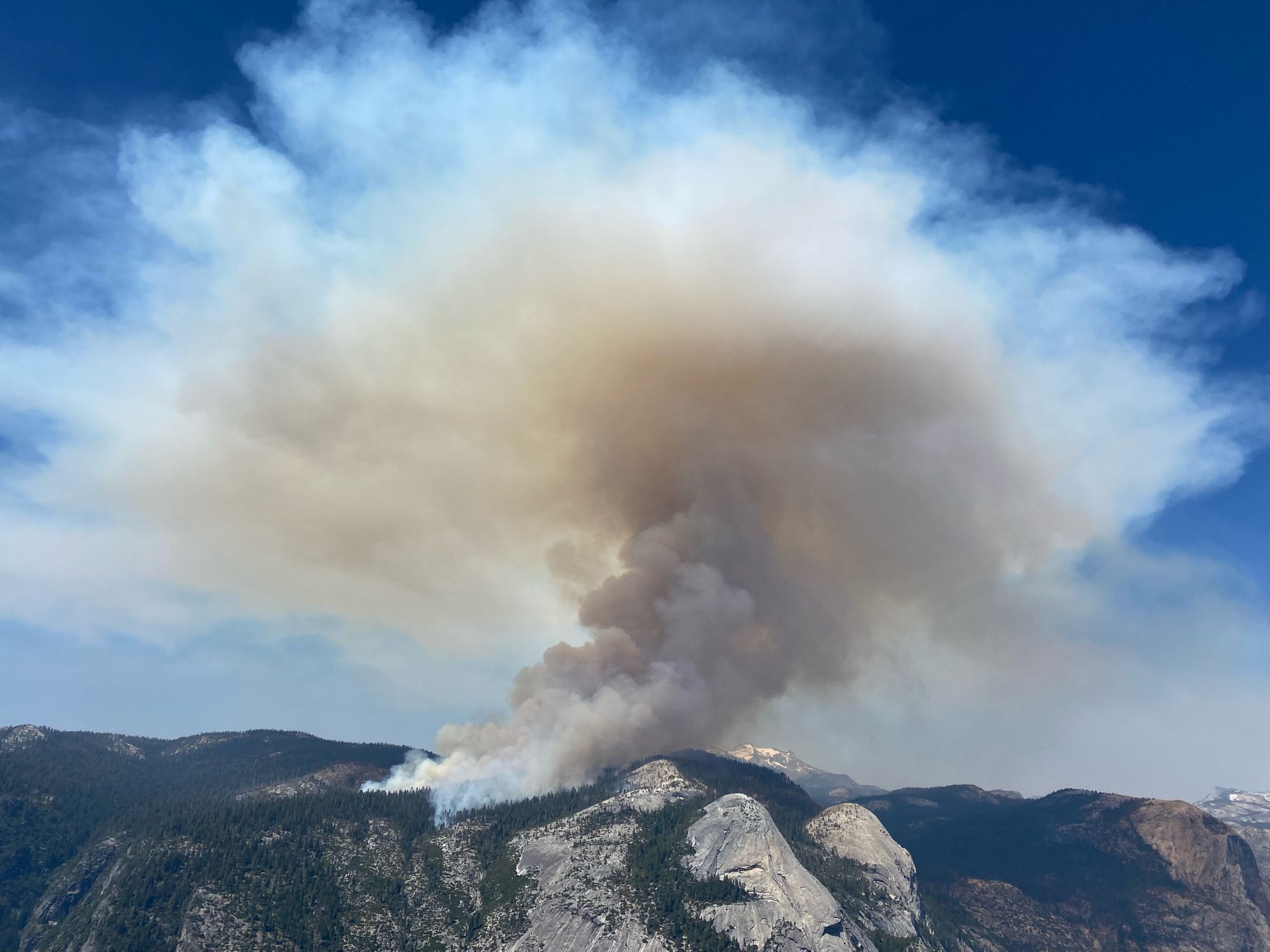






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Complex Relationship Between Fire and Yosemite: A Look at the History, Impact, and Management of Wildfires. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!