Russia’s Neighbors: A Geopolitical Overview
Related Articles: Russia’s Neighbors: A Geopolitical Overview
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Russia’s Neighbors: A Geopolitical Overview. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Russia’s Neighbors: A Geopolitical Overview
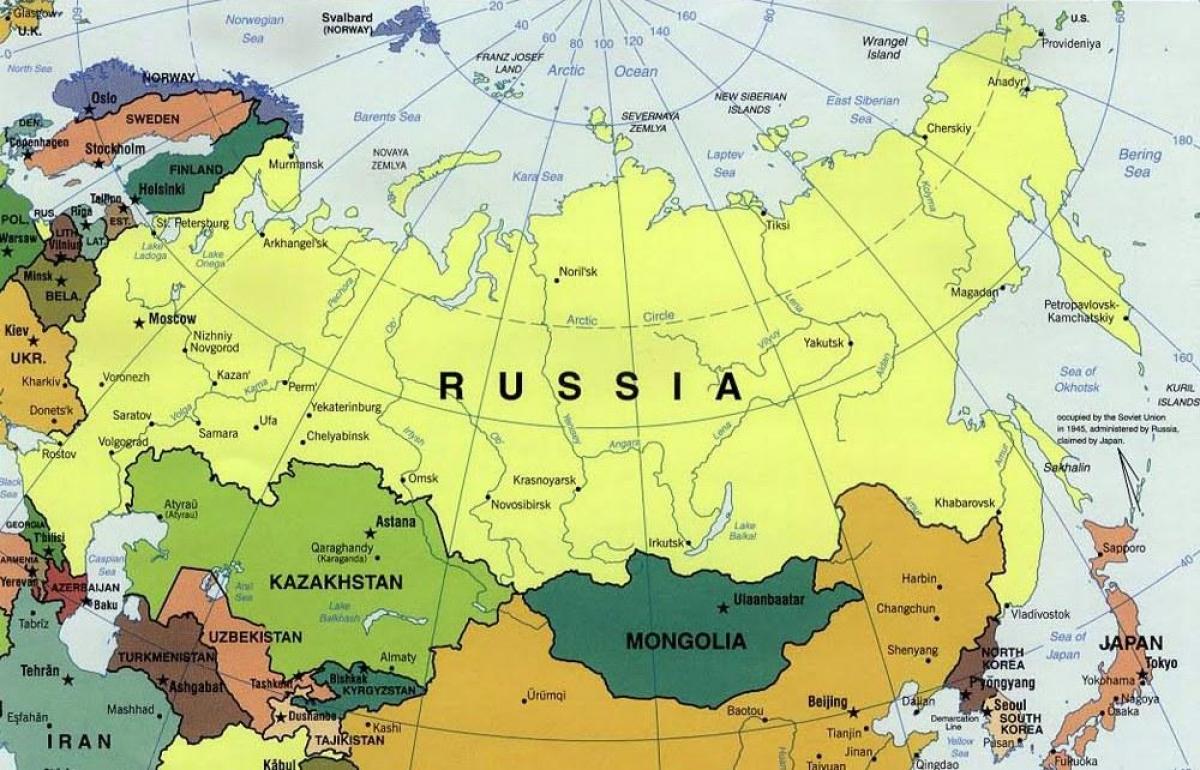
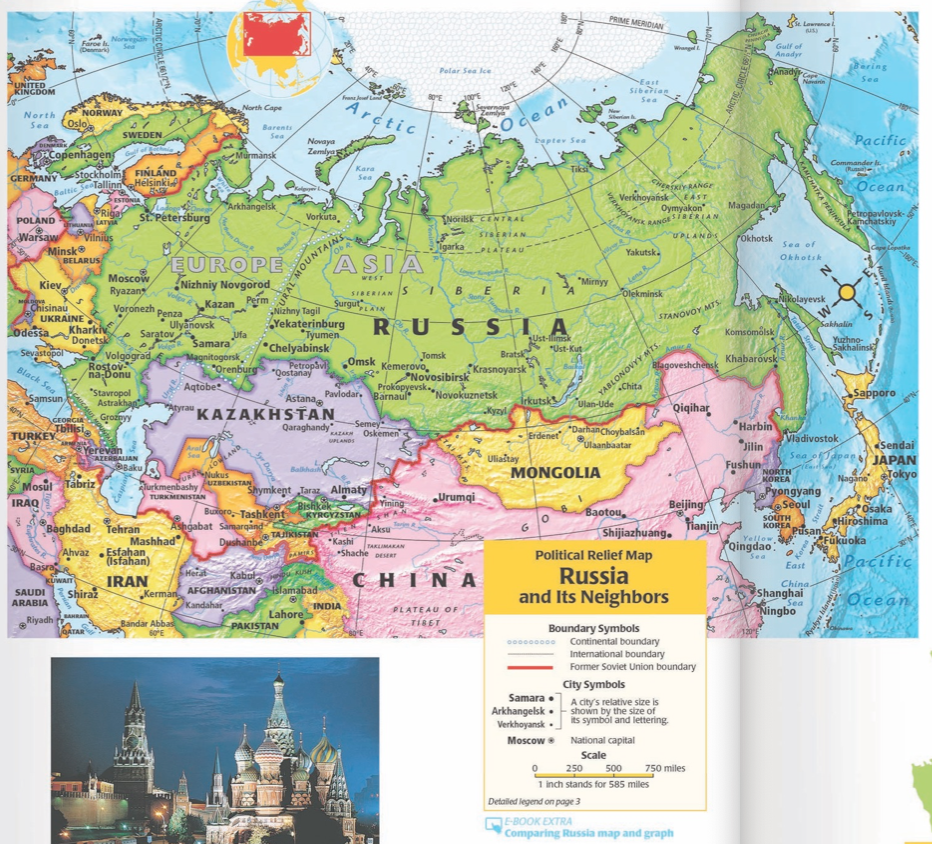
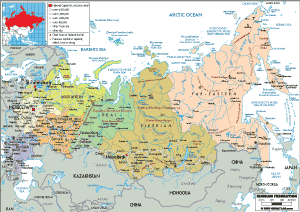
Russia, the largest country in the world by land area, shares its vast borders with fourteen countries, encompassing diverse cultures, political