Navigating the World with R: A Comprehensive Guide to Longitude and Latitude
Related Articles: Navigating the World with R: A Comprehensive Guide to Longitude and Latitude
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the World with R: A Comprehensive Guide to Longitude and Latitude. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Navigating the World with R: A Comprehensive Guide to Longitude and Latitude
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Navigating the World with R: A Comprehensive Guide to Longitude and Latitude
- 3.1 Understanding Longitude and Latitude: The Foundation of Geographic Coordinates
- 3.2 Utilizing R for Geospatial Analysis: A Powerful Toolkit
- 3.3 Essential R Packages for Geospatial Analysis
- 3.4 Practical Applications of Longitude and Latitude in R
- 3.5 FAQs about Longitude and Latitude in R
- 3.6 Tips for Working with Longitude and Latitude in R
- 3.7 Conclusion: Navigating the World of Geospatial Data with R
- 4 Closure
Navigating the World with R: A Comprehensive Guide to Longitude and Latitude

The world is a vast and complex place, and understanding its geography is crucial for a wide range of applications, from environmental monitoring to urban planning and even social science research. At the heart of this understanding lies the concept of geographic coordinates, specifically longitude and latitude. These two fundamental measurements, represented as points on a map, provide a unique identifier for every location on Earth. R, a powerful open-source statistical programming language, offers a robust toolkit for working with geographic data, enabling users to manipulate, visualize, and analyze spatial information with ease.
Understanding Longitude and Latitude: The Foundation of Geographic Coordinates
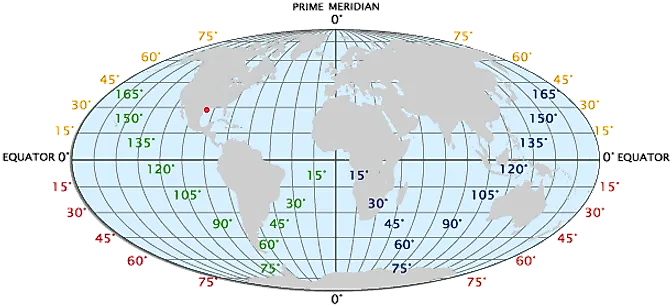
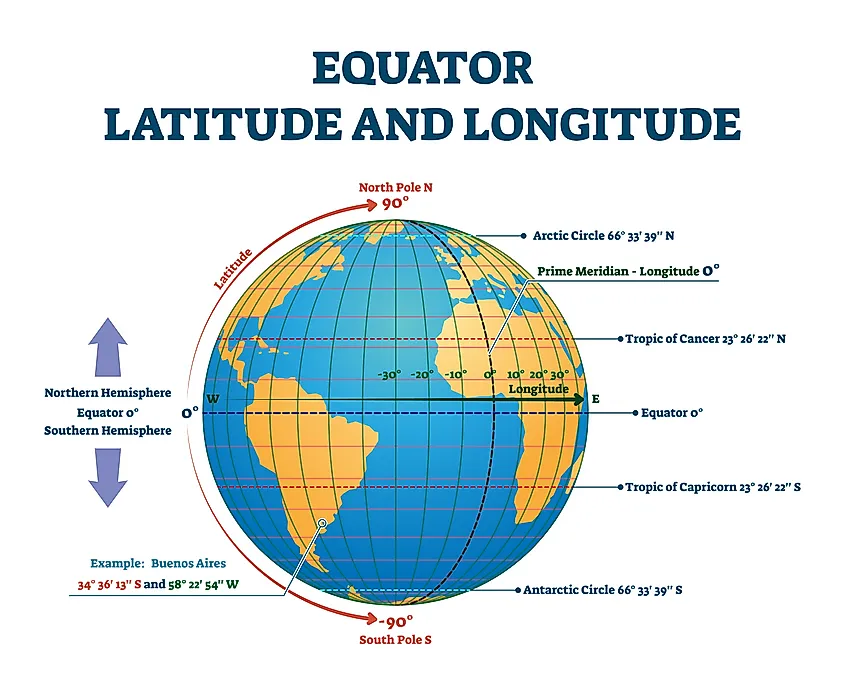
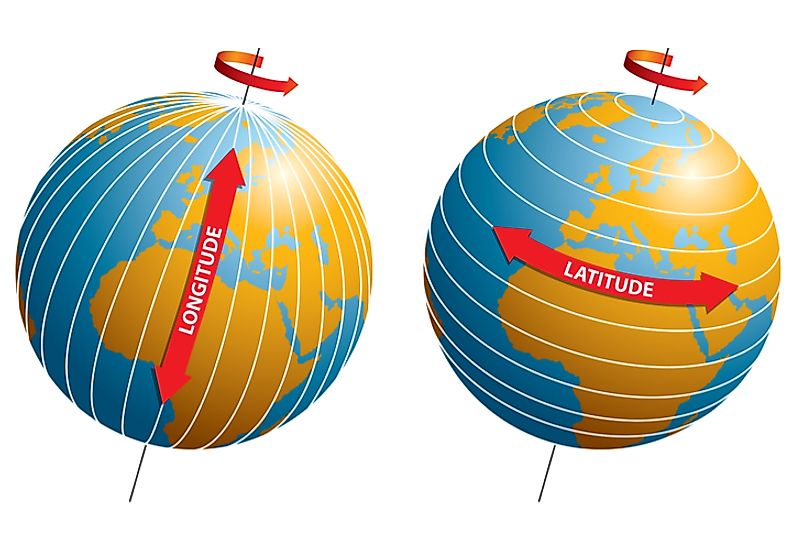
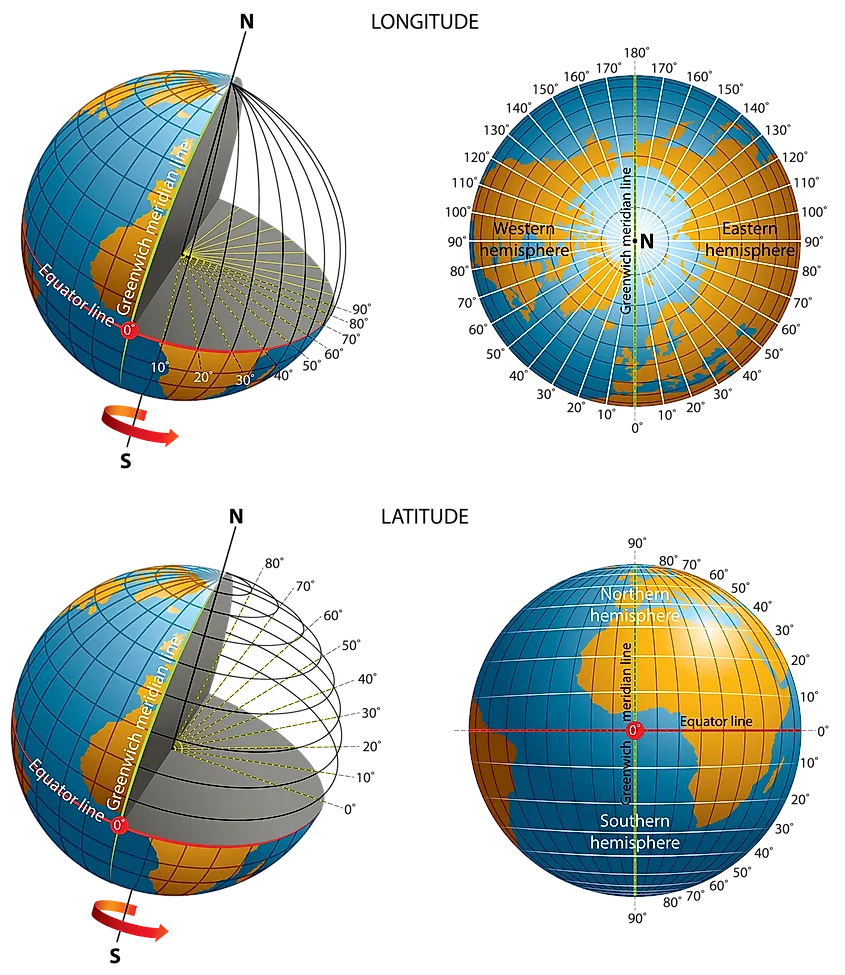
Longitude and latitude form the basis of a global coordinate system, enabling us to pinpoint any location on Earth’s surface. Imagine a grid superimposed on the globe, with lines running vertically and horizontally.
- Longitude: These lines run vertically, from the North Pole to the South Pole. They are measured in degrees, ranging from 0° at the Prime Meridian (which passes through Greenwich, England) to 180° east or west.
- Latitude: These lines run horizontally, parallel to the equator. They are also measured in degrees, ranging from 0° at the equator to 90° north or south.
