The Amazon River: A Lifeline Traversing the Equator
Related Articles: The Amazon River: A Lifeline Traversing the Equator
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Amazon River: A Lifeline Traversing the Equator. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Amazon River: A Lifeline Traversing the Equator

The Amazon River, a colossal artery of life coursing through the heart of South America, is a marvel of nature. Its vastness, biodiversity, and cultural significance make it a subject of constant fascination and study. A key element in understanding the river’s immense impact is its relationship with the equator. This article explores the Amazon River’s geography, its connection to the equator, and the profound implications of this unique positioning.
A River of Superlatives:
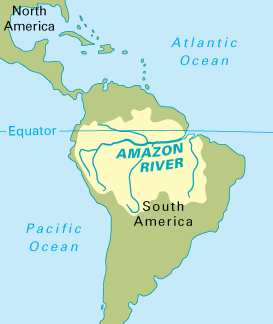
The Amazon River, the world’s largest river by volume of water discharged, originates in the Andes Mountains of Peru and flows eastward across the continent, emptying into the Atlantic Ocean. Its journey spans over 6,400 kilometers, traversing nine countries and encompassing a drainage basin that covers an area roughly the size of the continental United States. The Amazon River’s significance extends far beyond its impressive dimensions. It is a lifeline for millions of people, a haven for unparalleled biodiversity, and a crucial component of the global climate system.
The Equator’s Influence:
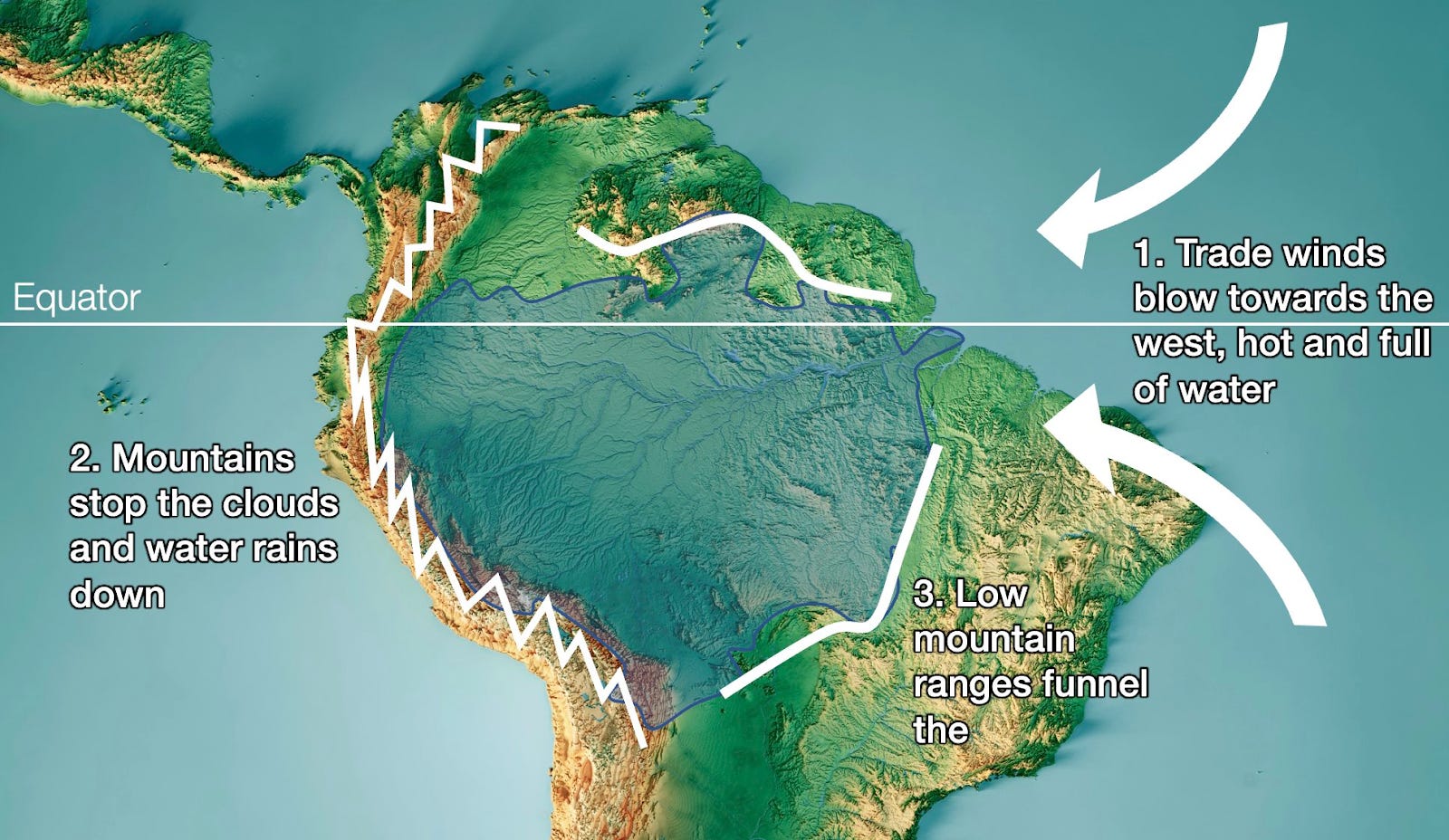
The Amazon River’s path is intimately intertwined with the equator. The river’s main channel lies almost entirely within the equatorial region, receiving a significant portion of its water from the heavy rainfall characteristic of this zone. The equator’s unique position, receiving direct sunlight year-round, creates a consistently warm and humid climate, leading to high levels of precipitation. This constant influx of water sustains the Amazon River’s vast flow, making it a vital source of life for the surrounding ecosystem.