systems, and economic landscapes. Understanding the geographical and geopolitical context of these neighboring nations is crucial for analyzing Russia’s foreign policy, regional dynamics, and global influence. This article delves into the intricacies of Russia’s surrounding countries, highlighting their strategic importance and multifaceted relationships with Moscow.
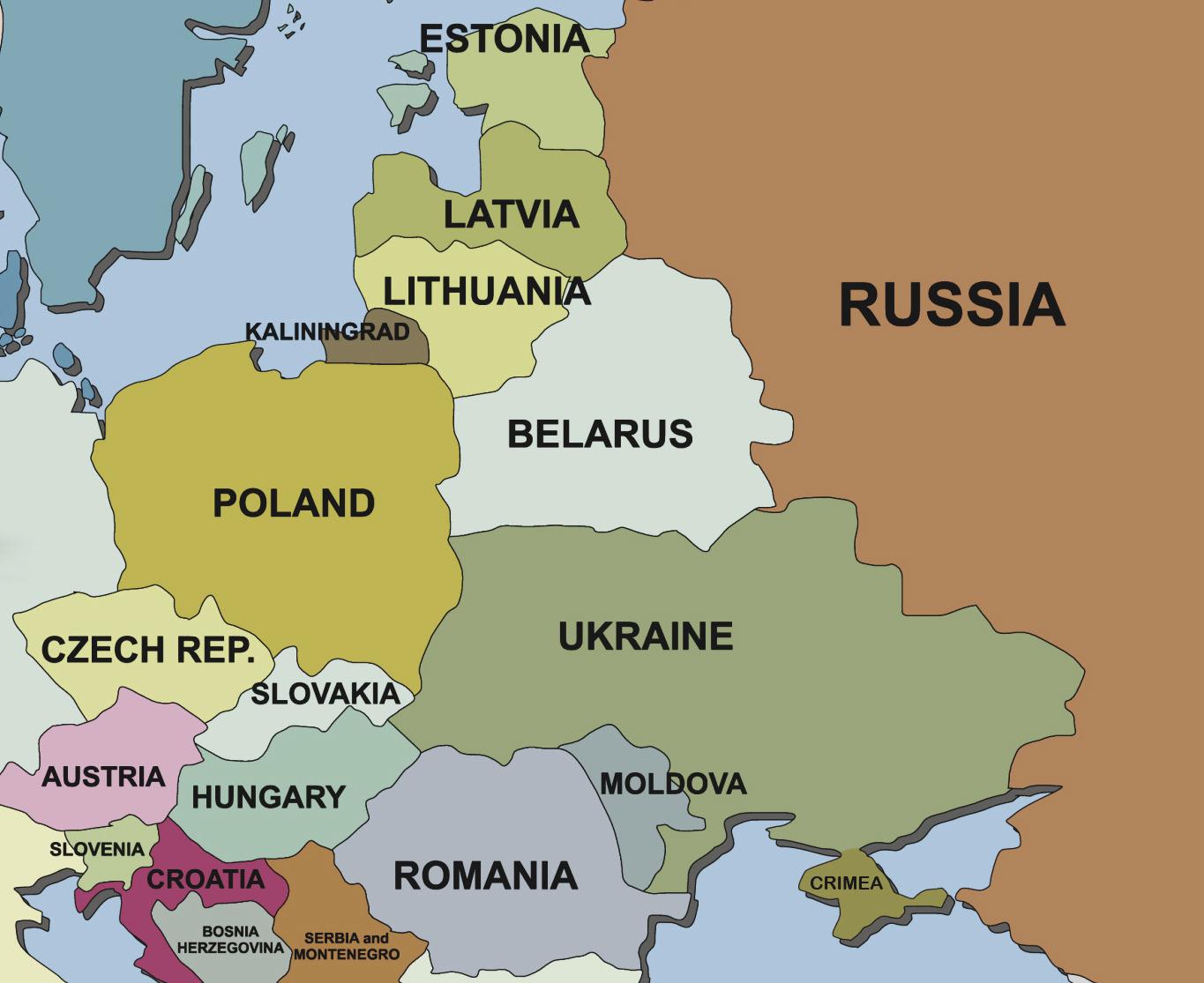
The Western Frontier: A Complex Tapestry
Russia’s western border is marked by a diverse array of nations, each with its own history and relationship with Russia.