Together, longitude and latitude form a unique pair of coordinates, allowing us to precisely locate any point on Earth. For example, the coordinates 40.7128° N, 74.0060° W represent the location of Times Square in New York City.
Utilizing R for Geospatial Analysis: A Powerful Toolkit
R’s extensive collection of packages, specifically designed for geographic data manipulation and visualization, makes it an ideal platform for working with longitude and latitude points. These packages provide a comprehensive suite of functions that empower users to:
- Import and Export Data: Load geographic data from various formats, including CSV, shapefiles, and GeoJSON, and export results in desired formats.
- Coordinate Transformation: Convert between different coordinate systems, such as decimal degrees, UTM, and geographic coordinates.
- Spatial Operations: Perform geometric operations on spatial data, such as calculating distances, areas, and intersections.
- Map Visualization: Create visually compelling maps using various basemaps and customization options, effectively communicating spatial patterns and relationships.
Essential R Packages for Geospatial Analysis
Several key packages are instrumental in working with longitude and latitude in R.
-
sf: This package provides a modern and efficient framework for handling spatial data. It allows users to read, write, manipulate, and analyze spatial objects, including points, lines, and polygons, seamlessly. -
sp: This package provides a foundational framework for spatial data analysis in R. It offers a wide range of functions for managing spatial objects and performing spatial operations. -
ggplot2: This versatile package, known for its elegant and customizable graphics, can be used to create informative and visually appealing maps. -
maptools: This package provides functions for working with spatial data, including conversion between different spatial data formats and manipulation of spatial objects. -
rgdal: This package facilitates the reading and writing of geospatial data from various sources, including shapefiles, GeoTIFFs, and other formats.
Practical Applications of Longitude and Latitude in R
The ability to work with longitude and latitude in R opens up a vast array of possibilities for data analysis and visualization. Here are some examples:
- Mapping Crime Data: Visualizing crime hotspots by plotting crime locations on a map using their longitude and latitude coordinates. This can help identify areas with high crime rates and inform crime prevention strategies.
- Analyzing Environmental Data: Mapping pollution levels, forest cover changes, or weather patterns using spatial data. This can help understand environmental trends and inform policy decisions.
- Urban Planning: Analyzing population density, transportation infrastructure, and land use patterns to optimize urban development and improve quality of life.
- Social Science Research: Mapping social indicators such as poverty rates, access to healthcare, or education levels to understand spatial disparities and inform targeted interventions.
FAQs about Longitude and Latitude in R
Q: How can I import data with longitude and latitude coordinates into R?
A: You can use the read.csv() function to import data from a CSV file or the read_sf() function from the sf package to import data from a shapefile or GeoJSON file.
Q: How can I plot longitude and latitude points on a map in R?
A: You can use the ggplot2 package to create maps. Use the geom_point() function to plot the points, and specify the longitude and latitude coordinates as the x and y values. You can also use basemaps from packages like maptools or ggmap to provide context.
Q: How can I calculate the distance between two points using their longitude and latitude coordinates in R?
A: You can use the distGeo() function from the geosphere package to calculate the great-circle distance between two points.
Q: How can I convert between different coordinate systems in R?
A: You can use the spTransform() function from the sp package to convert between different coordinate systems.
Tips for Working with Longitude and Latitude in R
- Data Quality: Ensure your data is accurate and consistent. Verify that the longitude and latitude coordinates are in the correct format and units.
- Coordinate Systems: Be aware of the coordinate system used for your data and ensure consistency throughout your analysis.
- Projection: Choose an appropriate map projection for your data and analysis. Different projections distort spatial relationships differently.
- Visualization: Use clear and informative map visualizations to effectively communicate spatial patterns and insights.
- Documentation: Keep track of your data sources, coordinate systems, and analysis methods for reproducibility and clarity.
Conclusion: Navigating the World of Geospatial Data with R
R, with its powerful packages and diverse functionalities, provides a robust and versatile platform for working with longitude and latitude points. This enables users to analyze, visualize, and interpret spatial data, unlocking a wealth of insights across various domains. From mapping crime hotspots to analyzing environmental trends, the ability to manipulate and visualize geographic coordinates empowers researchers, analysts, and decision-makers to understand and address complex spatial challenges, shaping a more informed and data-driven approach to understanding our world.

/Latitude-and-Longitude-58b9d1f35f9b58af5ca889f1.jpg)


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the World with R: A Comprehensive Guide to Longitude and Latitude. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!