A Cradle of Biodiversity:
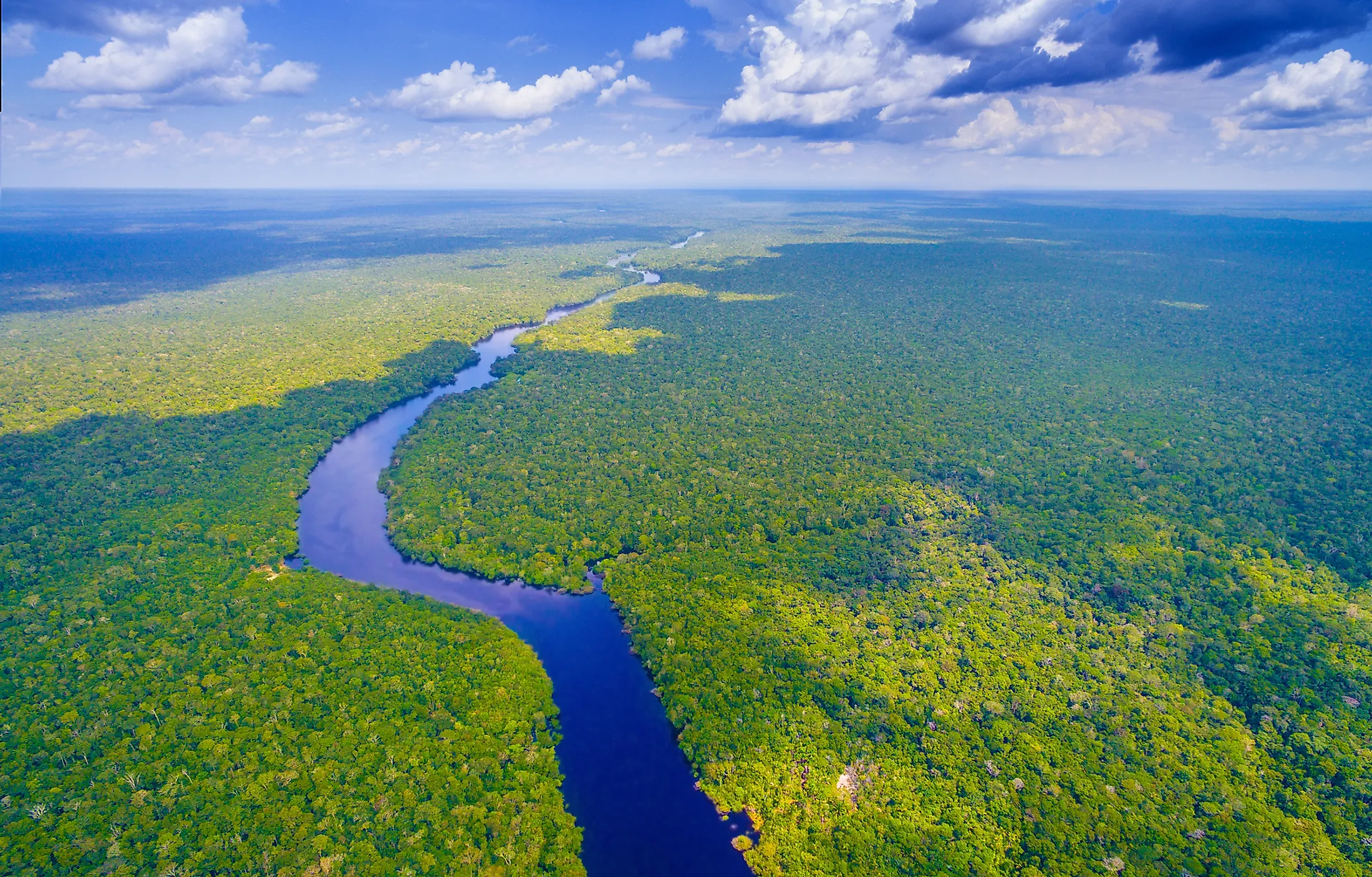
The Amazon River’s equatorial location contributes to its remarkable biodiversity. The consistently warm and wet conditions create an ideal environment for a wide range of plant and animal life. The river itself is home to an astonishing diversity of fish species, including the iconic piranha and the elusive arapaima. The surrounding rainforest, known as the Amazon rainforest, is considered the Earth’s largest and most biodiverse terrestrial ecosystem, harboring a staggering array of species, from jaguars and macaws to countless insects and plants.