-
Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania: These Baltic states, formerly part of the Soviet Union, regained independence in 1991 and are now members of NATO and the European Union. Their close ties to the West have strained relations with Russia, which continues to view their membership in NATO as a security threat.
-
Belarus: Often referred to as Russia’s "closest ally," Belarus maintains strong political and economic ties with Russia. The two countries have signed numerous agreements on military cooperation, economic integration, and political coordination. However, Belarus’s increasing dependence on Russia has raised concerns about its sovereignty and autonomy.
-
Ukraine: The conflict in Ukraine, which began in 2014, has significantly impacted Russia’s relations with its neighbor. Russia’s annexation of Crimea and support for separatists in eastern Ukraine have led to international condemnation and sanctions. The ongoing conflict has also fueled tensions between Russia and the West, highlighting the strategic importance of Ukraine for both sides.
-
Poland: Poland, a NATO member and a staunch supporter of Ukraine, has been a vocal critic of Russia’s actions in the region. The historical animosity between the two countries, stemming from past conflicts and territorial disputes, continues to influence their relationship.
-
Finland and Sweden: These Nordic countries share a long and complex history with Russia. While maintaining a neutral stance during the Cold War, they have gradually integrated with Western institutions. Their recent decisions to join NATO, driven by security concerns, have significantly altered the geopolitical landscape of Northern Europe.
The Southern Frontier: A Region of Diversity and Conflict
Russia’s southern border is marked by a diverse mix of cultures and political systems, including:
-
Georgia: Georgia, a former Soviet republic, has sought to strengthen its ties with the West, particularly with NATO and the European Union. Russia’s military intervention in Georgia in 2008, following the country’s aspirations for closer Western integration, has strained relations between the two nations.
-
Azerbaijan and Armenia: These two South Caucasus nations have been locked in a long-standing conflict over the disputed territory of Nagorno-Karabakh. Russia has played a role in mediating the conflict, but its close ties with both Armenia and Azerbaijan have made it difficult to act as an impartial mediator.
-
Kazakhstan, Uzbekistan, Turkmenistan, Kyrgyzstan, and Tajikistan: These five Central Asian republics, formerly part of the Soviet Union, have become independent states since the collapse of the USSR. While maintaining close economic ties with Russia, they have also sought to diversify their partnerships and strengthen relations with other regional and international actors.
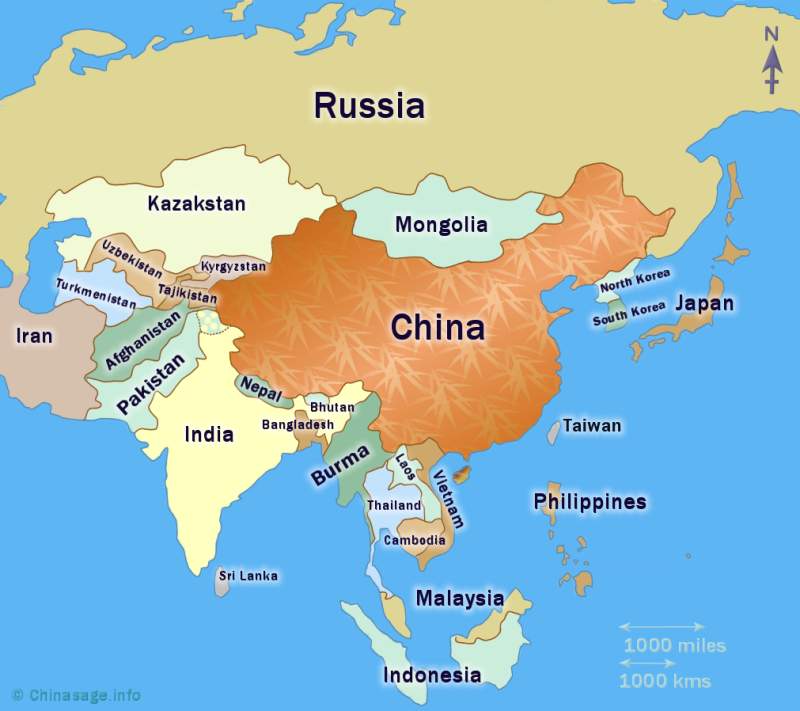
The Eastern Frontier: A Vast and Unsettled Border
Russia’s eastern border is defined by its vast expanse and its shared border with:
-
China: The relationship between Russia and China is a complex one, marked by both cooperation and competition. The two countries have forged strong economic ties, particularly in the energy sector, but also have territorial disputes and strategic rivalries. The growing economic and military power of China poses a challenge to Russia’s traditional sphere of influence in the region.
-
Mongolia: Mongolia, a landlocked country sandwiched between Russia and China, has traditionally maintained close ties with Russia. However, its recent economic and political reforms have led to increased engagement with other countries, particularly China.
The Importance of Russia’s Neighbors
Understanding the geopolitical landscape surrounding Russia is crucial for several reasons:
-
Security: Russia’s neighbors play a significant role in its national security. The expansion of NATO eastward and the presence of Western military forces near Russia’s borders have raised concerns about security threats.
-
Economic Ties: Russia’s neighbors are key partners in its economic development. The Eurasian Economic Union, a regional economic bloc led by Russia, aims to foster economic cooperation and integration among its member states.
-
Energy Security: Russia is a major energy exporter, and its neighbors are important markets for its oil and gas resources. The control over energy resources has become a key factor in Russia’s foreign policy.
-
Political Influence: Russia seeks to maintain its political influence in its surrounding region, particularly in former Soviet republics. The ongoing conflict in Ukraine and the tensions with the West demonstrate the importance of this goal.
-
Global Power: Russia’s relationship with its neighbors shapes its role in global affairs. The country’s ability to project power and influence beyond its borders depends on its relationships with its immediate neighbors.
FAQs about Russia’s Neighbors
Q: What are the main geopolitical challenges facing Russia in its relations with its neighbors?
A: Russia faces several geopolitical challenges in its relations with its neighbors, including:
- NATO Expansion: The expansion of NATO eastward has raised concerns about security threats to Russia.
- Western Influence: The increasing influence of the West in Russia’s neighborhood has led to tensions and competition for influence.
- Ethnic and Territorial Disputes: The region is plagued by ethnic and territorial disputes, which Russia often finds itself involved in.
- Economic Dependence: Some of Russia’s neighbors are economically dependent on Russia, which can create political leverage and potential for instability.
Q: What are the key factors shaping Russia’s foreign policy towards its neighbors?
A: Russia’s foreign policy towards its neighbors is shaped by several key factors, including:
- Security Concerns: Russia prioritizes its security and seeks to maintain control over its surrounding region.
- Economic Interests: Russia seeks to promote economic cooperation and integration with its neighbors.
- Historical Legacy: Russia’s historical ties and influence over its neighbors continue to shape its foreign policy.
- Global Power Projection: Russia aims to project its power and influence beyond its borders, and its relations with its neighbors are crucial to achieving this goal.
Q: How has the conflict in Ukraine impacted Russia’s relations with its neighbors?
A: The conflict in Ukraine has had a profound impact on Russia’s relations with its neighbors, leading to:
- Increased Tensions: The conflict has fueled tensions between Russia and the West, as well as between Russia and its neighbors.
- Economic Sanctions: Russia has been subject to economic sanctions from the West, which have impacted its economic ties with its neighbors.
- Military Buildup: The conflict has led to a military buildup in the region, increasing security concerns for Russia and its neighbors.
- Shifting Alliances: The conflict has led to a realignment of alliances in the region, with some countries moving closer to the West and others aligning with Russia.
Tips for Understanding Russia’s Neighbors
- Study the historical context: Understanding the historical relationships between Russia and its neighbors is crucial for comprehending their current dynamics.
- Analyze the geopolitical landscape: Pay attention to the strategic importance of different countries and their relationships with major powers.
- Follow the news: Stay updated on current events and developments in the region to understand the evolving geopolitical landscape.
- Consider different perspectives: Explore different viewpoints and analyses from experts and scholars on Russia’s relations with its neighbors.
Conclusion
Russia’s neighbors play a vital role in shaping its foreign policy, security, and global influence. The intricate web of relationships between Russia and its surrounding countries is characterized by a complex mix of cooperation, competition, and conflict. Understanding the geopolitical dynamics of this region is crucial for comprehending Russia’s place in the world and its impact on global affairs. As the region continues to evolve, the relationship between Russia and its neighbors will remain a key factor in shaping international relations and global security.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Russia’s Neighbors: A Geopolitical Overview. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!