Climate Regulation and Global Significance:
The Amazon River plays a crucial role in regulating the global climate. The vast rainforest acts as a carbon sink, absorbing a significant portion of the carbon dioxide released into the atmosphere. This process helps mitigate the effects of climate change, making the Amazon rainforest a vital component of the global climate system. The river’s water cycle, influenced by the equatorial climate, contributes to regional rainfall patterns and influences weather systems across South America and beyond.
Cultural Significance and Indigenous Communities:
The Amazon River has been a vital source of life for indigenous communities for millennia. These communities have developed intricate relationships with the river, relying on its bounty for sustenance, transportation, and spiritual connection. The river’s cultural significance is deeply embedded in the traditions, beliefs, and languages of these indigenous groups, highlighting the importance of preserving their knowledge and way of life.
Challenges and Conservation Efforts:
Despite its immense significance, the Amazon River faces numerous challenges, including deforestation, pollution, and climate change. These threats jeopardize the river’s ecosystem, the livelihoods of indigenous communities, and the global climate system. Conservation efforts are underway to protect the Amazon River and its surrounding rainforest, focusing on sustainable development, combating deforestation, and mitigating the effects of climate change.
FAQs:
Q: What is the relationship between the Amazon River and the equator?
A: The Amazon River’s main channel lies almost entirely within the equatorial region. The equator’s direct sunlight and high precipitation contribute to the river’s abundant water flow.
Q: How does the Amazon River’s location influence its biodiversity?
A: The equatorial climate creates warm and humid conditions, fostering a wide range of plant and animal life, making the Amazon River and its surrounding rainforest the most biodiverse ecosystems on Earth.
Q: What is the significance of the Amazon River in regulating the global climate?
A: The Amazon rainforest acts as a carbon sink, absorbing significant amounts of carbon dioxide. The river’s water cycle also influences regional and global weather patterns.
Q: What are some of the challenges facing the Amazon River?
A: Deforestation, pollution, and climate change pose significant threats to the river’s ecosystem, indigenous communities, and the global climate system.
Q: What are some conservation efforts being undertaken to protect the Amazon River?
A: Conservation efforts focus on sustainable development, combating deforestation, and mitigating the effects of climate change to protect the river’s ecosystem and its vital role in the global climate system.
Tips for Exploring the Amazon River:
- Respect the environment: Be mindful of your impact on the fragile ecosystem and dispose of waste responsibly.
- Support local communities: Engage with indigenous communities and learn about their culture and traditions.
- Choose sustainable tourism: Opt for eco-friendly tours and accommodations that prioritize environmental conservation.
- Learn about the challenges facing the Amazon River: Educate yourself about the threats to the ecosystem and support organizations working to protect it.
Conclusion:
The Amazon River, a magnificent river traversing the equator, is a testament to the power and beauty of nature. Its unique location, vastness, biodiversity, and cultural significance make it a vital resource for millions of people and a crucial component of the global climate system. Understanding the Amazon River’s relationship with the equator is essential for appreciating its profound impact and for ensuring its continued health and vitality for generations to come.

.png)




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Amazon River: A Lifeline Traversing the Equator. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!